SQLServer 学习笔记2
1.union、union all、except、intersect之间的区别
(1)union:取两个表的并集,如果有重复数据,则只留下一个
(2)union all:在并集的基础上,保留重复的数据
(3)except: 例如select * from A except select * from B,取差集,也就是去掉A和B之间的重复数据,只保留A表独有的部分


(4)intersect 只保留两张表之间相同的数据,也就是取交集
2.自连接
select * from Customers t1,Customers t2 where t1.City <> t2.City;
3.全连接
全连接类似于union,也就是两个表的并集,查询后的总条数:A表条数+B表条数-两者重复条数
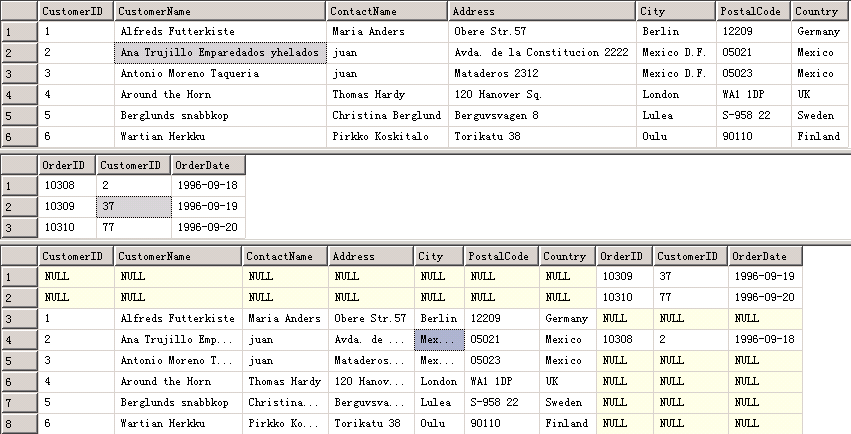
4.左连接、右连接
注意一对多、多对一的关系,例如A表有ID为1的一条数据,而B表有3条ID为1的数据,两表左、右连接,结果为
| ID | NAME | ID | NAME |
| 1 | A | 1 | a |
| 1 | A | 1 | b |
| 1 | A | 1 | c |
出现这一结果的原因为:1条父数据对应着3条子数据,父数据的信息会自动填充在每条子数据对应的父数据字段。
PS:需要注意的是,连接查询on之后的条件可以不是A表字段=B表字段,可以是其他条件。
另外SqlServer表别名可用不用AS 直接在后面填写即可,例如
select A.*,B.C#,B.score from (select * from SC where C# = '01')A --查询结果做A表 inner join (select * from SC where C# = '02')B--查询结果做B表 on A.S# = B.S# --两表连接查询 where A.score>B.score;
5.null的问题
例如:select * from Person where pname <> '张三';,如果pname这个字段内有null,则null对应的这行数据会被自动忽略,也就是说逻辑判断的值是不包含null的。
另外,在update 数据时,如果要填入null,直接填写字段=null即可,但是在判断时,要使用 where 字段 is null | is not null。
6.更新、删除数据时需要注意:
先使用select查询到要操作的信息,然后再用update、delete进行具体操作,防止误操作。
7.隐式转换问题
例如一个字段是int类型,在插入数据时插入'1',数据可以被正确存入,不报错,这是SQL自动将字符串类型转换为了整数类型,但是如果输入的是'a1',则会产生报错,因为'a1'是无法被转换为int类型的!
8.查找每门课最高分问题
先得到相同学科的最高分数,再查询Scores表,找到最高分数的记录:
select * from Scores a where a.sco_degree = (select max(b.sco_degree) from Scores b where a.sco_cour_id = b.sco_cour_id);
找到每门课的最高分数
select max(sco_degree) from Scores where sco_cour_id = a.sco_cour_id --先筛选出每门学科 即sco_cour_id = a.sco_cour_id,然后求最大值,得出的就是每门课的最高分
然后用本表去筛选这些最高分对应的信息:
select * from Scores a where sco_degree =
第二种方式:
(1)先按照课程id把成绩表分组,然后求出最高分
select max(sco_degree) score,sco_cour_id from Scores group by sco_cour_id;
(2)然后把上面的结果集做a表,然后成绩表做b表,查询两者成绩、课程编号一样的数据
select b.* from (select max(sco_degree)score,sco_cour_id from Scores group by sco_cour_id)a,Scores b where a.score = b.sco_degree and a.sco_cour_id = b.sco_cour_id;
9.数据类型
date与datetime的区别:
date时间格式为:yyyy-mm-dd
datetime时间格式为: yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss.ms,精确到毫秒时间,时间格式与getdate()函数格式一样,因此可以用来计算毫秒时间差,用于性能统计
declare @d datetime set @d = getdate() 数据操作语句,例如查询语句等 select ['语句执行耗时'] = datediff(ms,@d,getdate());
10.获取当月天数与当月最后一天、第一天
--当月第一天 --当前日期+(-当期日期天数+1) --例如 现在时间7月19号 19+(-19+1) = 1 select dateadd(d,-day(getdate())+1,getdate()); --当月最后一天 --下月的这一天减去现在日数 --例如现在时间7月19 下月 这一天8月19 8/19-19 = 8/0即 7/31 --即使这个月有31号而下月只有30天也没事,只要产生月份/0日这个结果就可以 select dateadd(d,-day(getdate()),dateadd(m,1,getdate())); --本月有多少天 select day(dateadd(d,-day(getdate()),dateadd(m,1,getdate())));
11,in 与 group by
学生表:
成绩表: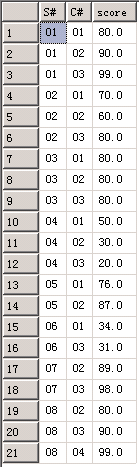
现在要查询和‘1’号学生所学科目完全相同的学生信息
首先要筛选学号,所学科目 in ‘1’号学生所学科目
select S# from SC where C# in (select C# from SC where S# = '01');
查询出的结果:
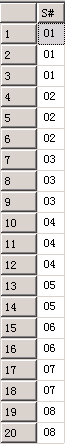
select C# from SC where S# = '01'; --查询出的结果是‘01’,‘02’,‘03’
只要在课程编号在'01','02','03'都被查询出来,拿08号学生来说,学习了02,03,04三门课,所以只匹配中了两门,S#查询出两个08
然后我们依据S#进行编组查询:
select S# from SC where C# in (select C# from SC where S# = '01') group by S#;
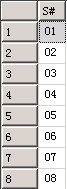
数据根据S#编组,重复出现的数据被合并,此时我们只需要知道每个S#对应的课程编号数量等于01学生所学的课程数量:
select S# from SC where C# in (select C# from SC where S# = '01') group by S#
having count(c#)=(select count(c#) from sc where S# = '01');
接下来只需查询Student表中对应这几个S#的学生信息即可:
select * from Student where S# in (select S# from SC where C# in (select C# from SC where S# = '01' )group by S# having count(c#)=(select count(c#) from sc where S# = '01'));
12.数据类型隐式转换
select count(*)*1.00 from SC group by sid;
count()得到是一个整数,*1.00后隐式转为浮点数
13.delete update 高级应用
利用join 会实现条件删除与更新数据
例:
根据课程表内语文课程考试成绩小于60分的学生学号去匹配学生表,匹配中的学生表记录删除
delete A from Student A left join Score B on A.sid = B.sid where course = '语文' and degree <60;
类似的,update也可以这样使用
update A set age = 100 from Student A left join Score B on .... where ....;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号