Java二叉树链表的建立及四种遍历方法
package Test; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; //二叉树树类 public class BinaryTree { public TreeNode root; //有一个根节点 public static int index; public TreeNode CreateBTree(char[] a) { TreeNode root = null; if (index==a.length ) { index=index-1; } if (a[index] != '#') { root = new TreeNode(a[index]); index++; root.setLChild(CreateBTree(a)); index++; root.setRChild(CreateBTree(a)); } return root; } //先序遍历 public void prevOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } System.out.print(root.getData() + ","); prevOrder(root.getLChild()); prevOrder(root.getRChild()); } // 中序遍历 public void midOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } midOrder(root.getLChild()); System.out.print(root.getData() + ","); midOrder(root.getRChild()); } // 后序遍历 public void postOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } postOrder(root.getLChild()); postOrder(root.getRChild()); System.out.print(root.getData() + ","); } // 获取树大小 private int getSize(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return 0; } else { return 1 + getSize(node.leftChild) + getSize(node.rightChild); } } /*求二叉树的高*/ public int getHeight() { return getHeight(this.root); } private int getHeight(TreeNode node) { if (node != null) { //左子树和右子树中谁大返回谁 int i = getHeight(node.leftChild); int j = getHeight(node.rightChild); return (i > j) ? i + 1 : j + 1; } else { return 0; } } //获得叶子数 public int getLeaf(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return 0; } if (node.leftChild == null && node.rightChild == null) { System.out.println("Leaf node: " + node.getData()); return 1; } else { return getLeaf(node.leftChild) + getLeaf(node.rightChild); } } //获得第K层节点数 public int getNodeKNum(TreeNode node, int k) { if (k == 1) { if (node == null) return 0; System.out.println("K Node:" + node.getData()); return 1; } return getNodeKNum(node.getLChild(), k - 1) + getNodeKNum(node.getRChild(), k - 1); } //查找某个节点 public TreeNode findNode(int data) { return findNode(this.root, data); } public TreeNode findNode(TreeNode node, int data) { if (node == null) { return null; } else if (node.getData() == data) { return node; } TreeNode leftNode = findNode(node.getLChild(), data); if (null != leftNode) return leftNode; TreeNode rightNode = findNode(node.getRChild(), data); if (null != rightNode) return rightNode; return null; } //返回某节点的父节点 public TreeNode getParent(int data) { return getParent(this.root, data); } public TreeNode getParent(TreeNode node, int data) { if (node == null) return null; TreeNode childL = node.getLChild(); TreeNode childR = node.getRChild(); if ((childL != null && childL.getData() == data) || childR != null && childR.getData() == data) return node; TreeNode parentL = getParent(node.getLChild(), data); if (parentL != null) return parentL; TreeNode parentR = getParent(node.getRChild(), data); if (parentR != null) return parentR; return null; } //层次遍历,用到队列 public void BTreeLevelOrder() { TreeNode root = this.root; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); LinkedList<TreeNode> list = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode pre = queue.poll(); list.add(pre); if (pre.getLChild() != null) queue.offer(pre.getLChild()); if (pre.getRChild() != null) queue.offer(pre.getRChild()); } Iterator<TreeNode> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { TreeNode cur = it.next(); System.out.print(cur.getData() + ", "); } } //判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树(层次遍历的变形) public boolean isCompleteBTree() { TreeNode root = this.root; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node == null) break; queue.offer(node.getLChild()); queue.offer(node.getRChild()); } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if (cur != null) return false; } return true; } class TreeNode { private TreeNode leftChild; private TreeNode rightChild; private char data; public TreeNode(char data) { this.data = data; } public void setLChild(TreeNode left) { this.leftChild = left; } public void setRChild(TreeNode right) { this.rightChild = right; } public void setData(char data) { this.data = data; } public char getData() { return this.data; } public TreeNode getLChild() { return this.leftChild; } public TreeNode getRChild() { return this.rightChild; } } public static void main(String[] agrs) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); char[] a = new char[]{'A','B','D','G','#','#','H','K','#','#','#','#','C','E','#','I','L','#','#','M','#','#','F','#','J','N','#','#','#'}; // int[] a = new int[]{1,2,3,4,'#','#',5,'#','#',6,7,'#','#',8,'#','#',9,10,11,'#','#',12,'#','#','#'}; //int[] a = new int[]{1,2,3,4,'#','#',5,6,'#','#','#','#',7,8,'#',9,10,'#','#',11,'#','#',12,'#',13,14,'#','#','#'}; // 1 // / \ // 2 5 // / \ / \ // 3 4 6 # // / \ / \ / \ // # # # # # # // 1 // / \ // 2 9 // / \ / \ // 3 6 10 # // / \ / \ / \ // 4 5 7 8 11 12 // / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ // # # # # # # # # # # # # tree.root = tree.CreateBTree(a); System.out.print("前序遍历:"); tree.prevOrder(tree.root); System.out.print("\n中序遍历:"); tree.midOrder(tree.root); System.out.print("\n后序遍历:"); tree.postOrder(tree.root); System.out.println(); System.out.print("层序遍历:"); tree.BTreeLevelOrder(); System.out.println(); } }
二叉树模型图:

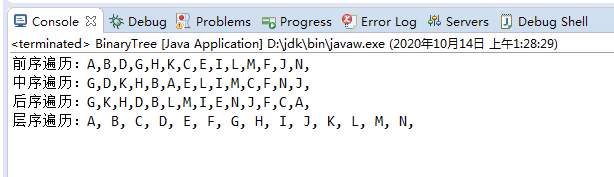
程序执行效果
本文来自博客园,作者:IT情深,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wh445306/p/16751782.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?