小范笔记:ASP.NET Core API 基础知识与Axios前端提交数据
跟同事合作前后端分离项目,自己对 WebApi 的很多知识不够全,虽说不必要学全栈,可是也要了解基础知识,才能合理设计接口、API,方便与前端交接。
晚上回到宿舍后,对 WebApi 的知识查漏补缺,主要补充了 WebAPi 的一些方法、特性等如何与前端契合,如何利用工具测试 API 、Axios 请求接口。
本文主要写 WebApi 前端请求数据到 API 、后端返回处理结果,不涉及登录、跨域请求、前端 UI 等。
前提:会一点点 VUE、会一点 Axios、会一点点 Asp.net Core。
工具:Visual Studio 2019(或者其它版本) + Visual Studio Code + Swagger +Postman
由于 Visual Studio 2019 写 ASP.NET Core 页面时,没有 Vue 的智能提示,所以需要使用 VSCode 来写前端页面。
一. 微软WebApi
| 特性 | 绑定源 |
|---|---|
| [FromBody] | 请求正文 |
| [FromForm] | 请求正文中的表单数据 |
| [FromHeader] | 请求标头 |
| [FromQuery] | 请求查询字符串参数 |
| [FromRoute] | 当前请求中的路由数据 |
| [FromServices] | 作为操作参数插入的请求服务 |
来一张 Postman 的图片:
HTTP 请求中,会携带很多参数,这些参数可以在前端设置,例如表单、Header、文件、Cookie、Session、Token等。
那么,上面的表格正是用来从 HTTP 请求中获取数据的 “方法” 或者说 “手段”。HttpContext 等对象不在本文讨论范围。
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 命名空间提供很多用于配置Web API 控制器的行为和操作方法的属性:
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| [Route] | 指定控制器或操作的 URL 模式。 |
| [Bind] | 指定要包含的前缀和属性,以进行模型绑定。 |
| [Consumes] | 指定某个操作接受的数据类型。 |
| [Produces] | 指定某个操作返回的数据类型。 |
| [HttpGet] | 标识支持 HTTP GET 方法的操作。 |
| [HttpPost] | 标识支持 HTTP POST 方法的操作。 |
| ... ... ... | ... ... ... |
WebApi 应用
首先创建一个 Asp.Net Core MVC 应用,然后在 Controllers 目录添加一个 API 控制器 DefaultController.cs。(这里不创建 WebApi 而是 创建 MVC,通过 MVC 创建 API 控制器)。
创建后默认代码:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DefaultController : ControllerBase
{
}
1. 安装 Swagger
在 Nuget 中搜索 Swashbuckle.AspNetCore,或打开 程序包管理器控制台 -> 程序包管理器控制台 ,输入以下命令进行安装
Install-Package Swashbuckle.AspNetCore -Version 5.0.0-rc2
打开 Startup 文件,添加引用
using Microsoft.OpenApi.Models;
上面是微软文档的安装方法,结果笔者测试。如果使用 Nuget 搜索,出现 Swashbuckle.AspNetCore 4.0.1 及以上,应当是引用
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger;
在 ConfigureServices 中添加服务,双引号文字内容随便改。
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "My API", Version = "v1" });
});
报错,则使用
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new Info { Title = "My API", Version = "v1" });
});
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
添加中间件
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseCookiePolicy();
// 添加下面的内容
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(c =>
{
c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "My API V1");
});
访问 /swagger 可以访问到 Swagger 的 UI 界面。
为了便于查看输出和固定端口,打开 Progarm,cs ,修改内容
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseUrls("https://*:5123")
.UseStartup<Startup>();
不要使用 IIS 托管运行。
注意:本文全部使用 [HttpPost] ;全局使用 JsonResult 作为返回类型。
二. 数据绑定与获取
1,默认不加
直接写 action,不使用特性,对于简单类型是 Query,对于复杂类型是 Json。
微软官方文档这样说明:
默认情况下,模型绑定以键值对的形式从 HTTP 请求中的以下源中获取数据:
表单域
请求正文(对于具有 [ApiController] 属性的控制器。)
路由数据
查询字符串参数
上传的文件
对于每个目标参数或属性,将按此列表中指示的顺序扫描源。 有几个例外情况:
路由数据和查询字符串值仅用于简单类型。
上传的文件仅绑定到实现 IFormFile 或 IEnumerable<IFormFile> 的目标类型。
也就是说,对于 WebApi 来说,如果默认不加任何注解,简单类型默认为 Query ,复杂类型为 Json。
如何是 MVC ,复杂类型则回产生多种情况,根据顺序进行区配。简单类型依然是 Query 。
这里先说 Query ,对于复杂类型(模型类等),在后面说明。
Query:
[HttpPost("aaa")]
public async Task<JsonResult> AAA(int? a, int? b)
{
if (a == null || b == null)
return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" });
return new JsonResult(new { code = 2000, result = a + "|" + b });
}
打开 https://localhost:5123/swagger/index.html 查看 UI 界面
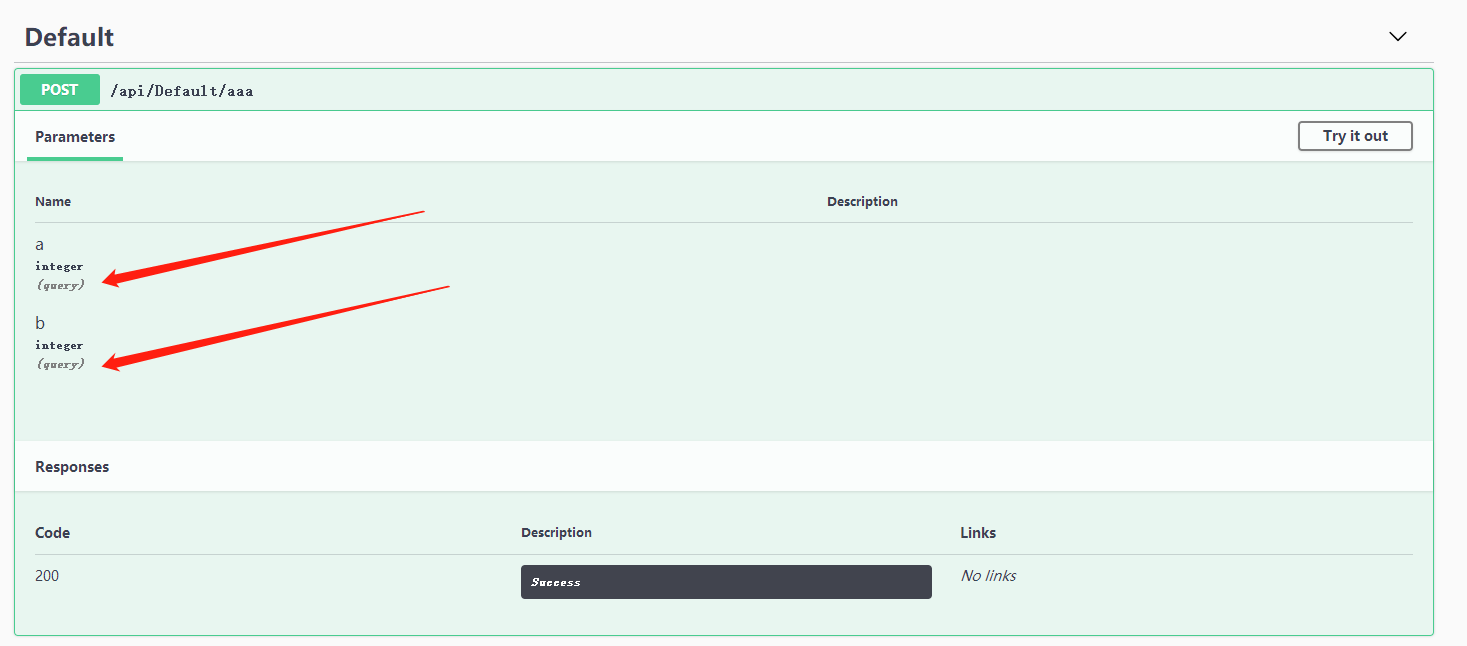
也就是说,创建一个 action ,什么都不加,默认是 query。
通过 Postman 提交数据、测试接口
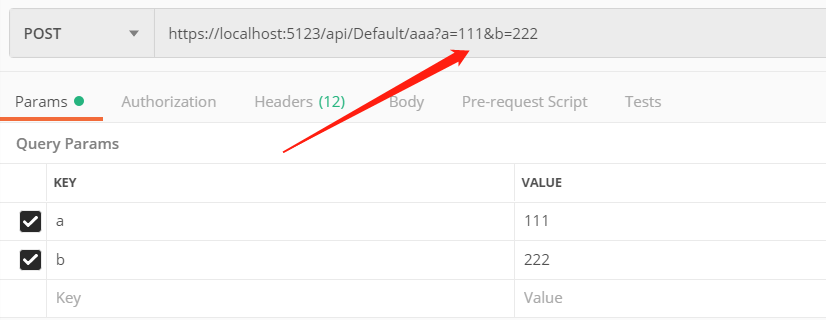
对于 Query 的 action 来说, axios 的写法
postaaa: function () { axios.post('/api/default/aaa?a=111&b=222' ) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
在网上查找资料时,发现有人说通过 params 添加数据也可以,不过笔者测试,貌似不行。
讲道理,别人可以,为啥我不行。。。
axios 代码:
postaaa: function () { axios.post('/api/default/aaa', { params: { a: 123, b: 234 } } ) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
包括下面的,都试过了,不行。
axios.post('/api/default/aaa', { a:1234, b:1122 } axios.post('/api/default/aaa', { data:{ a:1234, b:1122 } }
把 [HttpPost] 改成 [HttpGet] ,则可以使用
axios.post('/api/default/aaa', { params: { a: 123, b: 234 } } ... ...
