五.依赖注入
1. 注入方式
分别为
set注入 【重点】
依赖注入:set注入!
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
注入:bean对象的所有属性 由容器来注入
2.环境搭建
stuent类和address类
package com.why;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @program: Spring_Study
* @description:
* @author: @why
* @create: 2020-08-11 17:40
**/
public class Student {
//这2个赋值简单 就是引用类型了 你给啥我用啥了
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private Properties info;
private String wife;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("name的set");
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
System.out.println("address的set");
}
public String[] getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(String[] books) {
this.books = books;
System.out.println("book的set");
}
public List<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
}
public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
System.out.println("hobby的set");
}
public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
System.out.println("card的set");
}
public Set<String> getGames() {
return games;
}
public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
this.games = games;
System.out.println("game的set");
}
public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
System.out.println("info的set");
}
public String getWife() {
return wife;
}
public void setWife(String wife) {
this.wife = wife;
System.out.println("wife的set");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) +
", hobbys=" + hobbys +
", card=" + card +
", games=" + games +
", info=" + info +
", wife='" + wife + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.why; /** * @program: Spring_Study * @description: * @author: @why * @create: 2020-08-11 17:41 **/ public class Address { private String address; public Address(){ } public Address(String address) { this.address = address; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; System.out.println("地址定位"); } @Override public String toString() { return "Address{" + "address='" + address + '\'' + '}'; } }
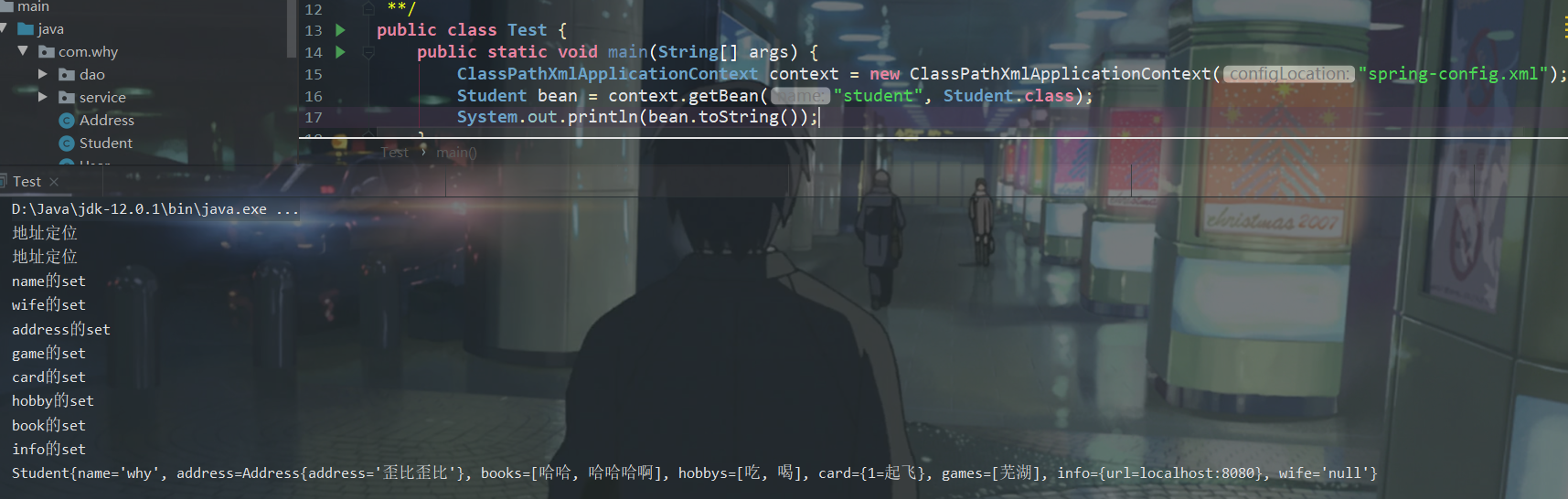
3.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--配置类:address--> <bean class="com.why.Address" id="address"> <property name="address" value="中国"/> </bean> <bean class="com.why.Student" id="student"> <!-- 基本属性赋值--> <property name="name" value="why"/> <!-- 赋空值--> <property name="wife"> <null/> </property> <!-- 可以ref引用上面的类型 也可以自己建立一个--> <property name="address"> <bean class="com.why.Address" name="address2"> <property name="address" value="歪比歪比"/> </bean> <!-- set注入--> </property> <property name="games"> <set> <value>芜湖</value> </set> </property> <!-- map注入--> <property name="card"> <map> <entry key="1" value="起飞"></entry> </map> </property> <!--list注入--> <property name="hobbys"> <list> <value>吃</value> <value>喝</value> </list> </property> <!--数组注入--> <property name="books"> <array> <value>哈哈</value> <value>哈哈哈啊</value> </array> </property> <!-- Properties类型注入 --> <property name="info"> <props> <prop key="url">localhost:8080</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
4.使用和输出