题目信息:伊雷娜想旅行
题目
描述
不知目标为何地只想越走越远,
将带不走的一切留在梦里。
因为曾经选择的都是我钟爱的事物,
才铸就今天的我。——《魔女之旅》
灰之魔女伊雷娜,一名只想着旅行的天才少女。
一天,她来到了某个国家。这个国家由\(n\)个风格不同的城市和\(m\)条单向通道组成,每个通道都有一个路程值。
现在伊雷娜在\(1\)号城市,她想参观至少\(k\)个城市(包括1号城市)。她听说星尘魔女在\(x\)号城市,因此一定要经过\(x\)号城市。
旅行需要食物,每完成一段路程,她都要吃掉和路程值相等的空间的食物。她可以在每个城市进行食物的补充,但是只能在\(1\)号城市购买装食物的背包。因为背包空间越大,价格越贵,所以伊雷娜想知道背包空间最少是多少?(贫穷.jpg)
输入格式
第一行有三个整数\(n,m,k,x(1\le n\le 10^5,\, 1\le m\le 10^6,\, 1\le k\le n, 1\le x\le n)\)
接下来\(m\)行每行三个整数\(u,v,w\;(1\le u,v \le n;\; 1\le w \le 10^9)\),表示城市\(u\)到城市\(v\)有一条长度为\(w\)的单向通道。
数据保证没有环,且有解。
输出格式
一个整数,表示背包最小空间。
输入样例1
5 7 4 2
1 2 1
1 4 6
4 2 4
4 5 1
2 5 5
3 4 4
1 3 5
输出样例1
5
输入样例2
5 7 4 2
1 2 1
1 4 6
4 2 4
4 5 1
2 5 5
3 4 4
1 3 7
输出样例2
6
题解
你需要知道的知识:
1.二分(如果对于1n中的某个数x,有1x都满足某个条件,x+1~n都不满足这个条件,则可以用log(n)次“检验一个数是否满足条件”的方式确定x)
2.拓扑序
3.bfs(广度优先搜索)
4.建图
二分背包大小,将不超过该大小的边放到新图中,并反向再建一个新图。以x为起点,在反向图中搜索到1的最长路径长度len2(此时设每条边边长为1),在正向图中搜索最长链长度len1。如果x能到达1且len1+len2+1>=k,则说明这个容量可行。
要注意dfs可能会爆栈,因此搜索需要用bfs实现。
std代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
int n, m, k, x;
vector<PII> Vall1[N], Vall2[N];
vector<int> V1[N], V2[N];
queue<int> Q;
int vis[N], degree[N], len[N];
void dfs(int start, int goal, vector<PII>*V, vector<int>*VV, int color, int dom){
while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop();
Q.push(start);
while(!Q.empty()){
int u=Q.front(); Q.pop();
if(u==goal) continue;
for(auto&e:V[u]) if(e.second<=dom){
int v=e.first;
VV[u].push_back(v);
degree[v]++;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=color;
Q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
void bfs(vector<int>*V){
while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop();
Q.push(x); len[x]=1;
while(!Q.empty()){
int u=Q.front(); Q.pop();
for(auto&v:V[u]){
len[v]=max(len[v],len[u]+1);
degree[v]--;
if(!degree[v]) Q.push(v);
}
}
}
bool check(int dom){
//init
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
V1[i].clear();
V2[i].clear();
len[i]=0;
degree[i]=0;
vis[i]=false;
}
dfs(x,1,Vall2,V2,2,dom);
dfs(x,0,Vall1,V1,1,dom);
//from x to 1
bfs(V2);
int len2=len[1];
//from x to others
bfs(V1);
int len1=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) if(vis[i]==1) len1=max(len1,len[i]);
//return
return len2>0 && len1+len2>k;
}
int main(){
int l, r, mid;
//input
cin>>n>>m>>k>>x;
for(int i=1, u, v, w; i<=m; ++i){
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);
Vall1[u].push_back(PII(v,w));
Vall2[v].push_back(PII(u,w));
l=i==1?w:min(l,w);
r=i==1?w:max(r,w);
}
//erfen
while(l<r-1){
mid=l+r>>1;
if(check(mid)) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
int ans=check(l)?l:r;
ans=ans*(check(r)?1:-1);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
数据构造
一共12个测试点:
1,2,3:m=1e6, 完全随机生成
4,5,6:由3坨组成
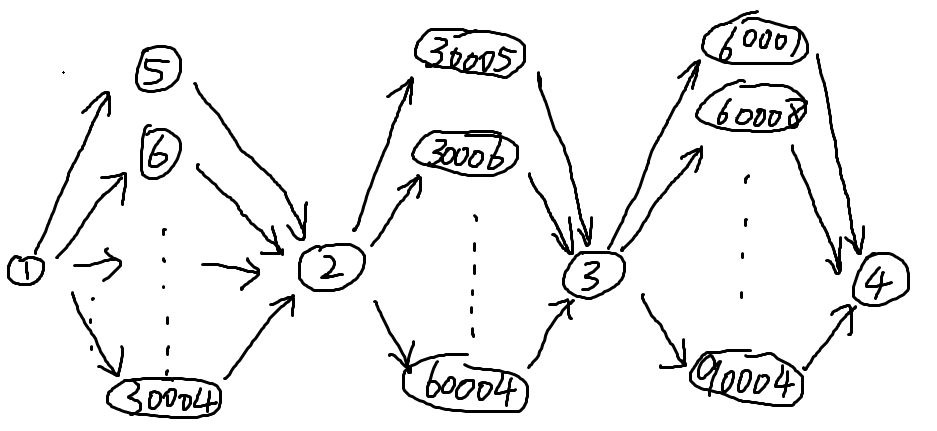
7,8,9:链状
10,11,12:网格形
