ntp同步Linux服务器时间
1.当前环境
服务端:192.168.1.100
客户端:192.168.1.101
客户端:192.168.1.102
系统都为CentOS7
2.服务端操作
检查是否安装ntp
rpm -q ntp

安装ntp服务
yum -y install ntp
修改ntp配置文件
vim /etc/ntp.conf
修改如下:
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift restrict default nomodify restrict 127.0.0.1 restrict ::1
# 配置允许连接服务端的网段 restrict 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
# 配置时间服务器 server ntp.aliyun.com iburst server ntp1.aliyun.com iburst
# 配置在无法连接到时间服务器时将本地时间同步到客户端 server 127.127.1.0 fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10 includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw keys /etc/ntp/keys disable monitor
启动ntp服务并配置开机自启
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl enable ntpd
查看状态,前面带*号表示当前连接的时间服务器
ntpq -p
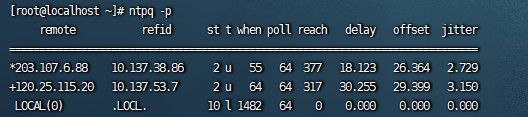
remote: *表示目前使用的ntp server;+表示备用服务器
st:即stratum阶层,值越小表示ntp serve的精准度越高;
when:几秒前曾做过时间同步更新的操作;
Poll表示,每隔多少毫秒与ntp server同步一次;
reach:已经向上层NTP服务器要求更新的次数;
delay:网络传输过程钟延迟的时间;
offset:时间补偿的结果;
jitter:Linux系统时间与BIOS硬件时间的差异时间
3.客户端操作
安装ntp服务,同服务端
修改配置文件
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery restrict 127.0.0.1 restrict ::1
# 配置服务端地址 server 192.168.1.100 iburst includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw keys /etc/ntp/keys disable monitor
启动ntp服务并配置开机自启
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl enable ntpd
查看状态 ntpq -p

4.ntpd和ntpdate的区别
ntpd在实际同步时间时是一点点的校准过来时间的,最终把时间慢慢的校正对。而ntpdate不会考虑其他程序是否会阵痛,直接调整时间。
一个是校准时间,一个是调整时间。我看好多攻略里还把ntpdate放到定时任务里,我觉得不需要,只要保证ntpd服务开机自启,每次服务器重启都会同步一次时间,后面时间出现偏移也会慢慢校对的。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具