MVC5+EF6 入门完整教程8:EF6 Code First 数据迁移
一、输入enable-migrations指令:

enable-migrations指令:
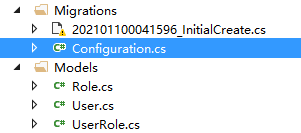
a.在项目根目录下创建了一个Migrations文件夹
b.在Migrations文件夹下新建一个Configuration.cs文件。
说明:执行enable-migrations指令后,Migrations将会找到已有的数据库MVCDemo然后自动执行add-migration指令(可以单独输入命令add-migration InitialCreate)。
Configuration类也包含一个Seed方法,当数据库新建或数据库结构更新后,这个方法会被调用,利用这个方法可以插入或更新test data.
internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<MVCDemo.DAL.DemoContext> { public Configuration() { AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false; } protected override void Seed(MVCDemo.DAL.DemoContext context) { // This method will be called after migrating to the latest version. // You can use the DbSet<T>.AddOrUpdate() helper extension method // to avoid creating duplicate seed data. E.g. // // context.People.AddOrUpdate( // p => p.FullName, // new Person { FullName = "Andrew Peters" }, // new Person { FullName = "Brice Lambson" }, // new Person { FullName = "Rowan Miller" } // ); // } }
二、配置Seed方法
使用DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges的方式时,因为每次model改变时数据库都会被删除,所有数据都会丢失,所以需要使用DAL.AccountInitializer.cs的Seed方法来插入测试数据。使用Code First Migrations方式,当数据库改变时数据会保留,所以包含test data的Seed方法一般不需要的。
如果我们要部署数据库到生产环境,事实上这种情况下我们也不想Seed方法来插入测试数据到生产环境中。
生产环境中用到Seed方法的例子: 比如在我们部署时获得了实际的初始化数据,如实际存在的组织部门这些初始化的信息。
我们为了做实验方便,还是插入一些测试数据。
先插入User和Role
protected override void Seed(MVCDemo.DAL.DemoContext context) { // This method will be called after migrating to the latest version. // You can use the DbSet<T>.AddOrUpdate() helper extension method // to avoid creating duplicate seed data. E.g. // // context.People.AddOrUpdate( // p => p.FullName, // new Person { FullName = "Andrew Peters" }, // new Person { FullName = "Brice Lambson" }, // new Person { FullName = "Rowan Miller" } // ); // var users = new List<User> { new User { UserName="Tom",Email="Tom@sohu.com",Password="123456"}, new User { UserName="Jerry",Email="Jerry@sohu.com",Password="123456"} }; users.ForEach(s => context.Users.AddOrUpdate(p => p.UserName, s)); context.SaveChanges(); var roles = new List<Role> { new Role { RoleName="admin",RoleDesc="have full authorization to perform system administration."}, new Role { RoleName="General Users",RoleDesc="General Users can access the shared data they are authorized for."} }; roles.ForEach(s => context.Roles.AddOrUpdate(p => p.RoleName, s)); context.SaveChanges(); }
Seed方法接收一个database context参数,利用这个参数添加新的实体到数据库中:
-
新建一个实体集合
-
添加到相应的DbSet属性
-
保存更改到数据库中
用AddOrUpdate方法来插入数据。
users.ForEach(s => context.Users.AddOrUpdate(p => p.UserName, s));
每次执行update-databse指令时都会执行Seed方法,一般来说,每次迁移后,你不仅仅是插入数据,例如你想要插入的数据在你创建数据库的第一次迁移后已经在数据库中了,这种情况下更新原有数据就可以了。
AddOrUpdate:
如果数据不存在,插入数据;如果数据存在,更新这笔数据。
context.Users.AddOrUpdate(p => p.UserName, s)
第一个参数p.UserName就是检查数据是否存在的主键。
我们的测试数据中,假设UserName都不能重复。
作为比较,我们添加UserRole实体类型的时候没有使用AddOrUpdate,直接人为判断是否存在,不存在再插入。
var userRoles = new List<UserRole> { new Models.UserRole { UserID=users.Single(s=>s.UserName=="Tom").ID, RoleID=roles.Single(u=>u.RoleName=="Administrators").ID }, new Models.UserRole { UserID=users.Single(s=>s.UserName=="Tom").ID, RoleID=roles.Single(u=>u.RoleName=="General Users").ID }, new Models.UserRole { UserID=users.Single(s=>s.UserName=="Jerry").ID, RoleID=roles.Single(u=>u.RoleName=="General Users").ID } };
foreach(UserRole item in userRoles) { var userRoleInDataBase = context.UserRoles.Where(s => s.UserID == item.UserID && s.RoleID == item.RoleID).SingleOrDefault(); if(userRoleInDataBase==null) { context.UserRoles.Add(item); } }
编译下项目,下面开始更新数据库。
三、执行迁移
前面执行 add-migration时,同样在Migrations文件夹里面,产生一个<timestamp>_InitialCreate.cs的文件,例如:202101100037534_InitialCreate.cs。
