TVM Pass优化 -- InferType 类型推导
定义(What)
InferType,类型推断,顾名思义,给表达式进行类型的推断
直接上代码
import tvm
from tvm import relay
import numpy as np
def get_demo_mod():
a = relay.var("a", shape=(2, 3, 10), dtype="float32")
b = relay.var("b", shape=(1, 10), dtype="float32")
c = relay.add(a, b)
func = relay.Function([a, b], c)
mod = tvm.IRModule.from_expr(func)
return mod
mod = get_demo_mod()
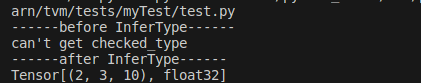
print("------before InferType------")
try:
print(mod["main"].body.checked_type)
except Exception:
print("can't get checked_type")
print("------after InferType------")
mod = relay.transform.InferType()(mod)
print(mod["main"].body.checked_type)
执行结果如下:
作用 (Why)
推断表达式的类型及输入输出尺寸
另:在 Relay 优化过程中, 每个 pass 都可以修改/添加/删除 op, 所以每个 pass 之后都需要重新 InferType
如,TVM Pass优化 -- 公共子表达式消除(Common Subexpr Elimination, CSE)对公共子表达式消除一节中FunctionPass()第四个参数就是InferType进行类型推断
怎么做(How)
这块代码主要在src/relay/transforms/type_infer.cc文件中,具体实现如下:
Pass InferType() {
auto pass_info = PassInfo(0, "InferType", {});
return tvm::transform::CreateModulePass(
[=](IRModule mod, const PassContext& pass_ctx) {
...
AddGlobalTypes(mod);
VLOG(1) << "AddGlobalTypes'" << PrettyPrint(mod);
std::vector<std::pair<GlobalVar, Function>> updates;
for (const auto& it : updated_mod->functions) {
if (auto func = it.second.as<Function>()) {
auto inferencer = TypeInferencer(mod, pass_ctx->diag_ctx.value());
VLOG(1) << "it.first'" << PrettyPrint(it.first) << "it.second"<< PrettyPrint(it.second);
auto updated_func = inferencer.Infer(it.first, func.value());
VLOG(1) << "updated_func'" << PrettyPrint(updated_func);
...
it.first->checked_type_ = updated_func->checked_type();
if (!WellFormed(updated_func, pass_ctx->diag_ctx)) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The type checked intermediate representation is malformed";
}
auto free_tvars = FreeTypeVars(updated_func, mod);
ICHECK(free_tvars.size() == 0)
<< "Found unbound type variables in " << updated_func << ": " << free_tvars;
EnsureCheckedType(updated_func);
updates.push_back({it.first, Downcast<Function>(updated_func)});
}
}
for (const auto& pair : updates) {
updated_mod->Add(pair.first, pair.second, true);
}
return updated_mod;
},
0, "InferType", {});
}
TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL("relay._transform.InferType").set_body_typed([]() { return InferType(); });
和公共子表达式消除的实现可发现,该算子调用的是CreateModulePass,因此它是一个模块级的优化,
模块级优化用于实现过程间优化和分析,模块级优化pass工作在tvm.IRModule对象上,将整个程序作为处理单元,几乎可以对程序执行任何操作。
其中,AddGlobalTypes 给mod添加全局参数,为后续的参数推断做准备,
真正进行推断的是TypeInferencer类的Infer()方法,实现如下:
Expr TypeInferencer::Infer(GlobalVar var, Function function) {
...
// Step 1: Populate the constraints.
GetType(function);
// Step 2: Solve the constraints.
Solve();
// Step 3: Attach resolved types to checked_type field.
auto resolved_expr = Resolver(type_map_, &solver_).VisitExpr(function);
...
