八.使用注解开发
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
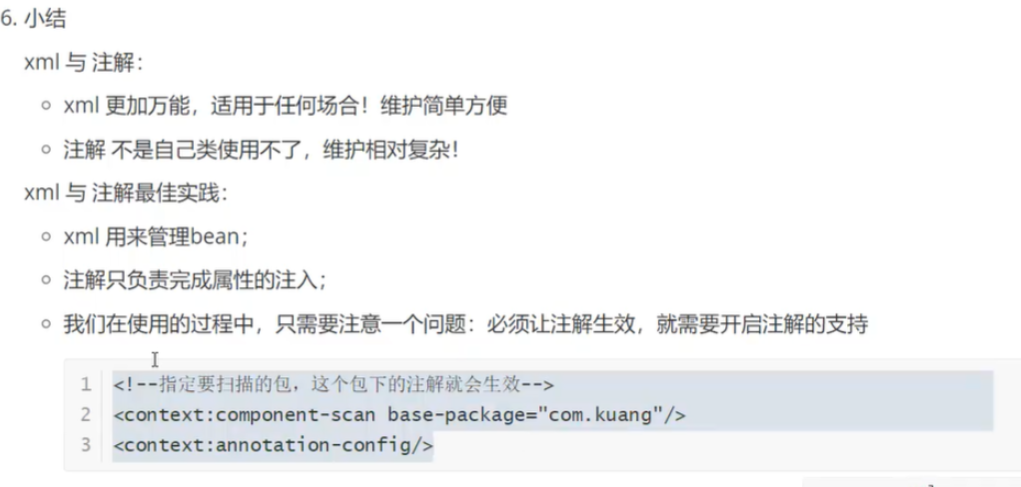
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
1.扫描bean
这个包下的加上注解的类都会加入spring容器中嗷。
<context:component-scan base-package="com.why"/> 使用逗号隔开,我们可以扫描多个包
-
dao @Repository 都表示注册到xml文件下 只不过dao用它
-
service @Service 同上
-
@value()
private List<String> name;
@Value("whysss,whywa")
public void setName(List<String> name) {
this.name = name;
}
4.@Autowired
(required = false):说明如果没有找到对应的bean 可以不报错并输出null
直接在属性上用就行 容器中加入的bean 才能@autoWired 没加入的 如String 没有导入容器 那就会报错!!!
//定义当前这个属性是否可以为null false 是允许 true 是不允许 @Autowired(required = false) private Dog dog; @Autowired(required = false) private Cat cat;
@Qualifier
如果我们xml中配置多个相同类型的bean,但是名字不同此时就可以根据名字为这个属性指定容器中的bean
@Autowired @Qualifier(value = "cat1") private Cat cat; <bean name="cat" class="com.why.Cat"/> <bean name="cat1" class="com.why.Cat"/> <bean name="cat2" class="com.why.Cat"/>
@Resource的装配顺序:
(1)、@Resource后面没有任何内容,默认通过name属性去匹配bean,找不到再按type去匹配
(2)、指定了name或者type则根据指定的类型去匹配bean
(3)、指定了name和type则根据指定的name和type去匹配bean,任何一个不匹配都将报错
然后,区分一下@Autowired和@Resource两个注解的区别:
(1)、@Autowired默认按照byType方式进行bean匹配,@Resource默认按照byName方式进行bean匹配
(2)、@Autowired是Spring的注解,@Resource是J2EE的注解,这个看一下导入注解的时候这两个注解的包名就一清二楚了