对于完全随机的数据,先随机了一个拓扑序,再依据拓扑序添加m条边。
造数据代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL,LL> PLL;
typedef tuple<int,int,int> TIII;
const int N=1e5+10, M=1e6+10, W=1e9;
int n, m, k, x;
vector<PLL> Topo;
int topo[N];
TIII Data[M];
void fun1(){
n=5000; m=1000000; k=rnd()%(n/50)+1; x=rnd()%n+1;
//Randomly generate topological order
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
Topo.push_back(PLL(rnd(),i));
}
puts("ok");
sort(Topo.begin(),Topo.end());
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
topo[Topo[i].second]=i+1;
}
puts("ok");
//Randomly generate edges
for(int i=1; i<=m; ++i){
int u, v;
do{
u=rnd()%n+1;
v=rnd()%n+1;
}while(u==v);
if(u>v) swap(u,v);
Data[i]=TIII(topo[u],topo[v],rnd()%W+1);
}
puts("ok");
//output
FILE *fw=fopen("3.in", "w");
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d %d\n", n, m, k, x);
for(int i=1, u, v, w; i<=m; ++i){
tie(u,v,w)=Data[i];
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d\n", u, v, w);
}
fclose(fw);
}
void fun2(){
n=90004; m=180000; k=6; x=4;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=5; i<30005; ++i){
Data[++cnt]=TIII(1,i,rnd()%W+1);
Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,2,rnd()%W+1);
}
for(int i=30005; i<60005; ++i){
Data[++cnt]=TIII(2,i,rnd()%W+1);
Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,3,rnd()%W+1);
}
for(int i=60005; i<90005; ++i){
Data[++cnt]=TIII(3,i,rnd()%W+1);
Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,4,rnd()%W+1);
}
//output
FILE *fw=fopen("6.in", "w");
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d %d\n", n, m, k, x);
for(int i=1, u, v, w; i<=m; ++i){
tie(u,v,w)=Data[i];
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d\n", u, v, w);
}
fclose(fw);
}
void fun3(){
n=100000; m=300000-3; k=11451; x=11451;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<n; ++i){
Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,i+1,rnd()%W+1);
Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,i+1,rnd()%W+1);
Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,i+1,rnd()%W+1);
}
//output
FILE *fw=fopen("8.in", "w");
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d %d\n", n, m, k, x);
for(int i=1, u, v, w; i<=m; ++i){
tie(u,v,w)=Data[i];
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d\n", u, v, w);
}
fclose(fw);
}
int main(){
n=100000; m=300000-3; k=514; x=514;
int cnt=0, r=1000, c=100;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if((i-1)/c<r-1) Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,i+c,rnd()%W);
if(i%c) Data[++cnt]=TIII(i,i+1,rnd()%W);
}
m=cnt;
//output
FILE *fw=fopen("12.in", "w");
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d %d\n", n, m, k, x);
for(int i=1, u, v, w; i<=m; ++i){
tie(u,v,w)=Data[i];
fprintf(fw, "%d %d %d\n", u, v, w);
}
fclose(fw);
}

