游戏编程里面有哪些经典或者非常酷的算法?
我挑一些有趣的算法。希望尽量提及相关算法在游戏中的应用。
全局光照
阴影
场景管理
动画/物理
碰撞測试
人工智能
(中午吃饭时间写不完,后补)
參考
[1] Bresenham, Jack E. "Algorithm for computer control of a digital plotter." IBM Systems journal 4.1 (1965): 25-30. http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~paragc/teaching/2011/cs475/papers/bresenham_line.pdf
[2] Bresenham, Jack. "A linear algorithm for incremental digital display of circular arcs."Communications of the ACM 20.2 (1977): 100-106. http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~paragc/teaching/2014/cs475/papers/bresenham_circle.pdf
[3] Catmull, Ed, and Alvy Ray Smith. "3-D transformations of images in scanline order." ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics. Vol. 14. No. 3. ACM, 1980. http://alvyray.com/Papers/CG/2pass80.pdf
[4] Pineda, Juan. "A parallel algorithm for polygon rasterization." ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics. Vol. 22. No. 4. ACM, 1988. http://people.csail.mit.edu/ericchan/bib/pdf/p17-pineda.pdf
[5] Sloan, Peter-Pike, Jan Kautz, and John Snyder. "Precomputed radiance transfer for real-time rendering in dynamic, low-frequency lighting environments." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG). Vol. 21. No. 3. ACM, 2002. http://www1.cs.columbia.edu/~ravir/6998/papers/p527-sloan.pdf
[6] Chen, Hao, and Xinguo Liu. "Lighting and material of Halo 3." ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Games. ACM, 2008. http://developer.amd.com/wordpress/media/2012/10/S2008-Chen-Lighting_and_Material_of_Halo3.pdf
[7] Mittring, Martin. "Finding next gen: Cryengine 2." ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 courses. ACM, 2007. http://developer.amd.com/wordpress/media/2012/10/Chapter8-Mittring-Finding_NextGen_CryEngine2.pdf
[8] Ritschel, Tobias, Thorsten Grosch, and Hans-Peter Seidel. "Approximating dynamic global illumination in image space." Proceedings of the 2009 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. ACM, 2009. https://people.mpi-inf.mpg.de/~ritschel/Papers/SSDO.pdf
[9] Kaplanyan, Anton. "Light propagation volumes in cryengine 3." ACM SIGGRAPH Courses 7 (2009): 2. http://www.crytek.com/download/Light_Propagation_Volumes.pdf
[10] Kaplanyan, Anton, and Carsten Dachsbacher. "Cascaded light propagation volumes for real-time indirect illumination." Proceedings of the 2010 ACM SIGGRAPH symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games. ACM, 2010. http://www.vis.uni-stuttgart.de/~dachsbcn/download/lpv.pdf
[11] Crassin, Cyril, et al. "Interactive indirect illumination using voxel cone tracing."Computer Graphics Forum. Vol. 30. No. 7. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2011. https://research.nvidia.com/sites/default/files/publications/GIVoxels-pg2011-authors.pdf
[12] Crow, Franklin C. "Shadow algorithms for computer graphics." ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics. Vol. 11. No. 2. ACM, 1977. http://excelsior.biosci.ohio-state.edu/~carlson/history/PDFs/crow-shadows.pdf
[13] Heidmann, Tim. "Real shadows, real time." Iris Universe 18 (1991): 28-31.
[14] Carmack, John, "e-mail to Mark Kilgard on Shadow Volume", 23 May 2000. http://web.archive.org/web/20090127020935/http://developer.nvidia.com/attach/6832
[15] Zhang, Fan, et al. "Parallel-split shadow maps for large-scale virtual environments." Proceedings of the 2006 ACM international conference on Virtual reality continuum and its applications. ACM, 2006.
