BindingSource
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/desktop/winforms/controls/bindingsource-component?view=netframeworkdesktop-4.8
BindingSource 组件
封装数据源以绑定到控件。
BindingSource 组件有两个用途。 首先,将一个窗体的控件绑定到数据时,该组件会提供一个间接层。 这是通过将 BindingSource 组件与你的数据源绑定,然后将窗体上的控件绑定到 BindingSource 组件完成的。 与数据的所有进一步交互(包括导航、排序、筛选和更新)都是通过调用 BindingSource 组件来完成的。
第二,BindingSource 组件可以充当强类型的数据源。 通过使用 Add 方法向 BindingSource 组件添加一个类型来创建该类型的列表。
二、作为中介的 BindingSource 组件
BindingSource 组件为窗体上的某些或全部控件充当数据源。 在 Visual Studio 中, BindingSource 可以通过属性将绑定到控件 DataBindings ,该属性可从 " 属性 " 窗口进行访问。 另请参阅如何:使用设计器将 Windows 窗体控件与 BindingSource 组件进行绑定。
可以将 BindingSource 组件同时绑定到两个简单的数据源(如一个对象或一个基本集合(如 ArrayList)的单个属性)和复杂的数据源(如数据库表)。 BindingSource 组件充当提供绑定和货币管理服务的中介。 在设计时或运行时中,通过将 BindingSource 组件的 DataSource 和 DataMember 属性分别设置为数据库和表,可将其绑定到复杂的数据源。 下图演示 BindingSource 组件在何处能够融入现有的绑定数据的体系结构。
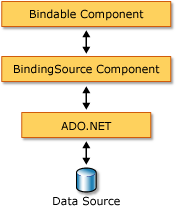
备注
在设计时,某些操作(如将数据库表从数据窗口拖到空白的窗体中)会创建 BindingSource 组件,将其绑定到基础数据源,并添加数据识别控件,而这些只需通过一个操作即可完成。 另请参阅在 Visual Studio 中将 Windows 窗体控件绑定到数据。
示例
下面的代码示例演示 ListBox 绑定到的 BindingSource 。 BindingSource绑定到 BindingList<T> 包含字体列表的。
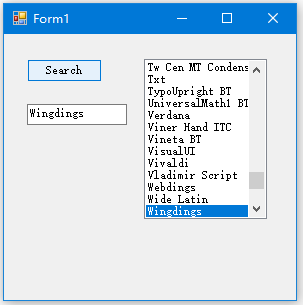
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { static class Program { /// <summary> /// 应用程序的主入口点。 /// </summary> [STAThread] static void Main() { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false); Application.Run(new Form1()); } } }
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); this.Load += new EventHandler(Form1_Load); } private TextBox textBox1; private Button button1; private ListBox listBox1; private BindingSource binding1; void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { //定义控件 listBox1 = new ListBox(); textBox1 = new TextBox(); binding1 = new BindingSource(); button1 = new Button(); listBox1.Location = new Point(140, 25); listBox1.Size = new Size(123, 160); textBox1.Location = new Point(23, 70); textBox1.Size = new Size(100, 20); textBox1.Text = "Wingdings"; button1.Location = new Point(23, 25); button1.Size = new Size(75, 23); button1.Text = "Search"; button1.Click += new EventHandler(this.button1_Click); //定义ClientSize , 加入控件 this.ClientSize = new Size(292, 266); this.Controls.Add(this.button1); this.Controls.Add(this.textBox1); this.Controls.Add(this.listBox1); MyFontList fonts = new MyFontList(); for (int i = 0; i < FontFamily.Families.Length; i++) //系统字体 { if (FontFamily.Families[i].IsStyleAvailable(FontStyle.Regular)) fonts.Add(new Font(FontFamily.Families[i], 11.0F, FontStyle.Regular)); } binding1.DataSource = fonts; // BindingSource绑定到数据源 listBox1.DataSource = binding1; // 控件绑定到BindingSource listBox1.DisplayMember = "Name"; } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (binding1.SupportsSearching != true) { MessageBox.Show("Cannot search the list."); } else { int foundIndex = binding1.Find("Name", textBox1.Text); if (foundIndex > -1) listBox1.SelectedIndex = foundIndex; else MessageBox.Show("Font was not found."); } } } public class MyFontList : BindingList<Font> { protected override bool SupportsSearchingCore { get { return true; } } protected override int FindCore(PropertyDescriptor prop, object key) { // Ignore the prop value and search by family name. for (int i = 0; i < Count; ++i) { if (Items[i].FontFamily.Name.ToLower() == ((string)key).ToLower()) return i; } return -1; } } }