提示:
... ... .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); })
.then 当请求成功时触发,请求失败时触发 catch 。res 是请求成功后返回的信息,res.data 是请求成功后服务器返回的信息。即是 action 处理数据后返回的信息。
在浏览器,按下 F12 打开控制台,点击 Console ,每次请求后,这里会打印请求结果和数据。
2, [FromBody]
官方文档解释:请求正文。[FromBody] 针对复杂类型参数进行推断。 [FromBody] 不适用于具有特殊含义的任何复杂的内置类型,如 IFormCollection 和 CancellationToken。 绑定源推理代码将忽略这些特殊类型。
算了,看得一头雾水,手动实际试试。
刚刚开始的时候,我这样使用:
public async Task<JsonResult> BBB([FromBody]int? a, [FromBody]int? b)
结果编译时就报错,提示只能使用一个 [FromBody],于是改成
[HttpPost("bbb")] public async Task<JsonResult> BBB([FromBody]int? a, int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 2000, result = a + "|" + b }); }
打开 Swagger UI 界面,刷新一下
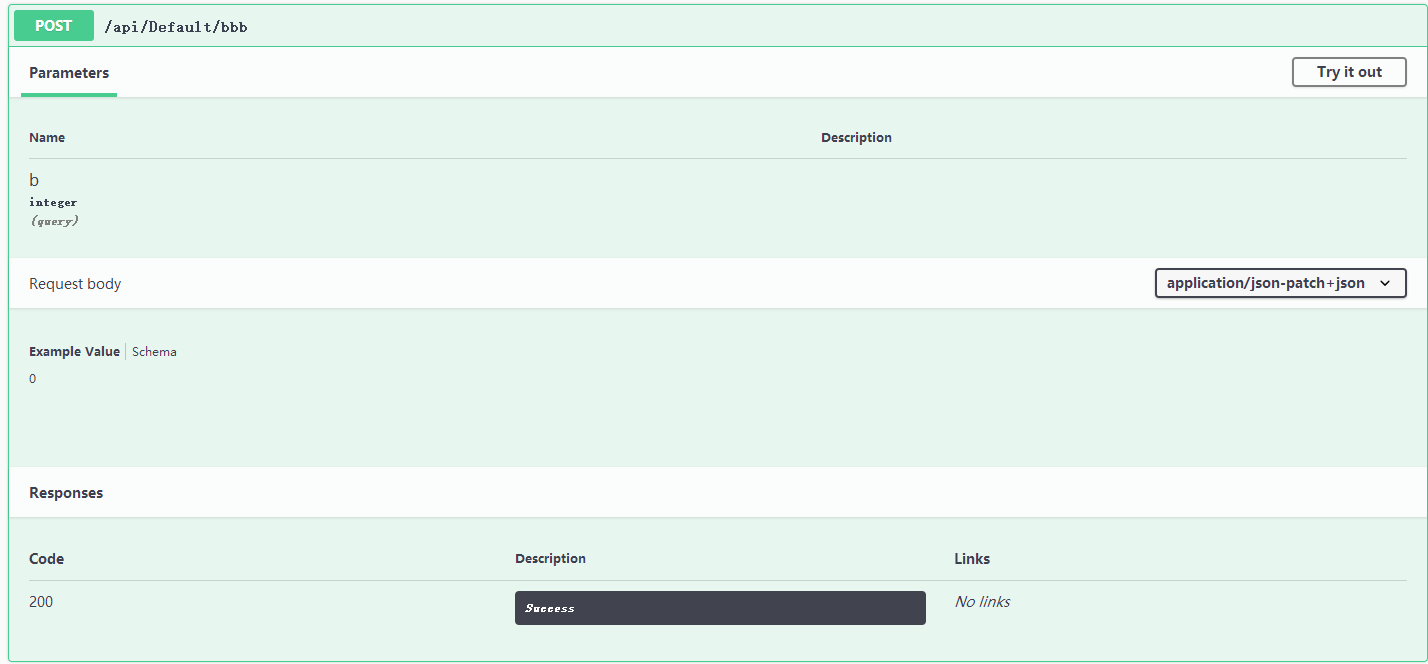
从图片中发现,只有 b,没有 a,而且右上角有下拉框,说明了加 [FromBody] 是 json 上传。
那么说明 [FromBody] 修饰得应当是对象,而不是 字段。
修改程序如下:
// 增加一个类型 public class AppJson { public int? a { get; set; } public int? b { get; set; } } [HttpPost("bbb")] public async Task<JsonResult> BBB([FromBody]AppJson ss) { if (ss.a == null || ss.b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 2000, result = ss.a + "|" + ss.b }); }
再看看微软的文档:[FromBody] 针对复杂类型参数进行推断。,这下可理解了。。。
即是不应该对 int、string 等类型使用 [FromBody] ,而应该使用一个 复杂类型。
而且,一个 action 中,应该只能使用一个 [FromBody] 。
打开 Swagger 界面(有修改需要刷新下界面,下面不再赘述)。

这样才是我们要的结果嘛,前端提交的是 Json 对象。
用 Postman 测试下
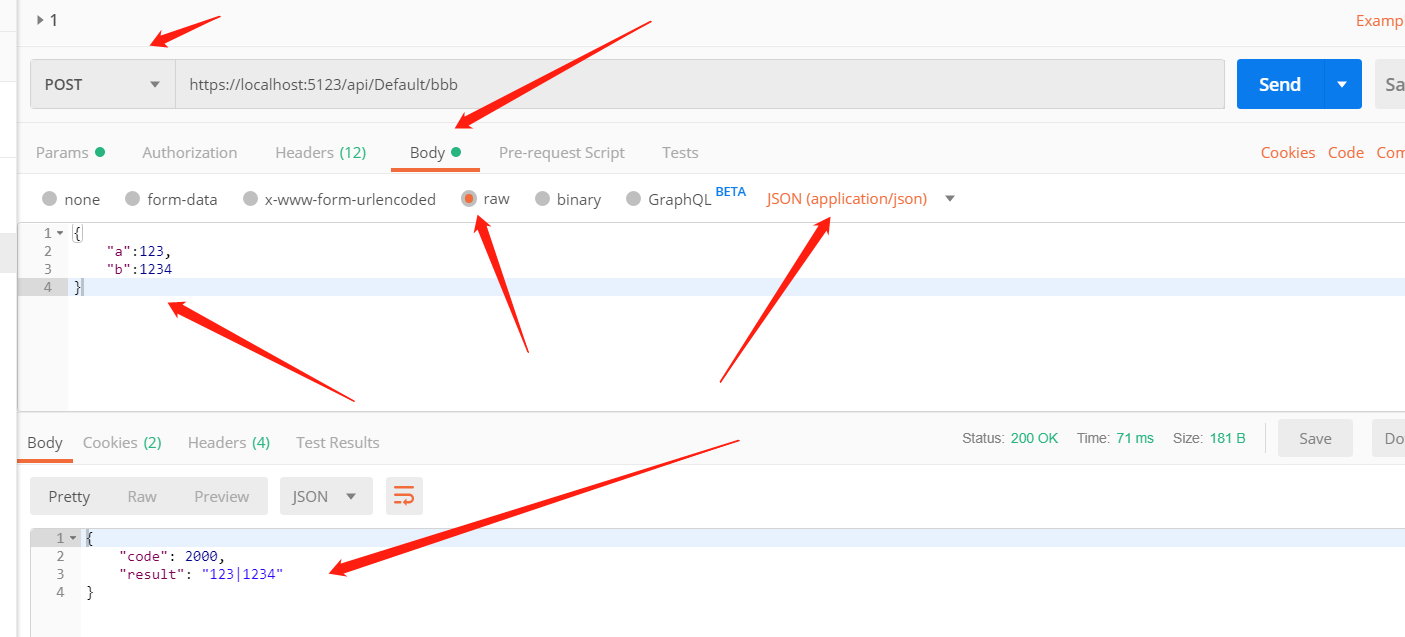
证实了猜想,嘿嘿,嘿嘿嘿。
