Servlet Class1
Servlet:
Java Servlet 是运行在 Web 服务器或应用服务器上的程序,它是作为来自 Web 浏览器或其他 HTTP 客户端的请求和 HTTP 服务器上的数据库或应用程序之间的中间层。
使用 Servlet,您可以收集来自网页表单的用户输入,呈现来自数据库或者其他源的记录,还可以动态创建网页。
Servlet 是服务 HTTP 请求并实现 javax.servlet.Servlet 接口的 Java 类,该接口位于Tomcat\lib下的servlet-api.jar。Web 应用程序开发人员通常编写 Servlet 来扩展 javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet,并实现 Servlet 接口的抽象类专门用来处理 HTTP 请求。
1.servlet工作流程:
(1)login.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>登录页面</title> </head> <body> <form action="login" method="post"> 账号: <input type="text" name="name"> <br> 密码: <input type="password" name="password"> <br> <input type="submit" value="登录"> </form> </body> </html>
(2)LoginServlet
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String name = request.getParameter("name"); String password = request.getParameter("password"); String html = null; if ("admin".equals(name) && "123".equals(password)) html = "<div style='color:green'>success</div>"; else html = "<div style='color:red'>fail</div>"; PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter(); pw.println(html); } }
(3)xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app> <servlet> <servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>LoginServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/login</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
流程:
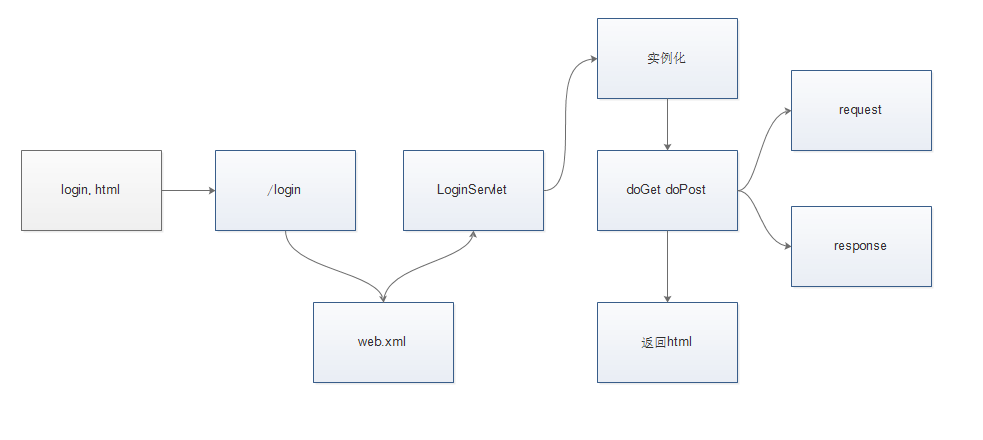
访问login.html,通过表单以post方式提交数据
把账号和密码,提交到/login这个路径,并且附带method="post"
tomcat接受到一个新的请求:http://127.0.0.1/login
其路径是/login,接着就到配置文件web.xml进行匹配,发现/login,对应的Servlet类是 LoginServlet
Tomcat 定位到了LoginServlet后,发现并没有LoginServlet的实例存在,于是就调用LoginServlet的public无参的构造方法LoginServlet()实例化一个LoginServlet对象以备后续使用,同时init()方法被执行。
Tomcat从上一步拿到了LoginServlet的实例之后,先调用service()方法,同时创建相应的request、response对象,根据页面login.html提交信息的时候带的method="post",去调用对应的doPost方法。
接着流程进入了doPost方法中,在这个方法中,通过之前创建的request对象,把页面上传递来的账号和密码信息取出来:
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
接着,根据账号和密码是否正确(判断是否是admin和123), 创建不同的html字符串。
然后把html字符串通过如下方式,设置在了response对象上。
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.println(html);
到这里,Servlet的工作就做完了。
在Servlet完成工作之后,tomcat拿到被Servlet修改过的response,根据这个response生成html 字符串,然后再通过HTTP协议,这个html字符串,回发给浏览器,浏览器再根据HTTP协议获取这个html字符串,并渲染在界面上。
2.生命周期问题:
- Servlet 通过调用 init () 方法进行初始化。
- Servlet 调用 service() 方法来处理客户端的请求。
- Servlet 通过调用 destroy() 方法终止(结束)。
- 最后,Servlet 是由 JVM 的垃圾回收器进行垃圾回收的。
init() 方法
init 方法被设计成只调用一次。它在第一次创建 Servlet 时被调用,在后续每次用户请求时不再调用。因此,它是用于一次性初始化,就像 Applet 的 init 方法一样。
Servlet 创建于用户第一次调用对应于该 Servlet 的 URL 时,但是您也可以指定 Servlet 在服务器第一次启动时被加载,需要在XML内添加<load-on-startup>启动顺序</load-on-startup>
当用户调用一个 Servlet 时,就会创建一个 Servlet 实例,每一个用户请求都会产生一个新的线程,适当的时候移交给 doGet 或 doPost 方法。init() 方法简单地创建或加载一些数据,这些数据将被用于 Servlet 的整个生命周期。
service() 方法
service() 方法是执行实际任务的主要方法。Servlet 容器(即 Web 服务器)调用 service() 方法来处理来自客户端(浏览器)的请求,并把格式化的响应写回给客户端。
每次服务器接收到一个 Servlet 请求时,服务器会产生一个新的线程并调用服务,即每一个请求都会调用service()方法,service() 方法检查 HTTP 请求类型(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等),并在适当的时候调用 doGet、doPost、doPut,doDelete 等方法。
service() 方法由容器调用,service 方法在适当的时候调用 doGet、doPost、doPut、doDelete 等方法。所以,您不用对 service() 方法做任何动作,您只需要根据来自客户端的请求类型来重写 doGet() 或 doPost() 即可,当然我们可以重写service()方法,在其中提供功能,这样就可以不区分请求方式。
destroy() 方法
destroy() 方法只会被调用一次,在 Servlet 生命周期结束时被调用。destroy() 方法可以让您的 Servlet 关闭数据库连接、停止后台线程、把 Cookie 列表或点击计数器写入到磁盘,并执行其他类似的清理活动。
3.XML配置
//类配置 <servlet> <servlet-name>MyServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>myservlet.MyServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> //虚拟路径配置 <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>MyServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>//完全匹配 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>//通配符,访问任何路径都会导致该路径被访问 <url-pattern>/a/b</url-pattern>//目录匹配 <url-pattern>*.jpg</url-pattern>//扩展名匹配 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>//缺省,当你访问资源地址所有的servlet都不匹配时,缺省的servlet负责处理,但这样会导致静态资源例如html访问不正常 </servlet-mapping>
服务器启动时会依次访问welcome-file-list
<welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list>
4.获取参数与返回响应
通过request.getParameter()方法来获取请求提交的参数
通过response.getWriter().println()来输出响应,一般是输出html标签,例
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet{ @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException,ServletException { String user = request.getParameter("user"); String pwd = request.getParameter("pwd"); String result = null; if(user.equals("admin")&pwd.equals("123456")) result= "<h3 style='color:green'>登录成功</h3>"; else result="<h3 style='color:red'>账户或密码错误</h3>"; response.getWriter().println(result); ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); String path = context.getRealPath("123.txt"); System.out.println(path); } }
响应的中文问题:
通过在输出响应前调用如下方法:
不仅发送到浏览器的内容会使用UTF-8编码,而且还通知浏览器使用UTF-8编码方式进行显示。所以总能正常显示中文
仅仅是发送的浏览器的内容是UTF-8编码的,至于浏览器是用哪种编码方式显示不管。 所以当浏览器的显示编码方式不是UTF-8的时候,就会看到乱码,需要手动再进行一次设置。
使用过滤器后仍然乱码问题:涉及到不同浏览器对get这种方式的处理手法有所区别的。 某些浏览器,会对get方式提交的数据进行二次编码,导致服务端取出数据无法正确解码,所以尽量使用post方式,确保中文可以正常处理。
请求的中文问题:
利用request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");来设置Tomcat接收请求的编码格式,只对POST方式提交的数据有效,对GET方式提交的数据无效!
