Spring在web容器中启动过程——源码分析
前言
spring的启动过程就是IOC容器的启动过程,spring可用于各种环境,对于不同环境下启动入口会有所差异。看过spring源码的朋友可能会说,spring启动入口不就是对AbstractApplicationContext#refresh的调用吗?很对,refresh()是统一入口,但它是通过什么样的方式才进入到对refresh()调用的呢?
下面就分析spring在web容器中怎么走到对refresh()的调用。
配置说明
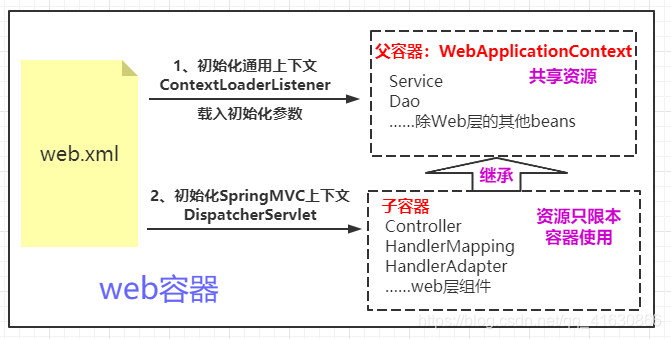
web容器中spring的启动要从web.xml说起,在web.xml中一般可以看到如下配置。
<!-- 上下文初始化参数 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
classpath:/config/spring-config.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Spring监听器 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- SpringMVC的Servlet配置 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:config/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>1)<context-param>
用来指定上下文初始化参数,作用于Servlet上下文初始化参数,参数名在整个web应用中是唯一的,在web应用的整个生命周期中上下文初始化参数都存在,任意的Servlet和jsp都可以随时随地访问它。
这儿的配置是在指定spring配置文件路径,若这儿不写,则spring默认加载 /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml 作为配置文件。
2)<listener>
配置spring必须要有<listener>,这儿的配置是用来初始化Spring父容器,ContextLoaderListener是一个实现了ServletContextListener接口的监听器,在项目启动时会调用contextInitialized(),项目关闭时会调用contextDestroyed()。
contextInitialized()主要完成的ApplicationContext对象创建操作,contextDestroyed()主要完成的ApplicationContext清理操作。
3)<servlet>
初始化servlet,这儿的配置是初始化SpringMVC子容器。上面配置中 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>表示在Servlet容器启动时就加载该servlet。(<load-on-startup>用来标识容器是否启动时就加载该servlet,值必须是大于等于0的整数;值越小就越优先加载、值相同则容器决定加载顺序、没有指定或值小于0则用到该servlet时才加载)
1、Spring监听器
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
// 【into】
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}2、创建web应用上下文
该步骤主要包含了创建web应该上下文,并刷新应用上下文。
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// ……
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// 【into】实例化web应用上下文
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 【into】设置配置文件路径,并刷新web应用上下文
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
// ……
return this.context;
}
// catch ……
}3、实例化web应用上下文
选择合适的策略确定上下文类,并实例化该上下文类。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// 【into】选择合适的策略确定上下文类,默认 XmlWebApplicationContext
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
// 实例化应用上下文
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}选择合适的策略确定上下文类,默认策略是XmlWebApplicationContext类,默认策略在ContextLoader.properties配置文件中配置的
/**
* Name of the class path resource (relative to the ContextLoader class)
* that defines ContextLoader's default strategy names.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
// 默认加载此路径下的 ContextLoader.properties 资源配置文件
// 在配置文件中可看到配置的默认处理策略的处理类
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// 获取到 org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
// 这儿的 defaultStrategies 在最上面静态代码块中赋值的
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}在看到org/springframework/web/context/ContextLoader.properties中的配置如下:
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader.
# Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
4、设置配置文件路径,并刷新web应用上下文
该步骤将<context-param>中设定的取名为 contextConfigLocation的配置文件路径设置到spring中,并刷新web应用上下文进入AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()的调用。
因为默认处理类是 XmlWebApplicationContext ,而它继承于AbstractApplicationContext。
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation";
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
// id: org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
// 获取到初始化参数,在<context-param>标签中配置的
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
// 设置到WebApplicationContext配置路径中
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
// 【into】进入到AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
wac.refresh();
}进入到refresh()的调用,就是大家熟悉的spring启动统一入口。
在完成该容器初始化后,就会初始化SpringMVC子容器。
5、初始化SpringMVC上下文
在初始化servlet时通过配置的DispatcherServlet将SpringMVC初始化。DispatcherServlet上下文在初始化的时候会建立自己的IOC上下文,用以持有SpringMVC相关的bean(处理器映射、视图解析器等)。在建立DispatcherServlet自己的IoC上下文时,会先从ServletContext中获取之前的根上下文作为自己的的parent上下文。有了这个parent上下文之后,再初始化自己持有的上下文。
每个servlet持有自己的上下文,即拥有自己独立的bean空间,同时各个servlet共享根容器的上下文。
DispatcherServlet初始化顺序:
它配置在<servlet>标签中,那么肯定继承了HttpServlet并重写了其init(),在init()中完成初始化操作。于是沿着DispatcherServlet的父类找上去发现HttpServletBean继承HttpServlet,并在里面重写了init()。在这init()中主要完成了3件事:1、将Servlet初始化参数(init-param)设置到该组件上(如contextAttribute、contextClass、namespace、contextConfigLocation);2、通过BeanWrapper简化设值过程,方便后续使用;3、提供给子类初始化扩展点,initServletBean(),该方法由FrameworkServlet覆盖。
FrameworkServlet继承HttpServletBean,通过initServletBean()进行Web上下文初始化,该方法主要完成两件事:1、初始化web上下文;2、提供给子类初始化扩展点。
DispatcherServlet继承FrameworkServlet,并实现了onRefresh()方法提供一些前端控制器相关的配置。
1)HttpServletBean#init()
1、将Servlet初始化参数(init-param)设置到该组件上(如contextAttribute、contextClass、namespace、contextConfigLocation);2、通过BeanWrapper简化设值过程,方便后续使用;3、提供给子类初始化扩展点,initServletBean(),该方法由FrameworkServlet覆盖。
// ========== HttpServletBean ==========
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// ……
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
// 读取Servlet初始化参数(<servlet>标签中的init-param)
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 定位资源,通过BeanWrapper简化设值过程,方便后续使用
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
// 加载配置信息
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// ……
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
// 【into】提供给子类的扩展点,由FrameworkServlet覆盖,通过它最终会调用refresh()
initServletBean();
// ……
}2)FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()
FrameworkServlet继承HttpServletBean,通过initServletBean()进行Web上下文初始化,该方法主要完成两件事:1、初始化web上下文;2、提供给子类初始化扩展点。
// ========== HttpServletBean的子类FrameworkServlet ==========
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// ……logger
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 【into】初始化web上下文,里面onRefresh()为子类提供扩展点
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
// ……logger
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 先从ServletContext中获得父容器WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
// 声明子容器
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 建立父、子容器之间的关联关系
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 这个方法里面调用了AbstractApplication的refresh()方法
// 【into】模板方法,规定IOC初始化基本流程
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 先去ServletContext中查找Web容器的引用是否存在,并创建好默认的空IOC容器
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 给上一步创建好的IOC容器赋值
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// 触发onRefresh方法
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
// 【into】初始化 9 大组件,为子类提供扩展点
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
// ……
}
return wac;
}
/*
* 模板方法,规定IOC初始化基本流程
*/
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
// 调用refresh()
wac.refresh();
}分析到这儿,已经在调用refresh()了,前面也已经分析过refresh().
另外调用完refresh()初始化IOC容器后接着在initWebApplicationContext()内会调用onRefresh()初始化9大组件。
3)DispatcherServlet#onRefresh()
初始化SpringMVC 9 大组件
// ========== DispatcherServlet ==========
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* 初始化策略
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 多文件上传的组件
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 初始化本地语言环境
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 初始化模板处理器
initThemeResolver(context);
// handlerMapping
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 初始化参数适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 初始化异常拦截器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 初始化视图预处理器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化视图转换器
initViewResolvers(context);
// FlashMap管理器
initFlashMapManager(context);
}执行完上面的初始化策略,初始化化阶段就完成了。
总结
对于web应用,它需要部署在web容器中,web容器提供了一个全局的上下文环境(即ServletContext),为Spring IOC容器提供了宿主环境。
web.xml中配置了ContextLoaderListener,在web容器启动时会触发初始化事件,ContextLoaderListener监听到这个事件后里面的contextInitialized()会被调用,然后就在这个方法中初始化一个Spring上下文,这个又被称为根上下文,即WebApplicationContext,默认实现类是XmlWebApplicationContext。这个容器初始化完毕后将其存储到ServletContext中,便于子容器获取。
通过配置的DispatcherServlet开始初始化SpringMVC,用来分发处理每个Servlet请求。SpringMVC上下文初始化时会建立自己的IOC上下文,用来持有自身需要的相关bean。在建立上下文时会先从ServletContext中获取根上下文,用来作为自己上下文的parent,有了parent之后再初始化自己的上下文(映射处理器bean、视图解析器bean等)。初始化完毕后spring以与servlet的名字相关(此处不是简单的以servlet名为 Key,而是通过一些转换,具体可自行查看源码)的属性为Key,也将其存到ServletContext中,以便后续使用。这样每个servlet持有自己的上下文,即拥有自己独立的bean空间,同时各个servlet共享根容器的上下文。
注意:用户可以配置多个DispatcherServlet来分别处理不同的url请求,每个DispatcherServlet上下文都对应一个自己的子Spring容器,他们都拥有相同的父Spring容器(业务层,持久(dao)bean所在的容器)。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号