前端提交的是 Json 对象,遵循 Json 的格式规范,那么 [FromBody] 把它转为 Object 对象。
前端 axios 写法:
methods: { postaaa: function () { axios.post('/api/default/bbb', { "a": 4444, "b": 5555 }) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) } }
3, [FromForm]
[HttpPost("ccc")] public async Task<JsonResult> CCC([FromForm]int? a, [FromForm]int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = a + "|" + b }); }
当然,这样写也行,多个字段或者对象都可以
[HttpPost("ccc")] public async Task<JsonResult> CCC([FromForm]AppJson ss) { if (ss.a == null || ss.b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = ss.a + "|" + ss.b }); }
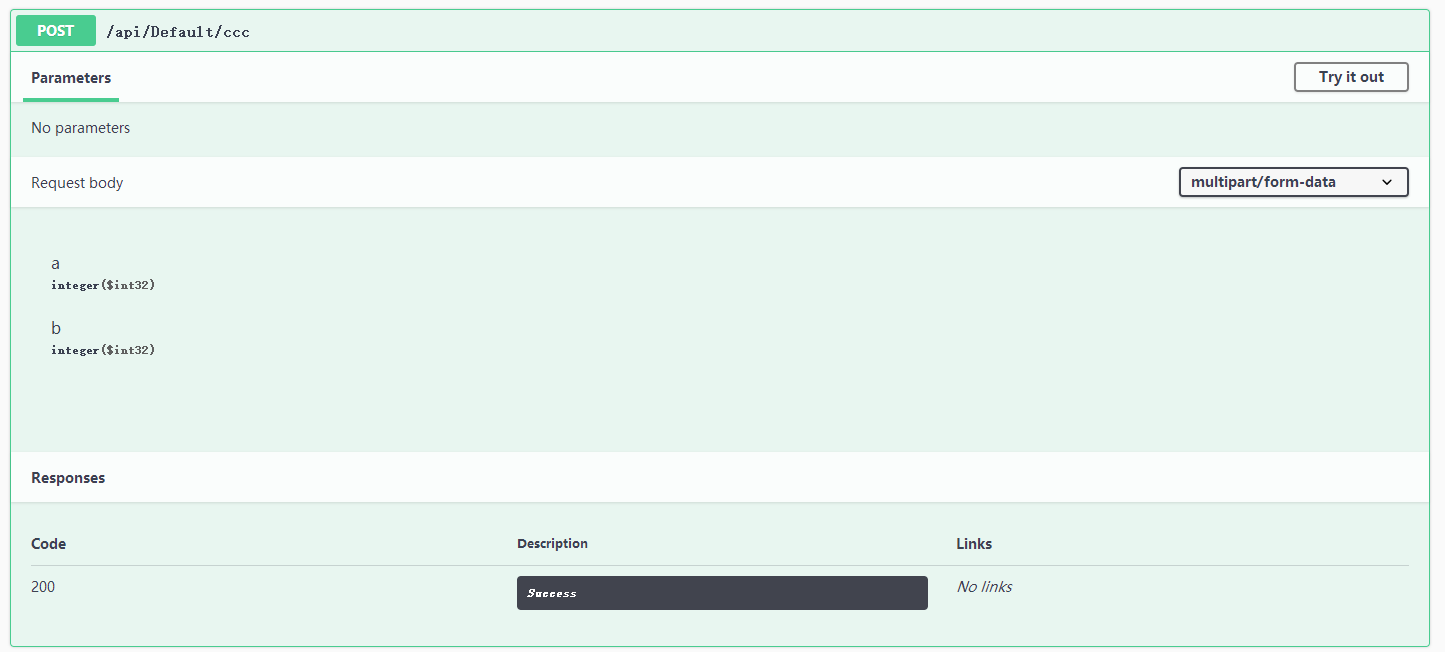
根据提示,使用 Postman 进行测试
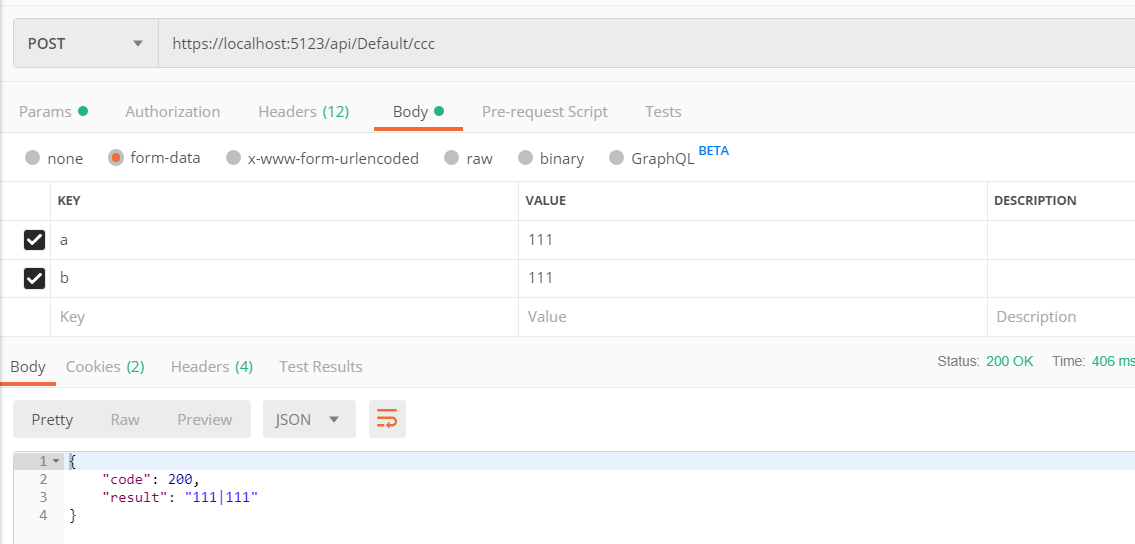
事实上,这样也行 ↓
form-data 和 x-www.form-urlencoded 都是键值形式,文件 form-data 可以用来上传文件。具体的区别请自行查询。
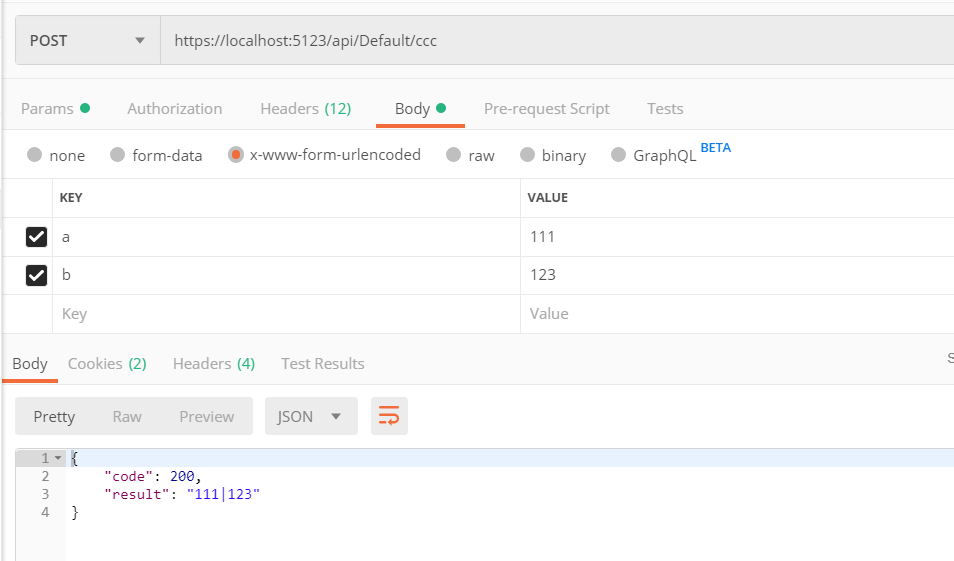
axios 写法(把 Content-Type 字段修改成 form-data 或 x-www.form-urlencoded )
postccc: function () { let fromData = new FormData() fromData.append('a', 111) fromData.append('b', 222) axios.post('/api/default/ccc', fromData, { headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' } }) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
4, [FromHeader]
[FromHeader] 不以表单形式上传,而是跟随 Header 传递参数。
[HttpPost("ddd")] public async Task<JsonResult> DDD([FromHeader]int? a, [FromHeader]int? b) { if (a == null || b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = a + "|" + b }); }
