java异常体系
一、异常体系图
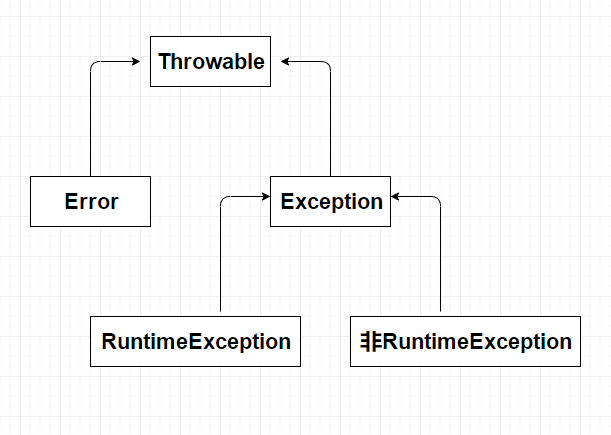
1、Error:程序无法处理的系统错误,编译器不做检查。一般与jvm相关,系统崩溃,虚拟机错误,内存空间不足。
2、Exception:程序可以处理的异常,捕获后可能恢复。
RuntimeException:不可预知的,程序应当自行避免。
非RuntimeException:可预知,从编译器检查异常。
从责任看:
1、Error属于JVM需要负担的责任。
2、RuntimeException是程序应该负担的责任。
3、Checked Exception是java编译器应该负担的责任。
在使用编译器编写代码时,非RuntimeException是需要在程序中被处理的,使用try-catch或throws抛出。
而RuntimeException异常,即使不做处理,代码同样可以编译通过。这就需要在代码中预测可能出现的异常,提前处理。
二、常见的Error和Exception异常
RuntimeException:
1、NullPointException 空指针引用异常
2、ClassCastException 类型强制转换异常
3、IllegalArgumentException 传递非法参数异常
4、IndexOutOfBoundsException 下标越界异常
5、NumberFormatException 数字格式异常
非RuntimeException:
1、ClassNotFoundException 找不到指定class的异常
2、IOException IO操作异常
Error:
1、NOClassDefFoundError 找不到class定义的异常
2、StackOverflowException 深递归导致栈被耗尽而抛出的异常
3、OutOfMemoryError 内存溢出异常
三、异常捕获处理
1、throws抛出
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class ExceptionTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { test(); } static void test() throws FileNotFoundException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(""); } }
一层层抛出,交给系统处理。
2、try-catch
只处理异常信息,不抛出异常,程序不会终止
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class ExceptionTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { test(); } static void test() { try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(""); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
处理异常信息,同时抛出RuntimeException异常,程序终止
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class ExceptionTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { test(); } static void test() { try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(""); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(); } } }
异常处理原则:
具体明确:抛出的异常应能通过异常名和message信息准确说明异常的类型和产生异常的原因。
提早抛出:应尽可能早的发现并抛出异常,便于精确定位。
延迟捕获:异常捕获和处理应尽可能延迟,让掌握更多信息的作用域来处理异常。将异常使用throws子句抛出给它的调用者,让调用者来明确异常信心。
四、注意事项
1、finally关键字,在return语句或throw之前执行,经常用于关闭io流。
2、自定义业务异常,继承RuntimeException。catch块中抛出的同样是RuntimeException异常。因为抛出非RuntimeException异常就需要再次try-catch。
3、异常处理会消耗性能,在某些情况下,可食用if检查来代替。消耗性能的原因:1、try-catch影响jvm的优化、2、异常对象实例需要保存栈快照等信息,消耗较大。
如下测试:
static void testIf(String[] array){ if(array != null){ System.out.println(array[0]); } else{ System.out.println("array is null"); } } static void testException(String[] array){ try{ System.out.println(array[0]); }catch (NullPointerException e){ System.out.println("arrays is null"); } }
测试if性能:
@Test public void testIf(){ long start = System.nanoTime();//纳秒 testIf(null); System.out.println(System.nanoTime() - start +"ns!"); }
结果(连续3次):
array is null 153000ns! array is null 124900ns! array is null 126100ns!
测试try-catch性能:
@Test public void testException(){ long start = System.nanoTime();//纳秒 testException(null); System.out.println(System.nanoTime() - start +"ns!"); }
结果(连续3次):
arrays is null 263800ns! arrays is null 212100ns! arrays is null 203000ns!
结果显示:try-catch使用之后性能消耗较大。



