SQL中Statement和PreparedStatement
原文 :https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42245375/article/details/102813200
一、常见数据库驱动
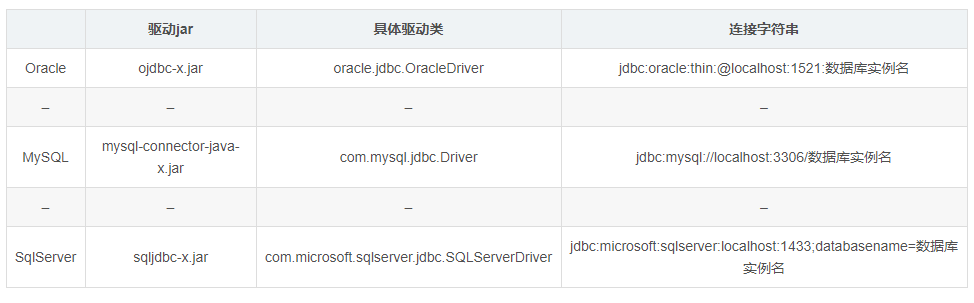
1.比较
(1)Statement操作数据库:
增删改:executeUpdate()
查询:executeQuery();
(2)PreparedStatement操作数据库:
public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement
因此
增删改:executeUpdate()
查询:executeQuery();
–此外
赋值操作 setXxx();
2.推荐PreparedStatement,
(1)编码更加简便(避免了字符串的拼接)
String name = “zs” ;
int age = 23 ;
stmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(’"+name+"’, “+age+” ) " ;
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
pstmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(?,?) " ;
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译SQL
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setInt(2,age);
(2)提高性能(因为 有预编译操作,预编译只需要执行一次)
需要重复增加100条数
stmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(’"+name+"’, “+age+” ) " ;
for(100)
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
pstmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(?,?) " ;
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译SQL
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setInt(2,age);
for( 100){
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
(3)安全(可以有效防止sql注入)
sql注入: 将客户输入的内容 和 开发人员的SQL语句 混为一体
stmt:存在被sql注入的风险
(例如输入 用户名:任意值 ’ or 1=1 –
密码:任意值)
分析:
select count() from login where uname=‘任意值 ’ or 1=1 --’ and upwd =‘任意值’ ;
select count() from login where uname='任意值 ’ or 1=1 ;
select count(*) from login ;
select count(*) from login where uname=’"+name+"’ and upwd =’"+pwd+"’
pstmt:有效防止sql注入
3.两种方式代码实现
(1)Statement方式
public class JDBCDemo { private static final String URL = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL"; private static final String USERNAME = "scott"; private static final String PWD = "tiger"; public static void update() {// 增删改 Connection connection = null; Statement stmt = null; try { // a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");// 加载具体的驱动类 // b.与数据库建立连接 connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD); // c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查) stmt = connection.createStatement(); //String sql = "insert into student values(1,'zs',23,'s1')"; // String sql = "update student set STUNAME='ls' where stuno=1"; String sql = "delete from student where stuno=1"; // 执行SQL int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // 返回值表示 增删改 几条数据 // d.处理结果 if (count > 0) { System.out.println("操作成功!"); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(stmt!=null) stmt.close();// 对象.方法 if(connection!=null)connection.close(); }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(2)PreparedStatement方式
public class JDBCPreparedStatementDemo { private static final String URL = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL"; private static final String USERNAME = "scott"; private static final String PWD = "tiger"; public static void update() {// 增删改 Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try { // a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");// 加载具体的驱动类 // b.与数据库建立连接 connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD); /* Statement // c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查) stmt = connection.createStatement(); //String sql = "insert into student values(1,'zs',23,'s1')"; // String sql = "update student set STUNAME='ls' where stuno=1"; String sql = "delete from student where stuno=1"; // 执行SQL int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // 返回值表示 增删改 几条数据 */ //PreparedStatement String sql = "insert into student values(?,?,?,?)"; pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译 pstmt.setInt(1, 36); pstmt.setString(2, "zhangsan"); pstmt.setInt(3, 56); pstmt.setString(4, "s3"); int count =pstmt.executeUpdate() ; // d.处理结果 if (count > 0) { System.out.println("操作成功!"); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(pstmt!=null) pstmt.close();// 对象.方法 if(connection!=null)connection.close(); }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void query() { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; ResultSet rs = null ; try { // a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类 Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");// 加载具体的驱动类 // b.与数据库建立连接 connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD); // c.发送sql,执行(增删改、【查】) Scanner input= new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String name = input.nextLine() ; System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String pwd = input.nextLine() ; // String sql = "select * from student where stuname like '%"+name+"%'"; // String sql = "select * from student where stuname like ?"; String sql ="select count(*) from login where uname= ? and upwd =?"; pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql) ; pstmt.setString(1, name); pstmt.setString(2, pwd); // String sql = "select stuno,stuname from student"; // 执行SQL(增删改executeUpdate(),查询executeQuery()) rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); // 返回值表示 增删改 几条数据 // d.处理结果 // while(rs.next()) { // int sno = rs.getInt( "stuno") ; // String sname = rs.getString("stuname") ; int sno = rs.getInt(1) ; //下标:从1开始计数 String sname = rs.getString(2) ; // System.out.println(sno+"--"+sname); // } int count = -1; if(rs.next()) { count = rs.getInt(1) ; } if(count>0) { System.out.println("登陆成功!"); }else { System.out.println("登陆失败!"); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("111"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(rs!=null) rs.close(); if(pstmt!=null) pstmt.close();// 对象.方法 if(connection!=null)connection.close(); }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }