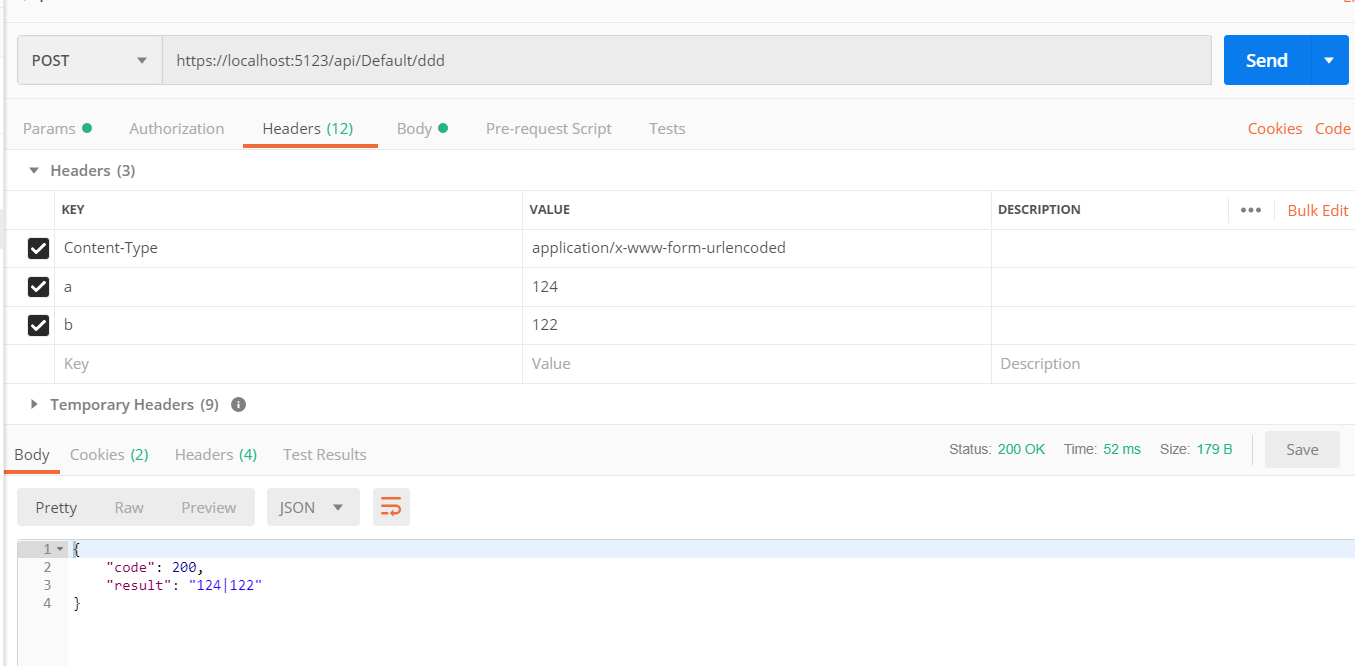
axios 写法
postddd: function () { axios.post('/api/default/ddd', {}, { headers: { a: 123, b: 133 } }) .then(res => { console.log(res.data) console.log(res.data.code) console.log(res.data.result) }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }) }
需要注意的是,headers 的参数,必须放在第三位。没有要提交的表单数据,第二位就使用 {} 代替。
params 跟随 url 一起在第一位,json 或表单数据等参数放在第二位,headers 放在第三位。
由于笔者对前端不太熟,这里有说错,麻烦大神评论指出啦。
5, [FromQuery]
前面已经说了,Action 参数不加修饰,默认就是 [FromQuery] ,参考第一小节。
有个地方需要记住, Action 参数不加修饰。默认就是 [FromQuery] ,有时几种参数并在一起放到 Action 里,会忽略掉,调试时忘记了,造成麻烦。
6, [FromRoute]
获取路由规则,这个跟前端上传的参数无关;跟 URL 可以说有关,又可以说无关。
[HttpPost("fff")] public async Task<JsonResult> FFFxxx(int a,int b, [FromRoute]string controller, [FromRoute]string action) { // 这里就不处理 a和 b了 return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = controller+"|"+action }); }
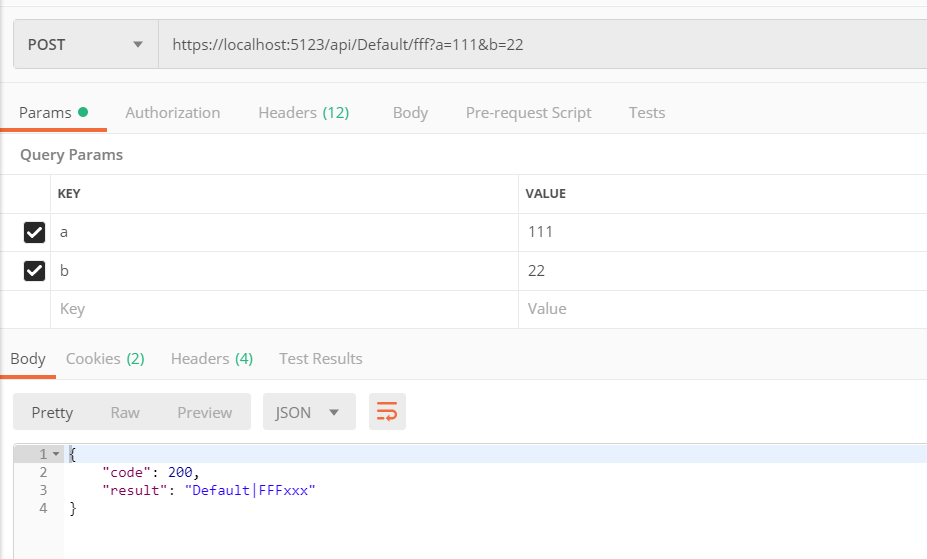
[FromRoute] 是根据路由模板获取的,上面 API 的两个参数和路由模板的名称是对应的:
[FromRoute]string controller, [FromRoute]string action
app.UseMvc(routes => { routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); });
当然,还可以加个 [FromRoute]int? id
[FromRoute] 和 [FromQuery] 区别
以此 URL 为例
https://localhost:5123/api/Default/fff?a=111&b=22
Route 会查到 controller = Default ,action = FFFxxx 。查询到的是代码里的真实名称。
Query 会查询到 a = 111 和 b = 22
那么,如果路由规则里,不在 URL 里出现呢?
