2017 济南考前集训DAY2.AM
T1


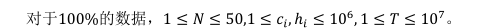
思路: 如果 楼高是有序的
在任意的两个楼之间跳跃 楼高的花费是一定的。
比如 楼的高度 为 1 2 3 5 7
我们从 第1栋楼跳到第5栋楼的代价 和从第一栋楼 跳到第二栋楼再跳到第5栋楼的代价 是一样的
但是我们可以多跳一步
所以我们可以按照 楼的高度排序
不妨设 dp[i][j] 为跳了i步 落在第j栋楼上
转移 就枚举他是从哪一栋楼上跳过来的即可

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cctype> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #define min(x,y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y)) 6 7 const int MAXN = 55; 8 9 int n,t; 10 11 int dp[MAXN][MAXN]; 12 13 struct node { 14 int h,c; 15 friend inline bool operator < (node x,node y) { 16 return x.h<y.h; 17 } 18 }; 19 node e[MAXN]; 20 21 inline void read(int&x) { 22 int f = 1;register char c = getchar(); 23 for(x = 0;!isdigit(c);c == '-'&&(f = -1),c = getchar()); 24 for(;isdigit(c);x = x * 10 + c - 48,c = getchar()); 25 x = x * f; 26 } 27 28 int main(int argc,char**argv) { 29 freopen("meet.in","r",stdin); 30 freopen("meet.out","w",stdout); 31 32 read(n); 33 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(e[i].c); 34 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(e[i].h); 35 read(t); 36 37 std::sort(e + 1,e + 1 + n); 38 memset(dp,63,sizeof dp); 39 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) dp[0][i]=e[i].c; 40 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 41 for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { 42 for(int k = 1; k < j; ++k) 43 dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][k] + e[j].h - e[k].h); 44 dp[i][j] += e[j].c; 45 } 46 47 for(int i = n; i >= 0; --i) 48 for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) 49 if(dp[i][j] <= t) { 50 printf("%d\n",i + 1); 51 return 0; 52 } 53 54 return 0; 55 }
T2



思路: 设给出的数 为 b1 b2 ..
我们要求 a1 a2 ..
我们知道 a1 + a2 == b1
a1 + a3 == b2
但是 a1 + a4 和 a2 + a3 哪一个更小我们不知道
所以我们可以令 a2 + a3 == x 就可以解的 a1 a2 a3 的值
在 b序列中删去 b1 b2 x 最小的数就是a4
再把 a2 + a4 a3 + a4 删去 最小的就是a5

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cctype> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 6 const int MAXN = 50000; 7 8 int n,t,tot; 9 10 int a[MAXN],ans[310][310],re[310]; 11 12 bool used[MAXN]; 13 14 inline void read(int&x) { 15 int f = 1; register char c=getchar(); 16 for(x = 0;!isdigit(c);c == '-'&&(f = -1),c = getchar()); 17 for(;isdigit(c);x = x * 10 + c - 48,c = getchar()); 18 x = x * f; 19 } 20 21 void check(int x) { 22 if((a[1] + a[2] + a[x])&1) return; 23 re[2] = (a[1] - a[2] + a[x]) >> 1; 24 re[1] = a[1] - re[2]; 25 re[3] = a[2] - re[1]; 26 27 memset(used,false,sizeof used); 28 used[1] = used[2] = used[x] = true; 29 int pos,r; 30 for(int i = 3,k = 4; i <= t; ++i) { 31 if(used[i]) continue; 32 re[k] = a[i] - re[1]; 33 34 for(int j = 1; j < k; ++j) { 35 r = re[j] + re[k]; 36 pos = std::lower_bound(a + 1,a + 1 + t,r)-a; 37 if(a[pos] != r) return; 38 while(pos < t && used[pos] && a[pos] == r) ++pos; 39 if(a[pos] != r) return; 40 used[pos] = true; 41 } 42 ++k; 43 } 44 45 ++tot; 46 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ans[tot][i] = re[i]; 47 } 48 49 int main(int argc,char**argv) { 50 freopen("city.in","r",stdin); 51 freopen("city.out","w",stdout); 52 53 read(n); 54 t = n * (n - 1) / 2; 55 for(int i = 1; i <= t; ++i) read(a[i]); 56 57 std::sort(a + 1,a + 1 + t); 58 for(int i = 3; i <= t; ++i) { 59 if(a[i] == a[i-1]) continue; 60 check(i); 61 } 62 63 printf("%d\n",tot); 64 for(int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i) { 65 for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) 66 printf("%d ",ans[i][j]); 67 printf("\n"); 68 } 69 return 0; 70 }
T3


思路:分块
对与 100 以内的 p
预处理除所有 a[i] % p
把余数相同的扔进一个 vector 中
每次查询 l~r 区间内的数时 二分找到 最小的左端点和做大的右端点 输出长度
对于 大于 100 的 p
我们发现 % p 为 v 的数最多会存在100 个
应为 % p 为 v 的数 只能是 v, v + p ,v + 2p , v + 3p, v + 4p ....
把每个数的位置记录在一个vector中 每次进行二分查找即可

1 #include <vector> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cctype> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 6 const int MAXN = 100010; 7 8 int n,m; 9 10 int a[MAXN]; 11 12 std::vector<int> v1[110][110],b[MAXN]; 13 14 inline void read(int&x) { 15 int f = 1; register char c = getchar(); 16 for(x = 0;!isdigit(c);c == '-'&&(f = -1),c = getchar()); 17 for(;isdigit(c); x = x * 10 + c - 48,c = getchar()); 18 x = x * f; 19 } 20 21 int main(int argc,char**argv) { 22 freopen("light.in","r",stdin); 23 freopen("light.out","w",stdout); 24 25 read(n);read(m); 26 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(a[i]),b[a[i]].push_back(i); 27 28 for(int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i) 29 for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) 30 v1[i][a[j]%i].push_back(j); 31 32 int l,r,p,v; 33 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { 34 read(l);read(r);read(p);read(v); 35 if(p <= 100) { 36 std::vector<int>::iterator L = std::lower_bound(v1[p][v].begin(), v1[p][v].end(), l); 37 std::vector<int>::iterator R = std::upper_bound(v1[p][v].begin(), v1[p][v].end(), r); 38 printf("%d\n",R - L); 39 } 40 else { 41 int _l = v,ans = 0; 42 while(_l <= 10000) { 43 std::vector<int>::iterator L = std::lower_bound(b[_l].begin(), b[_l].end(), l); 44 std::vector<int>::iterator R = std::upper_bound(b[_l].begin(), b[_l].end(), r); 45 ans += R - L; 46 _l+=p; 47 } 48 printf("%d\n",ans); 49 } 50 } 51 52 return 0; 53 }
作者:乌鸦坐飞机
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/whistle13326/
新的风暴已经出现
怎么能够停止不前
穿越时空 竭尽全力
我会来到你身边
微笑面对危险
梦想成真不会遥远
鼓起勇气 坚定向前
奇迹一定会出现