}
return resolved_expr;
}
第一步,填充约束
Type GetType(const Expr& expr) {
auto it = type_map_.find(expr);
if (it != type_map_.end() && it->second.checked_type.defined()) {
return it->second.checked_type;
}
Type ret = this->VisitExpr(expr);
ICHECK(ret.defined()) << "expression:" << std::endl << PrettyPrint(expr);
KindCheck(ret, mod_, this->diag_ctx);
ResolvedTypeInfo& rti = type_map_[expr];
rti.checked_type = ret;
return ret;
}
会先从type_map_map表中查找该Expr,第一次执行,如果type_map_中未找到该expr,便会通过VisitExpr()方法在该map表中添加,具体实现如下:
void VisitLeaf(const Expr& expr) {
if (!memo_.count(expr)) {
Type ret = this->DispatchVisitExpr(expr);
memo_[expr] = ret;
}
}
bool CheckVisited(const Expr& expr) {
if (memo_.count(expr)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
Type DispatchVisitExpr(const Expr& expr) { return ExprFunctor::VisitExpr(expr); }
Type VisitExpr(const Expr& expr) final {
auto fcheck_visited = [this](const Expr& expr) { return this->CheckVisited(expr); };
auto fvisit_leaf = [this](const Expr& expr) { return this->VisitLeaf(expr); };
if (memo_.count(expr)) {
return memo_[expr];
} else {
ExpandDataflow(expr, fcheck_visited, fvisit_leaf);
return memo_[expr];
}
}
其中fcheck_visited()匿名函数通过调用VisitLeaf方法中的DispatchVisitExpr方法,该函数会调用到ExprFunctor类中构建的包含各种类型的虚表中,根据类型调用对应的VisitExpr_方法,如CallNode类型的参数,代码如下:
Type VisitExpr_(const CallNode* call) final {
Array<Type> arg_types;
for (Expr arg : call->args) {
arg_types.push_back(GetType(arg));
}
if (const OpNode* opnode = call->op.as<OpNode>()) {
Type rtype =
PrimitiveCall(opnode->op_type.as<FuncTypeNode>(), arg_types, call->attrs, call->span);
if (rtype.defined()) {
AddTypeArgs(GetRef<Call>(call), arg_types);
return rtype;
}
}
其中,AddTypeArgs()会向type_map_表中插入该expr
void AddTypeArgs(const Expr& expr, Array<Type> type_args) {
auto type_info = type_map_.find(expr);
if (type_info == type_map_.end()) {
type_map_.insert({expr, ResolvedTypeInfo(Type(), type_args)});
} else {
ICHECK(!type_info->second.type_args.defined());
type_info->second.type_args = type_args;
}
}
第二步,解决约束
bool TypeSolver::Solve() {
while (!update_queue_.empty()) {
RelationNode* rnode = update_queue_.front();
const auto& rel = rnode->rel;
update_queue_.pop();
ICHECK(!rnode->resolved);
// update the relation with given evidence.
Array<Type> args;
for (auto* tlink = rnode->type_list.head; tlink != nullptr; tlink = tlink->next) {
args.push_back(Resolve(tlink->value->FindRoot()->resolved_type));
ICHECK_LE(args.size(), rel->args.size());
}
// We need to set this in order to understand where unification
// errors generated by the error reporting are coming from.
reporter_->SetSpan(rnode->span);
try {
// Call the Type Relation's function.
bool resolved = rel->func(args, rel->num_inputs, rel->attrs, reporter_);
if (resolved) {
++num_resolved_rels_;
}
rnode->resolved = resolved;
} catch (const CompileError& err) {
this->Emit(Diagnostic::Error(rnode->span) << err.what());
rnode->resolved = false;
}
// Mark inqueue as false after the function call
// so that rnode itself won't get enqueued again.
rnode->inqueue = false;
}
// This criterion is not necessarily right for all the possible cases
// TODO(tqchen): We should also count the number of in-complete types.
return num_resolved_rels_ == rel_nodes_.size();
}
通过调用 Solve() 方法,我们求解填充好的类型约束。解决约束的过程使用了类型约束求解器(constraint solver)来尝试找到满足约束条件的类型赋值方案。
第三步,
Resolver(const std::unordered_map<Expr, ResolvedTypeInfo, ObjectPtrHash, ObjectPtrEqual>& tmap,
TypeSolver* solver)
: tmap_(tmap), solver_(solver) {}
Expr MixedModeMutator::VisitExpr(const Expr& expr) {
auto fcheck_visited = [this](const Expr& expr) { return this->CheckVisited(expr); };
auto fvisit_leaf = [this](const Expr& expr) { return this->VisitLeaf(expr); };
if (memo_.count(expr)) {
return memo_[expr];
} else {
ExpandDataflow(expr, fcheck_visited, fvisit_leaf);
return memo_[expr];
}
}
使用 Resolver 类的实例来将解析后的类型信息附加到已解析的表达式的checked_type 字段上。Resolver 类是负责类型解析和处理的工具类。它通过访问表达式的结构,并使用之前求解出的类型信息来确定每个表达式的准确类型。
respect~