[HttpPost("/ooo")] public async Task<JsonResult> FFFooo(int a, int b, [FromRoute]string controller, [FromRoute]string action) { // 这里就不处理 a和 b了 return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = controller + "|" + action }); }
那么,访问地址变成 https://localhost:5123/ooo
通过 Postman ,测试

说明了 [FromRoute] 获取的是代码里的 Controller 和 Action 名称,跟 URL 无关,根据测试结果推断跟路由表规则也无关。
7, [FromService]
这个是与依赖注入容器有关,跟 URL 、路由等无关。
新建一个接口、一个类
public interface ITest { string GGG { get; } } public class Test : ITest { public string GGG { get { return DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString(); } } }
在 ConfigureServices 中 注入
services.AddSingleton<ITest, Test>();
在 DefaultController 中,创建构造函数,然后
private readonly ITest ggg; public DefaultController(ITest ttt) { ggg = ttt; }
添加一个 API
[HttpPost("ggg")] public async Task<JsonResult> GGG([FromServices]ITest t) { return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = t.GGG }); }
访问时,什么参数都不需要加,直接访问此 API 即可。
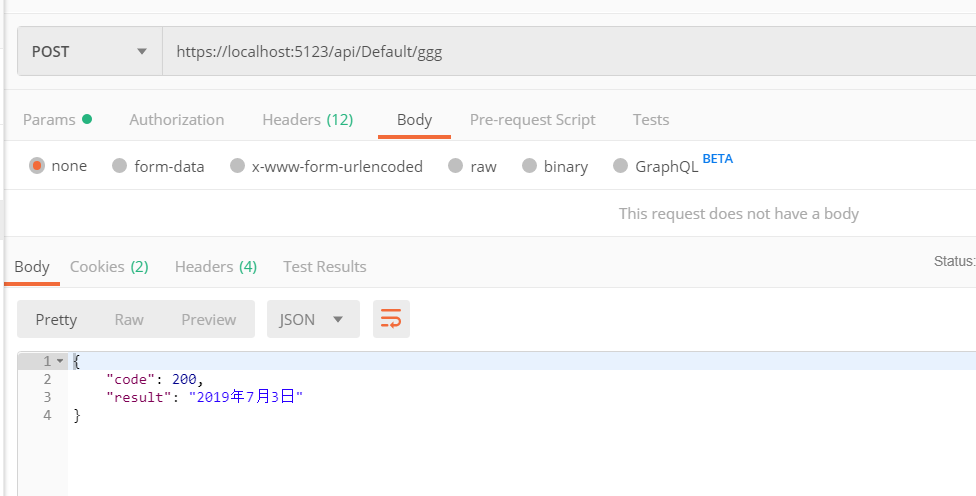
[FromService] 跟后端的代码有关,跟 Controller 、Action 、URL、表单数据等无关。
小结:
特性可以几种放在一起用,不过尽量每个 API 的参数只使用一种特性。
优先取值 Form > Route > Query。
IFromFile 由于文件的上传,本文就不谈这个了。
关于数据绑定,更详细的内容请参考:
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/mvc/models/model-binding?view=aspnetcore-2.2
三. action 特性方法
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 命名空间提供可用于配置 Web API 控制器的行为和操作方法的属性。
下表是针对于 Controller 或 Action 的特性.
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| [Route] | 指定控制器或操作的 URL 模式。 |
| [Bind] | 指定要包含的前缀和属性,以进行模型绑定。 |
| [Consumes] | 指定某个操作接受的数据类型。 |
| [Produces] | 指定某个操作返回的数据类型。 |
| [HttpGet] | 标识支持 HTTP GET 方法的操作。 |
| ... | ... |
下面使用这些属性来指定 Controller 或 Action 接受的 HTTP 方法、返回的数据类型或状态代码。
1, [Route]
在微软文档中,把这个特性称为 属性路由 ,定义:属性路由使用一组属性将操作直接映射到路由模板。
请教了大神,大神解释说,ASP.NET Core 有路由规则表,路由表是全局性、唯一性的,在程序运行时,会把所有路由规则收集起来。
MVC 应用中设置路由的方法有多种,例如
app.UseMvc(routes => { routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); });
[Route("Home/Index")] public IActionResult Index() { return View(); }
[Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class DefaultController : ControllerBase { }
路由是全局唯一的,可以通过不同形式使用,但是规则不能发生冲突,程序会在编译时把路由表收集起来。
根据笔者经验,发生冲突,应该就是在编译阶段直接报错了。(注:笔者不敢确定)
关于路由,请参考 :
2, [Bind]
笔者知道这个是绑定模型的,但是对原理不太清楚。ASP.NET Core 自动生成的可读写的 Controller ,默认都是使用 [Bind] 来绑定数据。
文档定义:用于对复杂类型的模型绑定。
有下面几种相近的特性:
[BindRequired][BindNever][Bind]
微软文档提示:如果发布的表单数据是值的源,则这些属性会影响模型绑定。
就是说,上面的特性是针对类、接口等复杂类型(下面统称模型),对于 int、string 这些类型,可能出毛病。
[BindRequired] 、[BindNever] 只能应用于模型的属性,如