或者可以使用:
String text = request.getParameter("text");
text = new String(text.getBytes("iso8859-1"),"utf-8");
终极解决方案:
要设置GET的编码,可以修改server.xml文件中,相应的端口的Connector的属性:URIEncoding="UTF-8",这样,GET方式提交的数据才会被正确解码。
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" URIEncoding="UTF-8" />
5.通过配置文件连接数据库:
请注意:工程在tomcat服务器中运行时,编译好的class文件是存放在tomcat目录下的classes文件夹中,例如E:\Tomcat\webapps\Login\WEB-INF\classes,存放在工程中src下的配置文件也会被复制过来,如果通过DButil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("")来获取输入流,最后运行、连接数据库时报空指针异常,请检查配置文件有没有被正确复制,简单点的办法就是把servers下的该工程remove,重新加载运行。
另外在servlet中,可以通过String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("");获取到工程下的指定文件路径,例如E:\Tomcat\webapps\Web01\123.txt,不管该文件位于src下或者WEB-INF下,都能获取到。
如下代码可实现简单的用户登录验证:
DButil:
public class DButil { private DButil() {}; public static Connection getConn() { try(InputStream in = DButil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("DButil.properties");){ Properties pro = new Properties(); pro.load(in); String driver = pro.getProperty("driver"); String url = pro.getProperty("url"); String user = pro.getProperty("user"); String password = pro.getProperty("password"); Class.forName(driver); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); return conn; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("连接数据库失败!"+e); } } public static void close(Statement sta,Connection conn) { if(sta!=null) { try { sta.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn!=null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void close(ResultSet rs,Statement sta,Connection conn) { if(rs!=null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } close(sta,conn); } }
DAO:
public class UserDAO { public ArrayList<UserBean> allUsers(){ try { Connection conn = DButil.getConn(); String sql = "select * from usersaccount"; ArrayList<UserBean> list = new ArrayList<UserBean>(); Statement s = conn.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery(sql); while(rs.next()) { UserBean a = new UserBean(rs.getInt(1),rs.getString(2),rs.getString(3),rs.getString(4),rs.getInt(5),rs.getString(6)); list.add(a); } DButil.close(rs,s,conn); return list; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("获取数据失败"+e); } } public boolean login(String user,String pwd){ try { Connection conn = DButil.getConn(); String sql = "select * from userscount where uname=? and upwd=?"; PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, user); ps.setString(2, pwd); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); boolean flag = rs.next(); DButil.close(rs,ps,conn); return flag; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("获取数据失败"+e); } } }
Servlet:
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet{ private UserDAO userDAO = new UserDAO(); @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException,ServletException { String user = request.getParameter("user"); String pwd = request.getParameter("pwd"); String result = null; if(userDAO.login(user, pwd)) result= "<h3 style='color:green'>登录成功</h3>"; else result="<h3 style='color:red'>账户或密码错误</h3>"; response.getWriter().println(result); } }
html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <link href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/ bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"> </head> <body style="overflow:hidden;"> <form class="form-horizontal" role="form" action="login" method="post"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="firstname" class="col-sm-2 control-label">用户名</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" class="form-control" id="firstname" placeholder="请输入用户名" name="user" style="width:200px;"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="lastname" class="col-sm-2 control-label">密码</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="password" class="form-control" id="lastname" placeholder="请输密码" name="pwd" style="width:200px;"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10"> <div class="checkbox"> <label> <input type="checkbox">请记住我 </label> </div> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">登录</button> </div> </div> </form> </body> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery.js"></script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap /3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-Tc5IQib027qvyjSMfHjOMaLkfuWVxZxUPnCJA7l2mCWNIpG9mGCD8wGNIcPD7Txa" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> </html>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号