下载缓存
以下内容是《用python写网络爬虫》的读书笔记
之所以要缓存下载页面,是为了避免重复下载所造成的资源浪费。
一、为链接爬虫添加缓存支持
我们将重写download函数,将其变成一个类。
所谓的为链接爬虫添加缓存支持,就是在每次下载页面的时候判断以下这个页面是不是之前已经下载过了,如果已经下载过了,那么我们直接从cache中提取相应的值就可以了,如果还没有下载过那么就要去下载。相当于用空间换时间。
from Chapter1 import Throttle import logging import random import urllib2 import urlparse ''' predifine the parameters ''' Delay_Time = 5 User_Agent = "wuyanjing" Proxies = None Num_Tries = 2 Cache = None class Downloader: def __init__(self, delay=Delay_Time, user_agent=User_Agent, proxies=Proxies, num_tries=Num_Tries, cache=Cache, opener=None): ''' init all parameters :param delay: the delay time bettween two same download :param user_agent: :param proxies: :param num_tries: the try times of download :param cache: save the html :param opener: get the opener for download html ''' self.throttle = Throttle.Throttle(delay) self.user_agent = user_agent self.proxies = proxies self.num_tries = num_tries self.cache = cache self.opener = opener def __call__(self, url, *args, **kwargs): ''' get the html of the special url :param url: :param args: :param kwargs: :return: html ''' result = None if self.cache: try: result = self.cache[url] except KeyError: logging.info("the key is not in the cache") pass else: if self.num_tries > 0 and 500 <= result['code'] < 600: result = None if result is None: self.throttle.wait(url) proxy = random.choice(self.proxies)if self.proxies else None headers = {"User_agent": self.user_agent} result = self.download(url, headers, proxy, self.num_tries) if self.cache: self.cache[url] = result return result['html'] def download(self, url, headers, proxy, numtries, data=None): ''' download the url html, if there are 5xx error it will try numtries times :param url: :param headers: :param proxy: :param numtries: :param data: :return {html:value, code:value}: the html and code ''' print "downloading : ", url request = urllib2.Request(url, data, headers or {}) opener = self.opener or urllib2.build_opener() if proxy: proxy_params = {urlparse.urlparse(url).scheme: proxy} opener.add_handler(urllib2.ProxyHandler(proxy_params)) try: response = opener.open(request) html = response.read() code = response.code except Exception as e: print "download error is ", e.message html = '' if hasattr(e, 'code'): code = e.code if numtries > 0 and 500 <= code < 600: return self.download(url, headers, proxy, numtries-1, data) else: code = None print "download successfully : ", url return {"html": html, "code": code}
download函数被重写了,所以我们还需要重写以下link_crawl函数
import robotparser import download import urlparse import re def linkcrawler(url, delay=5, user_agent="wuyanjing", proxies=None, num_tries=2, cache=None, link_regex=None, max_depth=-1, max_urls=-1, scrape_callback=None): ''' it will tell people whether the html is download or not maybe the html will be blocked by the robots.txt :param url: :param delay: :param user_agent: :param proxies: :param num_tries: :param cache: :param link_regex: :param max_depth: :param max_urls: :param scrape_callback: :return: return nothing ''' crawl_queue = [url] seen = {url: 0} num_urls = 0 rp = getrobots(url) d = download.Downloader(delay=delay, user_agent=user_agent, proxies=proxies, num_tries=num_tries, cache=cache) while crawl_queue: url = crawl_queue.pop() depth = seen[url] if rp.can_fetch(user_agent, url): html = d(url) links = [] if scrape_callback: links.extend(scrape_callback(url, html) or {}) if depth != max_depth: # find all links in the html which is match the link_regex if link_regex: links.extend(link for link in getlinks(html) if re.match(link_regex, link)) for link in links: link = normalize(url, link) if link not in seen: seen[link] = depth+1 if same_domain(url, link): # success add the link into the queue crawl_queue.append(link) # check whether have reached download maximun num_urls += 1 if num_urls == max_urls: break else: print "blocked by robots.txt", url def getrobots(url): ''' catch the robotparser :param url: set the url of robots :return robotparser: record the robotparser ''' rp = robotparser.RobotFileParser() rp.set_url(url+'/robots.txt') rp.read() return rp def getlinks(html): ''' get a lists of link of the html :param html: :return list: a lists of link ''' web_regex = re.compile('<a[^>]+href=["\'](.*?)["\']', re.IGNORECASE) return web_regex.findall(html) def normalize(url, link): ''' return a new url :param url: :param link: :return url: it is a new url ''' # split the url into two part, the first part is url without fragment, # the second part the removed fragment link, _ = urlparse.urldefrag(link) return urlparse.urljoin(url, link) def same_domain(url, link): ''' judge that if the url and link has the domain :param url: :param link: :return boolean: true, they have the same domain;false, they don't have the same domain ''' return urlparse.urlparse(url).netloc == urlparse.urlparse(link).netloc if __name__ == '__main__': linkcrawler("http://www.zhipin.com", link_regex=".*/.*?query=.*", delay=1, num_tries=2) linkcrawler('http://hf.meituan.com', link_regex='.*', delay=1, num_tries=1)