public class TestB { [BindNever] public int ID { get; set; } [BindRequired] public string Name { get; set; } }
但是 [BindRequired] 、[BindNever] 不在讨论范围内,这里只说 [Bind]。
[Bind] 用于类或方法(Controller、Action),指定模型绑定中应包含的模型属性。
在微软官方文档,对于[Bind] 的解释:
[Bind]属性可用于防止“创建”方案中的过多发布情况 。 由于排除的属性设置为 NULL 或默认值,而不是保持不变,因此它在编辑方案中无法很好地工作;- 因为
Bind特性将清除未在 某个 参数中列出的字段中的任何以前存在的数据。
一脸懵逼。
下面是我的踩坑过程,不感兴趣的话直接跳过吧。笔记笔记,记得当然是自己觉得要记的哈哈哈。
新建一个类
public class TestBind { public string A { get; set; } public string B { get; set; } public string C { get; set; } public string D { get; set; } public string E { get; set; } public string F { get; set; } public string G { get; set; } }
新建 API
[HttpPost("hhh")] public async Task<JsonResult> HHH([Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(test); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
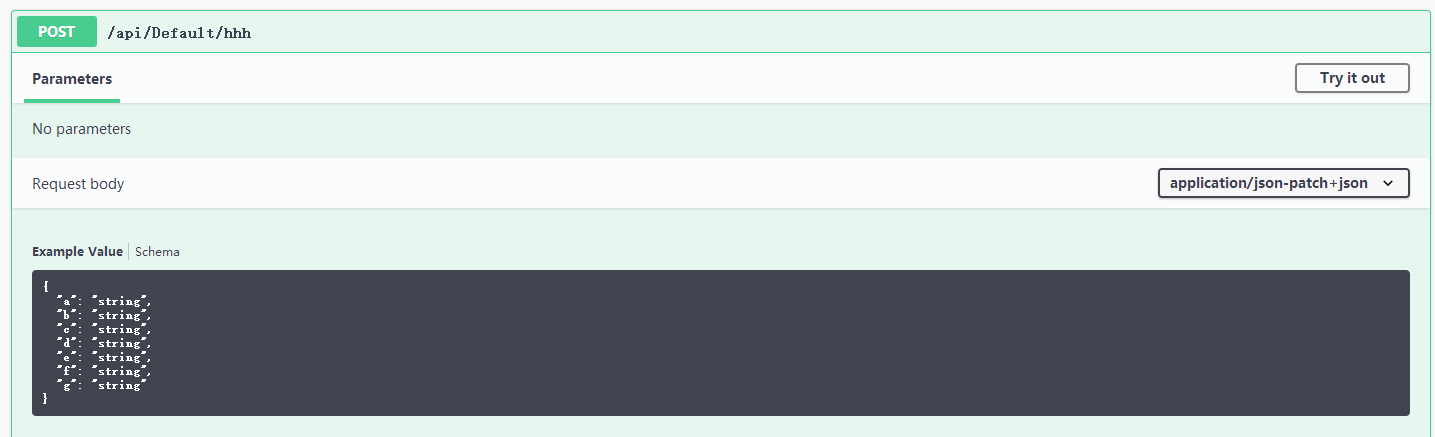
使用 Postman 进行,测试,发现必须使用 Json 形式,才能访问到这个 Action ,其它方式会直接 返回 错误。
{ "errors": { "": [ "A non-empty request body is required." ] }, "title": "One or more validation errors occurred.", "status": 400, "traceId": "0HLO03IFQFTQU:00000007"}
通过两次 Postman 进行测试
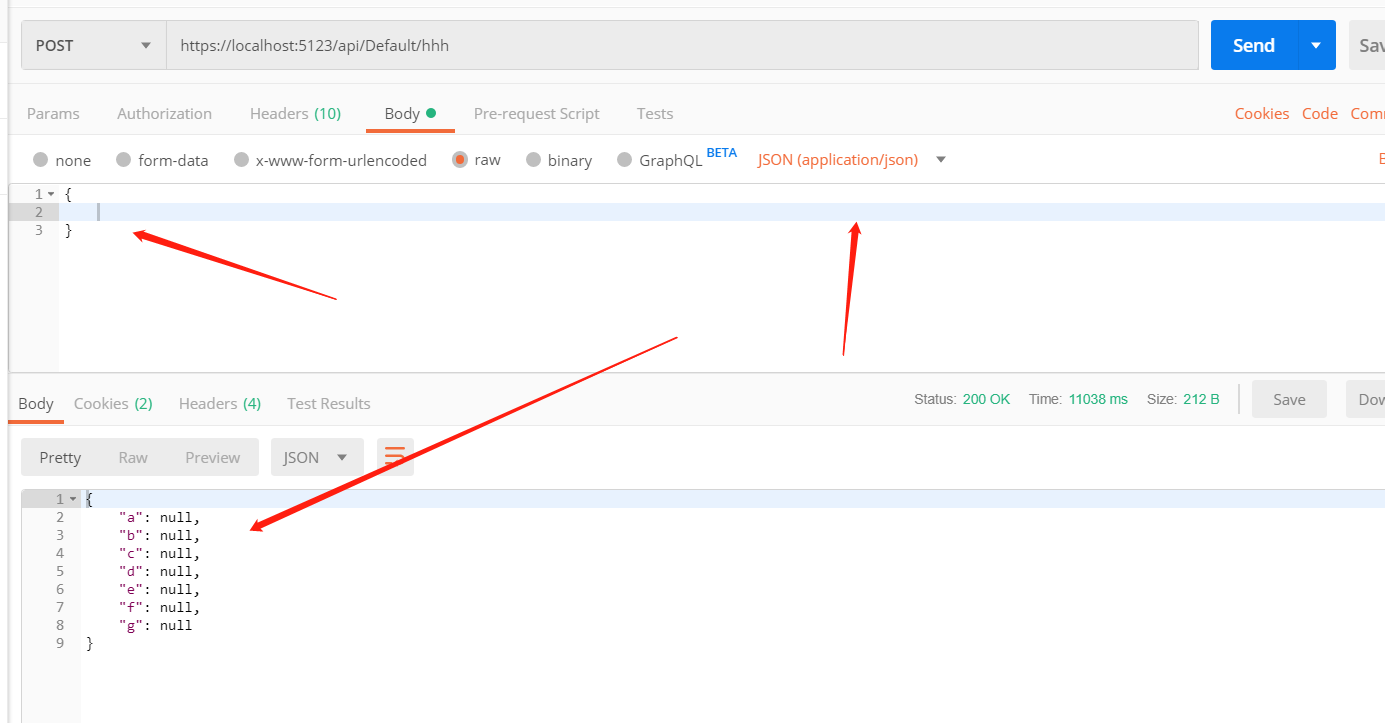
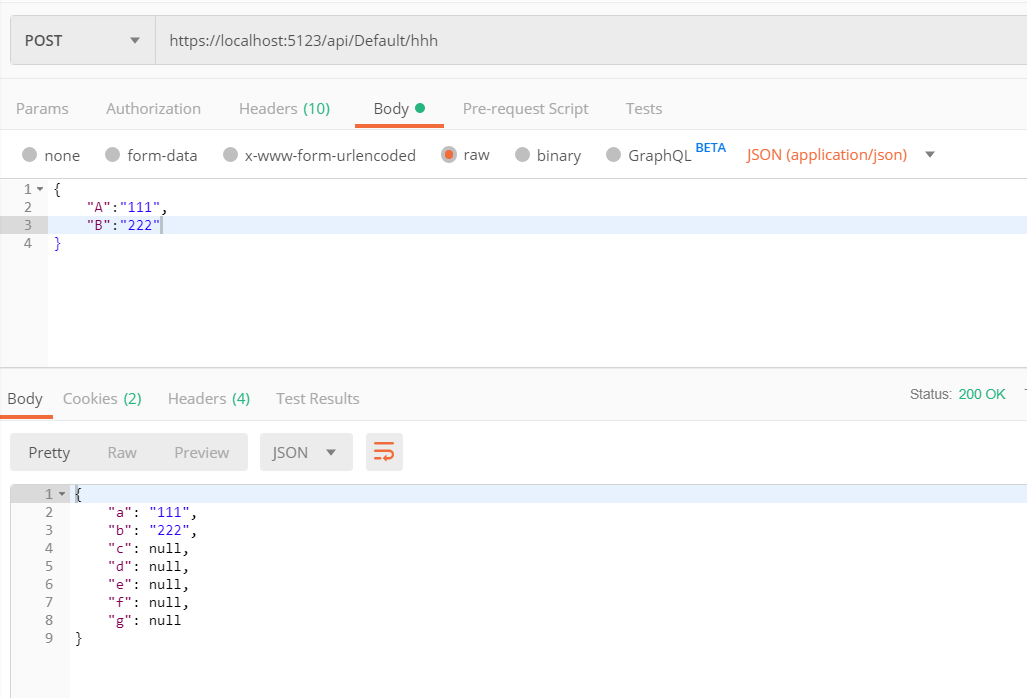
经过测试,我猜想
ModelState.IsValid 跟模型里的验证规则有关系,跟 [Bind] 没关系(尽管用于测试的 TestB 类中没有写验证规则),因此不能使用 ModelState.IsValid 验证 [Bind] 是否符合规则。
Action 的参数:[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test,刚开始的时候我以为请求的数据中必须包含 A、B、C。
测试后发现不是。。。再认真看了文档 :因为 Bind 特性将清除未在 某个 参数中列出的字段中的任何以前存在的数据。
我修改一下:
[HttpPost("hhh")] public async Task<JsonResult> HHH( string D, string E,[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(new { data1 = test, data2 = D, data3 = E }); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
参数变成了 string D, string E,[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test
使用 Swagger 进行测试:
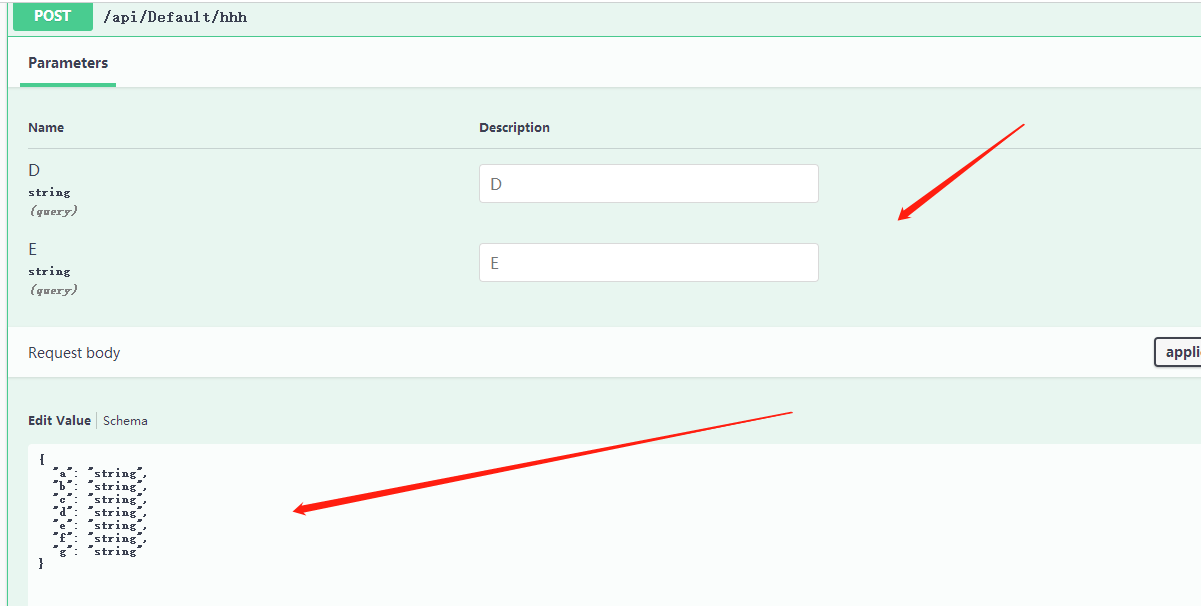 返回结果
返回结果
{ "data1": { "a": "string", "b": "string", "c": "string", "d": "string", "e": "string", "f": "string", "g": "string" }, "data2": null, "data3": null}
改成
[HttpPost("hhh")] public async Task<JsonResult> HHH([Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test, string J, string Q) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(new { data1 = test, data2 = J, data3 = Q }); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
返回结果
{ "data1": { "a": "string", "b": "string", "c": "string", "d": "string", "e": "string", "f": "string", "g": "string" }, "data2": null, "data3": null}
文档中对 [Bind] 描述最多的是:防止过多发布。
通过上面的测试,首先肯定的是一个 Action 里,有多个参数 如
[Bind("A,B,C")] TestBind test, string D, string E string J, string Q。
注意,下面的结论是错的!
