洛谷 P1213 时钟 &&IOI 1994 The Clocks
题目描述
考虑将如此安排在一个 3 x 3 行列中的九个时钟:
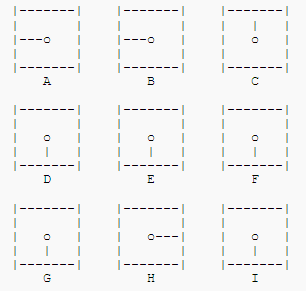
目标要找一个最小的移动顺序将所有的指针指向12点。下面原表格列出了9种不同的旋转指针的方法,每一种方法都叫一次移动。选择1到9号移动方法,将会使在表格中对应的时钟的指针顺时针旋转90度。
移动方法 受影响的时钟
1 ABDE
2 ABC
3 BCEF
4 ADG
5 BDEFH
6 CFI
7 DEGH
8 GHI
9 EFHI
Example
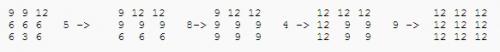
[但这可能不是正确的方法,请看下面]
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第1-3行: 三个空格分开的数字,每个数字表示一个时钟的初始时间,3,6,9,12。数字的含意和上面第一个例子一样。
输出格式:
单独的一行包括一个用空格分开的将所有指针指向12:00的最短移动顺序的列表。
如果有多种方案,输出那种使其连接起来数字最小的方案。(举例来说5 2 4 6 < 9 3 1 1)。
输入输出样例
9 9 12 6 6 6 6 3 6
4 5 8 9
说明
题目翻译来自NOCOW。
USACO Training Section 1.4
暴力bfs 在vijos 上是可以A的
但是在洛谷 会被卡掉两个点 1.3s 死活没法再优化了
若有会的dalao 帮帮我
换dfs
每一种变换 最多变3次 第四次就回到原来的状态
所以我们可以dfs每一种变换方式的次数 最多三次
bfs超时数据 dfs 0.1s毫无压力
#include <queue>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
/*int z[9][9]={{1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0},
{0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1},
{0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1},
};*/
int z[10][10] = {{0},{1,2,4,5},{1,2,3},{2,3,5,6},{1,4,7},{2,4,5,6,8},
{3,6,9},{4,5,7,8},{7,8,9},{5,6,8,9}};
int s[10];
struct node {
int s[10];
int cnt;
int path[100];
friend bool operator < (node x,node y) {
return x.cnt>y.cnt;
}
};
node a,now,t;
bool f[4][4][4][4][4][4][4][4][4];
inline void read(int&x) {
register char c=getchar();
for(x=0;!isdigit(c);c=getchar());
for(;isdigit(c);x=x*10+c-48,c=getchar());
}
inline bool pd(int*p) {
for(int i=0;i<9;++i) if(p[i]) return false;
return true;
}
inline bool check(int*p) {
if(f[p[0]][p[1]][p[2]][p[3]][p[4]][p[5]][p[6]][p[7]][p[8]]) return false;
f[p[0]][p[1]][p[2]][p[3]][p[4]][p[5]][p[6]][p[7]][p[8]]=1;
return true;
}
inline void BFS() {
std::priority_queue<node> q;
memcpy(a.s,s,sizeof s);
q.push(a);
while(!q.empty()) {
now=q.top();
q.pop();
for(int i=1;i<=9;++i) {
t=now;
if(pd(now.s)) {
std::sort(now.path+1,now.path+now.cnt+1);
for(int k=1;k<=now.cnt;++k) printf("%d ",now.path[k]);
return;
}
for(int j=0;z[i][j];++j) {
++t.s[z[i][j]-1];
if(t.s[z[i][j]-1]>=4) t.s[z[i][j]-1]-=4;
}
if(check(t.s)) {
t.path[++t.cnt]=i;
q.push(t);
}
}
}
return;
}
int hh() {
freopen("1.out","r",stdin);
int t=clock();
for(int x,i=0;i<9;++i)
read(x),x=(x/3)%4,s[i]=x;//
f[s[0]][s[1]][s[2]][s[3]][s[4]][s[5]][s[6]][s[7]][s[8]]=1;
BFS();
printf("%d\n",clock());
return 0;
}
int sb=hh();
int main(int argc,char**argv) {;}
#include <queue>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
const int MAXN=10;
int z[9][9]={{1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0},
{0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0},
{0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1},
{0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1},
};
int s[MAXN],tmp[MAXN],ans[MAXN];
inline void read(int&x) {
register char c=getchar();
for(x=0;!isdigit(c);c=getchar());
for(;isdigit(c);x=x*10+c-48,c=getchar());
}
inline bool check() {
for(int i=0;i<9;++i) if(tmp[i]) return false;
return true;
}
inline void print() {
for(int i=0;i<9;++i)
for(int j=0;j<ans[i];++j)
printf("%d ",i+1);
exit(0);
}
inline void DFS(int step) {
memcpy(&tmp,&s,sizeof tmp);
for(int i=0;i<9;++i)
for(int j=0;j<9;++j)
tmp[i]=(tmp[i]+z[j][i]*ans[j])%4;
if(check()) {print();}
if(step==9) return;
for(int i=0;i<4;++i)
ans[step]=i,DFS(step+1);
return;
}
int hh() {
// freopen("1.out","r",stdin);
// int t=clock();
for(int x,i=0;i<9;++i)
read(x),x=(x/3)%4,s[i]=x;
DFS(0);
// printf("%d\n",clock());
return 0;
}
int sb=hh();
int main(int argc,char**argv) {;}
作者:乌鸦坐飞机
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/whistle13326/
新的风暴已经出现
怎么能够停止不前
穿越时空 竭尽全力
我会来到你身边
微笑面对危险
梦想成真不会遥远
鼓起勇气 坚定向前
奇迹一定会出现