二、磁盘缓存
要想把我们保存在cache中的结果保存在文件中,我们首先需要以每个url作为文件名,然后将相应的内容写入到文件中。但是我们知道不同的平台它对于文件的命名方式是有要求的,要求如下:
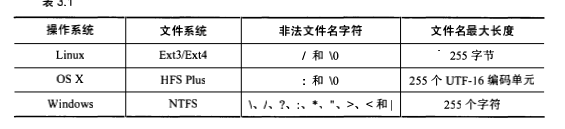
不过不管是哪个平台,只要我们将url路径只保留数字,字母然后将其他符合都替代为下划线,然后限制文件名和它的父目录的字符长度在255以内,那么它就是合法的。但是也有极少数例外的情况,那就是url的路径它是以斜杠结尾的,那么这个时候如果我们单纯的适用以上的原则,就会使得文件不合法。为了避免这个问题,我们就要将斜杠前的那个字符串s作为一个目录,然后再在这个目录下创建一个名为s.html的文件,记录当前的url路径。
根据url有了文件名,那么我们就可以根据url对文件进行读写操作。
import os import urlparse import re import pickle import LinkCrawler import time class DiskCache: def __init__(self, cache="cache", max_length=255): ''' define the cache locate and max_length of the filename :param cache: :param max_length: ''' self.cache_dir = cache self.max_length = max_length def urltopath(self, url): ''' define a file according to the url :param url: define the filename according to the url :return: os path of the file ''' compements = urlparse.urlparse(url) path = compements.path if not path: path = "/index.html" elif path.endswith("/"): path += "/index.html" fullpath = compements.netloc + path + compements.query filenames = re.sub('[^/a-zA-Z0-9\-,.;_]', "_", fullpath) filename = '/'.join(segment[:self.max_length]for segment in filenames.split('/')) return os.path.join(self.cache_dir, filename) def __getitem__(self, url): ''' get data from the disk for the url :param url: :return: ''' path = self.urltopath(url) if os.path.exists(path): with open(path, "rb") as fb: return pickle.load(fb) else: raise KeyError(url + "not exists") def __setitem__(self, url, value): ''' set data to the disk for the url :param url: :param value: :return: ''' path = self.urltopath(url) folder = os.path.dirname(path) if not os.path.exists(folder): os.makedirs(folder) with open(path, "wb") as fb: # use the pickle to dump the value fb.write(pickle.dumps(value)) if __name__ == "__main__": start = time.time() LinkCrawler.linkcrawler("http://example.webscraping.com/", link_regex=".*/index", cache=DiskCache()) end = time.time() print end-start
为了减少存储空间,我们可以对存储的数据进行压缩。以下是压缩的方式:
三、数据库缓存
关系数据库不适合进行数据缓存,因为它不适合分布式系统。NOSQL是一种比较合适的数据库,我们使用针对文档数据的MongoDb数据库,因为我们下载的html文件本质上就相当于文档。当然Nosql数据库还有其他的类型,比如:针对列数据存储的HBase,针对键值存储的Redis,和针对图形的Neo4j
首先我们就要安装Mongodb数据库。附上它的安装教程 。
有了Mongodb数据库之后我们就可以进行数据存储。我们要实现的目标就是对于同一个url,数据库只保存最新的数据,这只需要用update操作代替insert操作。同时为了节省空间,还需要进行数据压缩,这使用之前介绍的压缩方法即可。当然了,为了消除失效页面我们也需要定义时间戳,定期的删除失效数据,这里要注意的是,Mongodb数据的删除操作是批处理的,即使你把失效的时间戳设置为0,你也必须等到一分钟(最短删除间隔执行时间)后才能看到效果。
from pymongo import MongoClient from datetime import datetime, timedelta from bson.binary import Binary import LinkCrawler import zlib import pickle class MongoDb: def __init__(self, client=None, expires=timedelta(days=30)): # if the client is not define # try to connect to the default client self.client = MongoClient("localhost", 27017) if client is None else client self.db = self.client.cache self.db.webpage.create_index('timestamp', expireAfterSeconds=expires.total_seconds()) def __getitem__(self, url): ''' decompress the html and get it :param url: :return: ''' record = self.db.webpage.find_one({'_id': url}) if record: return pickle.loads(zlib.decompress(record['result'])) else: raise KeyError(url + " not exits") def __setitem__(self, url, value): ''' compress the html and save it we will just save the newest value of url,and delete data if overtime :param url: :param value: :return: ''' record = {'result': Binary(zlib.compress(pickle.dumps(value))), 'timestamp': datetime.utcnow()} self.db.webpage.update({'_id': url}, {'$set': record}, upsert=True) if __name__ == "__main__": LinkCrawler.linkcrawler("http://example.webscraping.com/", link_regex=".*/index", cache=MongoDb())
四、小节
通过对已经下载过的页面进行缓存,可以大大的减少下一次访问同一页面的时间。这是典型的一种是空间换时间的方式。保存缓存有两种方式:一种是直接以文件的形式保存在本地,但是这种方式受到文件系统的诸多限制;另一种是保存在Mongodb数据库中,这个方式简单便捷,推荐使用。
下载缓存的时候,为了节省空间,我们需要对数据进行压缩,然后在需要用到数据的时候再进行解压。另外呢,为了保持动态页面的有效性,我们需要定期的删除失效 页面,失效时间可以根据具体情况自己确定。