那么 D、E 因为于 除了 Test, J、Q就会无效,通过百度,[Bind] 修饰的 Action ,前端请求的数据只有 Test 里面的数据有效,其它 Query等形式一并上传的数据都会失效,防止黑客在提交数据时掺杂其它特殊参数。应该就是这样理解吧。
上面是一开始我的结论,直到多次测试,我发现是错的。
可是有一个地方不明白,
[Bind("A,B,C")]
[Bind("A,B,C,D,E,F,G")]
这两者的区别是是什么。还是没搞清楚。
突然想到 Query,当字段没有使用特性修饰时,默认为 Query 。
最终踩坑测试代码
模型类
public class TestBind { public string A { get; set; } public string B { get; set; } public string C { get; set; } public string D { get; set; } public string E { get; set; } public string F { get; set; } public string G { get; set; } }
Action
[HttpPost("hhh")] public async Task<JsonResult> HHH( string A, string B, string E, string F, string G, [Bind("A,B,C,D")] TestBind test, string C, string D, string J, string Q) { if (ModelState.IsValid == true) return new JsonResult(new { data1 = test, dataA = A, dataB = B, dataC = C, dataD = D, dataE = E, dataF = F, dataG = G, dataJ = J, dataQ = Q }); return new JsonResult(new { Code = 0, Result = "验证不通过" }); }
Swagger 测试
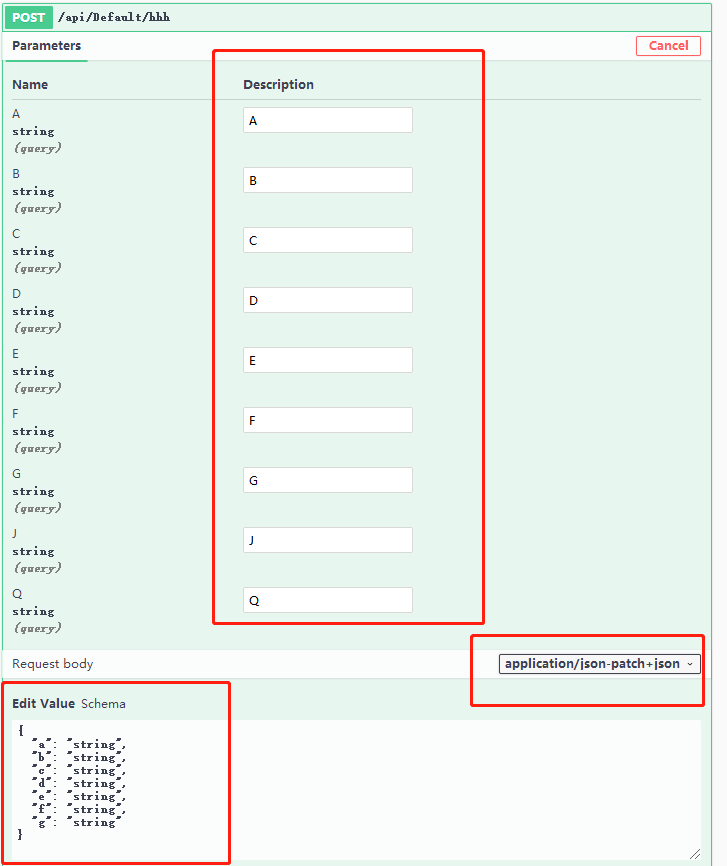
Postman 测试
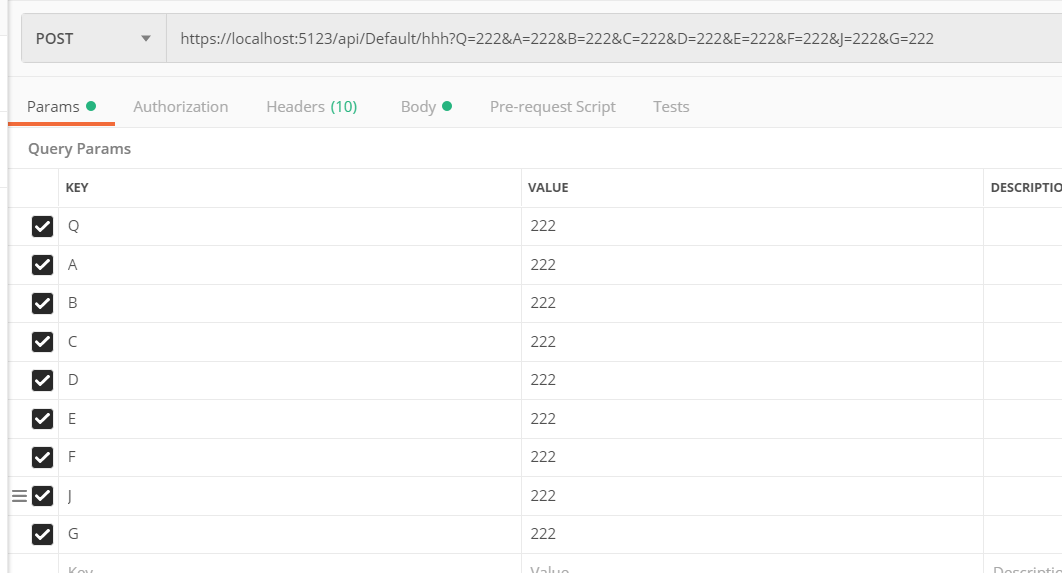
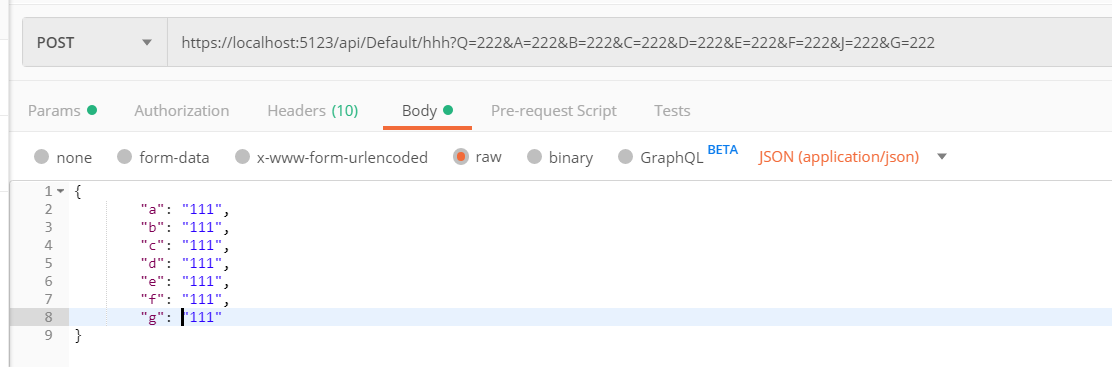
{ "data1": { "a": "111", "b": "111", "c": "111", "d": "111", "e": "111", "f": "111", "g": "111" }, "dataA": "222", "dataB": "222", "dataC": "222", "dataD": "222", "dataE": "222", "dataF": "222", "dataG": "222", "dataJ": "222", "dataQ": "222"}
再在 Swagger 或 Postman ,换着法子尝试各种不同组合的输入。
我懵逼了。试了半天试不出什么。
实在不理解 [Bind] 里,“防止过多发布” 是什么意思
[Bind("A,B,C")]
[Bind("A,B,C,D,E,F,G")]
这两者的区别是是什么。还是没搞清楚。算了,不踩了。
我再到 stackoverflow 提问题,地址 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56884876/asp-net-core-bind-how-to-use-it/56885153#56885153
获得一个回答:
What's the difference between [Bind("A,B,C")] and [Bind("A,B,C,D,E,F,G")]?The former tells the model binder to include only the properties of TestBind named A, B and C. The latter tells the model binder to include those same properties plus D, E, F and G.Are you testing by posting data for all properties of your model? You should notice that the values you post for the excluded properties are not bound.