[16] Zhang, Fan, Hanqiu Sun, and Oskari Nyman. "Parallel-split shadow maps on programmable gpus." GPU Gems 3 (2007): 203-237. GPU Gems 3 - Chapter 10. Parallel-Split Shadow Maps on Programmable GPUs
[17] Dimitrov, Rouslan. "Cascaded shadow maps." Developer Documentation, NVIDIA Corp (2007). http://www.cse.chalmers.se/edu/year/2011/course/TDA361/Advanced%20Computer%20Graphics/cascaded_shadow_maps.pdf
[18] Donnelly, William, and Andrew Lauritzen. "Variance shadow maps."Proceedings of the 2006 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. ACM, 2006. http://www.punkuser.net/vsm/vsm_paper.pdf
光栅化
- Bresenham's line algorithm [1]:经典的绘画直线算法,后来还能够稍作改动用于绘画圆弧[2],都不用三角函数或除数。仅仅需用整数加法、减法和乘法。
- Perspective-Correct Texture Mapping [3]:透视正确的光栅化纹理贴图算法是1980才出现的。
第一代Quake引擎引入后。才開始支持不垂直的墙、不水平的地面天花。
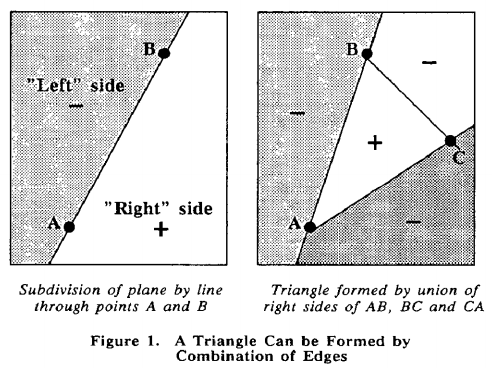
- Polygon Rasterization with Edge Function [4]:Bresenham算法假设用来画多边形,两个多边形的共边会被重绘。
后来发明了使用简单的edge function去解决问题,并且适合并行的硬件实现。
如今的GPU都是使用这个算法。
全局光照
- Precomputed Radiance Transfer (PRT) with Spherical Harmonics(SH)[5]:储存静态环境对于各个方向光源的漫反射数据。能够实现动态低频光源的全局光照效果。这样的表示方式非常奇妙。Halo 3也使用到这样的技术[6]。
- Screen-space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO)[7]:Crytek提出的首个屏幕空间环境光遮蔽算法,之后引来大量的研究及改进算法。也实用相似的概念去做近距离的反射,如SSDO[8]。
- Light Propagation Volume (LPV)[9]:Crytek提出的首个动态全局光照算法,不须要估计算。但要在体积数据中计算传播。性能较慢,所以之后再优化成 Cascaded LPV [10]。
- Voxel Cone Tracing [11]:也是不须要估计算的动态全局光照算法。把场景动态生成层阶式的体素数据(像mipmap那样的pre-filtering)。从光源视角计算直接光照。然后逐像素追踪这组数据获取非直接光照。结果比LPV精确。也能够做到光泽反射(glossy reflection)。
阴影
- Shadow Volume [12]:阴影体积是1977年发表的阴影技术。在屏幕空间光栅化阴影体积,可准确推断每一个屏幕像素是否在阴影之内。
能够处理平行光源和点光源的阴影。1991年[13]讲述如何用stencil buffer来实现此算法,适合在图形加速硬件(当时还没有所谓GPU)上使用。但非常多人发现,假设摄像机在阴影体积内,就会出错。在1998至2000年有多人发现一种解决方法,须要把John Carmack在2000年的电邮[14]中提及这个想法,后来成为2004年《毁灭战士3(Doom 3)》引擎的重要特徵,因他把这项技术发扬光大,即使他非首个发明人,此项技术通常被称为Carmack's Reverse。
- Parallel Split Shadow Map (PSSM) [15][16] / Cascaded Shadow Map(CSM)[17]:尽管Shadow Volume非常吸引,但它须要大量的内存频宽,并且通常不能实现软阴影。
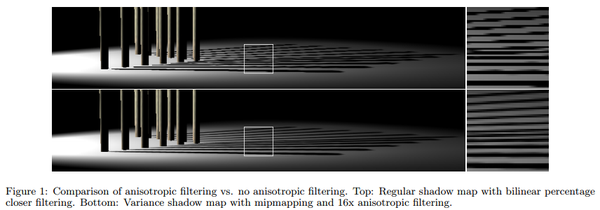
后来大部分游戏改为使用Shadow Map(阴影贴图),这更适合GPU,并且能够通过多次採样(Percentage Closer Filtering, PCF)来实现软阴影。
然而。阴影贴图也有很多问题,比如远近景物都採用同一张纹理。就会令到近景的精度不足。出现锯齿。2006年香港中文大学的博士生Fan Zhang等人发表了一种 PSSM 算法 [15],为不同距离的场景渲染多张阴影贴图,在採样的时候按距离决定使用那一张。这种方法的变种CSM。在分割上和PSSM有点差异。被广泛使用于现时大部分游戏引擎中。
- Variance Shadow Map(VSM)[18]:之前谈到用PCF做软阴影。它的坏处就是要做多次採样。那么可否把阴影贴图直接模糊化来实现软阴影?答案是否定的。可是在2006年有学者发表了VSM。它是一种用统计方式来逼近软阴影的效果。
场景管理
- Binary Space Partitioning (BSP)
- Portal rendering
- Quadtree、Octree:游戏场景管理的八叉树算法是如何的? - Milo Yip 的回答
- Potential Visibility Set (PVS)
- Occlusion Culling by Software Rasterization
动画/物理
- Particle System
- Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics(SPH)
- Curl Noise
- Dual Quaternion Skinning
碰撞測试
- Hyperplane separation theorem (或称separating axis theorem/SAT):凸形状相交測试的基本原理。在如何推断平面上一个矩形和一个圆形是否有重叠? - Milo Yip 的回答中,事实上背后也是使用了SAT。
- Gilbert-Johnson-Keerthi distance algorithm (GJK距离算法):计算两个凸形状的距离(可用于相交測试)
- Sweep and prune:用于broad phase碰撞检測,找出物体AABB是否相交。对于时空上连续的物体运动,算法最坏O(n^2)、最好O(n)。
人工智能
- Minimax
- Alpha-Beta Pruning
- A* path finding
- Dijkstra's algorithm
- Finite-state machine
- Behavior Tree
(中午吃饭时间写不完,后补)
參考
[1] Bresenham, Jack E. "Algorithm for computer control of a digital plotter." IBM Systems journal 4.1 (1965): 25-30. http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~paragc/teaching/2011/cs475/papers/bresenham_line.pdf
[2] Bresenham, Jack. "A linear algorithm for incremental digital display of circular arcs."Communications of the ACM 20.2 (1977): 100-106. http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~paragc/teaching/2014/cs475/papers/bresenham_circle.pdf
[3] Catmull, Ed, and Alvy Ray Smith. "3-D transformations of images in scanline order." ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics. Vol. 14. No. 3. ACM, 1980. http://alvyray.com/Papers/CG/2pass80.pdf
[4] Pineda, Juan. "A parallel algorithm for polygon rasterization." ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics. Vol. 22. No. 4. ACM, 1988. http://people.csail.mit.edu/ericchan/bib/pdf/p17-pineda.pdf
[5] Sloan, Peter-Pike, Jan Kautz, and John Snyder. "Precomputed radiance transfer for real-time rendering in dynamic, low-frequency lighting environments." ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG). Vol. 21. No. 3. ACM, 2002. http://www1.cs.columbia.edu/~ravir/6998/papers/p527-sloan.pdf
[6] Chen, Hao, and Xinguo Liu. "Lighting and material of Halo 3." ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Games. ACM, 2008. http://developer.amd.com/wordpress/media/2012/10/S2008-Chen-Lighting_and_Material_of_Halo3.pdf
[7] Mittring, Martin. "Finding next gen: Cryengine 2." ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 courses. ACM, 2007. http://developer.amd.com/wordpress/media/2012/10/Chapter8-Mittring-Finding_NextGen_CryEngine2.pdf
[8] Ritschel, Tobias, Thorsten Grosch, and Hans-Peter Seidel. "Approximating dynamic global illumination in image space." Proceedings of the 2009 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. ACM, 2009. https://people.mpi-inf.mpg.de/~ritschel/Papers/SSDO.pdf
[9] Kaplanyan, Anton. "Light propagation volumes in cryengine 3." ACM SIGGRAPH Courses 7 (2009): 2. http://www.crytek.com/download/Light_Propagation_Volumes.pdf
[10] Kaplanyan, Anton, and Carsten Dachsbacher. "Cascaded light propagation volumes for real-time indirect illumination." Proceedings of the 2010 ACM SIGGRAPH symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games. ACM, 2010. http://www.vis.uni-stuttgart.de/~dachsbcn/download/lpv.pdf
[11] Crassin, Cyril, et al. "Interactive indirect illumination using voxel cone tracing."Computer Graphics Forum. Vol. 30. No. 7. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2011. https://research.nvidia.com/sites/default/files/publications/GIVoxels-pg2011-authors.pdf
[12] Crow, Franklin C. "Shadow algorithms for computer graphics." ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics. Vol. 11. No. 2. ACM, 1977. http://excelsior.biosci.ohio-state.edu/~carlson/history/PDFs/crow-shadows.pdf
[13] Heidmann, Tim. "Real shadows, real time." Iris Universe 18 (1991): 28-31.
[14] Carmack, John, "e-mail to Mark Kilgard on Shadow Volume", 23 May 2000. http://web.archive.org/web/20090127020935/http://developer.nvidia.com/attach/6832
[15] Zhang, Fan, et al. "Parallel-split shadow maps for large-scale virtual environments." Proceedings of the 2006 ACM international conference on Virtual reality continuum and its applications. ACM, 2006.
[16] Zhang, Fan, Hanqiu Sun, and Oskari Nyman. "Parallel-split shadow maps on programmable gpus." GPU Gems 3 (2007): 203-237. GPU Gems 3 - Chapter 10. Parallel-Split Shadow Maps on Programmable GPUs
[17] Dimitrov, Rouslan. "Cascaded shadow maps." Developer Documentation, NVIDIA Corp (2007). http://www.cse.chalmers.se/edu/year/2011/course/TDA361/Advanced%20Computer%20Graphics/cascaded_shadow_maps.pdf
[18] Donnelly, William, and Andrew Lauritzen. "Variance shadow maps."Proceedings of the 2006 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. ACM, 2006. http://www.punkuser.net/vsm/vsm_paper.pdf











 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号