算了,嘿嘿,测试不出来,放弃。
3, [Consumes]、[Produces]
[Consumes("application/json")] [Produces("application/json")] [Produces("application/xml")] [Produces("text/html")] ... ...
目前只了解到 [Consumes]、[Produces] 是筛选器,用来表示 Controller 或 Action 所能接受的数据类型。大概就是像下面这样使用:
[Consumes("application/json")] [Produces("application/json")] public class DefaultTestController : ControllerBase { }
但是如何实际应用呢?我找了很久,都没有找到什么结果。在 stackoverflow 找到一个回答:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41462509/adding-the-produces-filter-globally-in-asp-net-core
4, [HttpGet]、[HttpPost]、[HttpDelete]、[HttpPut]
修饰 Action ,用来标识这个 Action 能够通过什么方式访问、访问名称。
例如:
[Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class DefaultController : ControllerBase { [HttpPost("aaa")] public async Task<JsonResult> AAA(int? a, int? b) { if (a == null | b == null) return new JsonResult(new { code = 0, result = "aaaaaaaa" }); return new JsonResult(new { code = 200, result = a + "|" + b }); } }
访问地址 https://localhost:5123/api/Default/aaa
使用时,会受到 Controller 和 Action 路由的影响。
但 本身亦可控制路由。以上面的控制器为例
[HttpPost("aaa")] //相对路径
访问地址 xxx:xxx/api/Default/aaa
[HttpPost("/aaa")] //绝对路径
访问地址 xxx:xxx/aaa
四,返回类型
1, 查询备忘表
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 命名空间中,包含控制 MVC 的各种操作方法和类型,笔者从命名空间中抽出与 MVC 或 API 返回类型有关的类型,生成表格:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| AcceptedAtActionResult | An ActionResult that returns a Accepted (202) response with a Location header. |
| AcceptedAtRouteResult | An ActionResult that returns a Accepted (202) response with a Location header. |
| AcceptedResult | An ActionResult that returns an Accepted (202) response with a Location header. |
| AcceptVerbsAttribute | Specifies what HTTP methods an action supports. |
| ActionResult | A default implementation of IActionResult. |
| ActionResult | A type that wraps either an TValue instance or an ActionResult. |
| BadRequestObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Bad Request (400) response. |
| BadRequestResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Bad Request (400) response. |
| ChallengeResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.ChallengeAsync. |
| ConflictObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Conflict (409) response. |
| ConflictResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Conflict (409) response. |
| ContentResult | |
| CreatedAtActionResult | An ActionResult that returns a Created (201) response with a Location header. |
| CreatedAtRouteResult | An ActionResult that returns a Created (201) response with a Location header. |
| CreatedResult | An ActionResult that returns a Created (201) response with a Location header. |
| EmptyResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will do nothing. |
| FileContentResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will write a binary file to the response. |
| FileResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will write a file as the response. |
| FileStreamResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will write a file from a stream to the response. |
| ForbidResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.ForbidAsync. |
| JsonResult | An action result which formats the given object as JSON. |
| LocalRedirectResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header to the supplied local URL. |
| NotFoundObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Not Found (404) response. |
| NotFoundResult | Represents an StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Not Found (404) response. |
| OkObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed performs content negotiation, formats the entity body, and will produce a Status200OK response if negotiation and formatting succeed. |
| OkResult | An StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce an empty Status200OK response. |
| PartialViewResult | Represents an ActionResult that renders a partial view to the response. |
| PhysicalFileResult | A FileResult on execution will write a file from disk to the response using mechanisms provided by the host. |
| RedirectResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header to the supplied URL. |
| RedirectToActionResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header. Targets a controller action. |
| RedirectToPageResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302) or Moved Permanently (301) response with a Location header. Targets a registered route. |
| RedirectToRouteResult | An ActionResult that returns a Found (302), Moved Permanently (301), Temporary Redirect (307), or Permanent Redirect (308) response with a Location header. Targets a registered route. |
| SignInResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.SignInAsync. |
| SignOutResult | An ActionResult that on execution invokes AuthenticationManager.SignOutAsync. |
| StatusCodeResult | Represents an ActionResult that when executed will produce an HTTP response with the given response status code. |
| UnauthorizedObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Unauthorized (401) response. |
| UnauthorizedResult | Represents an UnauthorizedResult that when executed will produce an Unauthorized (401) response. |
| UnprocessableEntityObjectResult | An ObjectResult that when executed will produce a Unprocessable Entity (422) response. |
| UnprocessableEntityResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a Unprocessable Entity (422) response. |
| UnsupportedMediaTypeResult | A StatusCodeResult that when executed will produce a UnsupportedMediaType (415) response. |
| ViewComponentResult | An IActionResult which renders a view component to the response. |
| ViewResult | Represents an ActionResult that renders a view to the response. |
| VirtualFileResult | A FileResult that on execution writes the file specified using a virtual path to the response using mechanisms provided by the host. |
留着写 WebApi 时查询备忘嘿嘿。
那些类型主要继承的两个接口:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IActionResult | Defines a contract that represents the result of an action method. |
| IViewComponentResult | Result type of a ViewComponent. |
注意的是,上面有些是抽象类,例如 FileResult,而 FileStreamResult 实现了 FileResult 。有些类是继承关系。
2, 返回的数据类型
- 特定类型
- IActionResult 类型
- ActionResult 类型
Action 的 return ,返回的数据类型必定是上面三种。
3, 直接返回基元或复杂数据类型
[HttpGet]public IEnumerable<Product> Get(){ return _repository.GetProducts();}
4, IActionResult 类型
响应状态码、Json、重定向、URL 跳转等,属于 IActionResult。
MVC 的 Controller 与 API 的 Controller 有很多相同的地方,亦有很多不同的地方。
API 的 Controller 继承 ControllerBase
MVC 的 Controller 继承 Controller而 Controller 继承
Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IFilterMetadata, IAsyncActionFilter, IDisposable
API 里的 Controller 是最原始的。
API 里的 返回类型需要实例化, new 一下; MVC 里的返回类型,“不需要实例化”。
当然,有些例如 FileResult 是抽象类,不能被实例化。
API:
[HttpGet("returnaaa")] public async Task<IActionResult> ReturnAAA() { return new ViewResult(); return new JsonResult(new { code="test"}); return new RedirectToActionResult("DefaultController","ReturnAAA",""); return new NoContentResult("666"); return new NotFoundResult(); ... }
MVC
public async Task<IActionResult> Test() { return View(); return Json(new { code = "test" }); return RedirectToAction("DefaultController", "ReturnAAA", ""); return NoContent("666"); return NotFound(); ... }
MVC 中,Action 默认是 [HttpGet],不加也可以被访问到;
而 API 的Action,不加 [Httpxxx],则默认不能被访问到。