里面有两个方法,Up和Down:
Up方法创建数据库表,Down方法删除表。
public override void Up() { CreateTable( "dbo.Roles", c => new { ID = c.Int(nullable: false, identity: true), RoleName = c.String(), RoleDesc = c.String(), }) .PrimaryKey(t => t.ID); CreateTable( "dbo.UserRoles", c => new { ID = c.Int(nullable: false, identity: true), UserID = c.Int(nullable: false), RoleID = c.Int(nullable: false), }) .PrimaryKey(t => t.ID) .ForeignKey("dbo.Roles", t => t.RoleID, cascadeDelete: true) .ForeignKey("dbo.Users", t => t.UserID, cascadeDelete: true) .Index(t => t.UserID) .Index(t => t.RoleID); CreateTable( "dbo.Users", c => new { ID = c.Int(nullable: false, identity: true), UserName = c.String(nullable: false, maxLength: 50), Email = c.String(), Password = c.String(nullable: false, maxLength: 50), }) .PrimaryKey(t => t.ID); } public override void Down() { DropForeignKey("dbo.UserRoles", "UserID", "dbo.Users"); DropForeignKey("dbo.UserRoles", "RoleID", "dbo.Roles"); DropIndex("dbo.UserRoles", new[] { "RoleID" }); DropIndex("dbo.UserRoles", new[] { "UserID" }); DropTable("dbo.Users"); DropTable("dbo.UserRoles"); DropTable("dbo.Roles"); }
下面我们就执行正式迁移。打开Package Manager Console
输入 update-database
PM> update-database 指定“-Verbose”标志以查看应用于目标数据库的 SQL 语句。 没有挂起的显式迁移。 正在运行 Seed 方法。 System.InvalidOperationException: 序列不包含任何匹配元素 在 System.Linq.Enumerable.Single[TSource](IEnumerable`1 source, Func`2 predicate) 在 MVCDemo.Migrations.Configuration.Seed(DemoContext context) 位置 E:\MVCDemo\MVCDemo\MVCDemo\Migrations\Configuration.cs:行号 48 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrationsConfiguration`1.OnSeed(DbContext context) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrator.SeedDatabase() 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Infrastructure.MigratorLoggingDecorator.SeedDatabase() 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrator.Upgrade(IEnumerable`1 pendingMigrations, String targetMigrationId, String lastMigrationId) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Infrastructure.MigratorLoggingDecorator.Upgrade(IEnumerable`1 pendingMigrations, String targetMigrationId, String lastMigrationId) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrator.UpdateInternal(String targetMigration) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrator.<>c__DisplayClassc.<Update>b__b() 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrator.EnsureDatabaseExists(Action mustSucceedToKeepDatabase) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Infrastructure.MigratorBase.EnsureDatabaseExists(Action mustSucceedToKeepDatabase) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.DbMigrator.Update(String targetMigration) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Infrastructure.MigratorBase.Update(String targetMigration) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Design.ToolingFacade.UpdateRunner.Run() 在 System.AppDomain.DoCallBack(CrossAppDomainDelegate callBackDelegate) 在 System.AppDomain.DoCallBack(CrossAppDomainDelegate callBackDelegate) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Design.ToolingFacade.Run(BaseRunner runner) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.Design.ToolingFacade.Update(String targetMigration, Boolean force) 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.UpdateDatabaseCommand.<>c__DisplayClass2.<.ctor>b__0() 在 System.Data.Entity.Migrations.MigrationsDomainCommand.Execute(Action command) 序列不包含任何匹配元素 PM>
update-database指令调用了Up方法来新建database的表(和data model entity set 对应), 然后调用Seed方法来填充测试数据。
这个时候测试下程序,打开数据库看下,完全符合我们的预期。
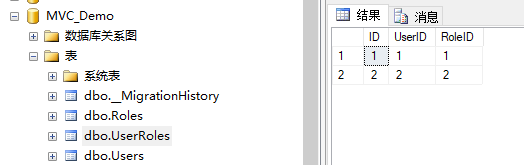
验证正常。
四、添加一个表Test
先添加一个Model
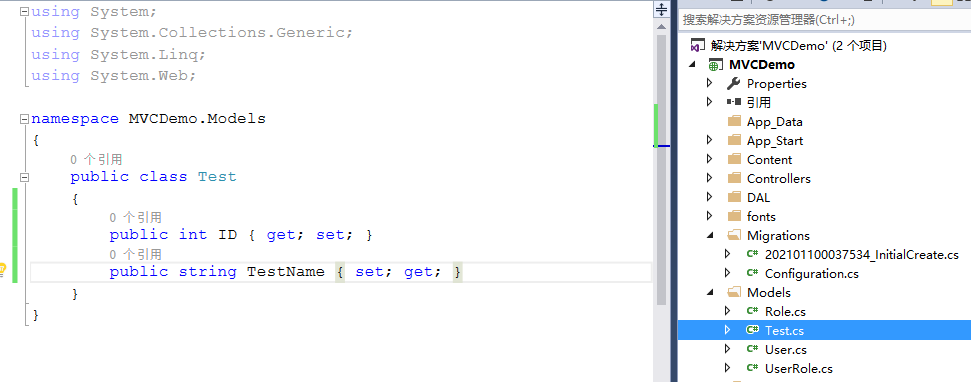
修改AccountContext.cs, 增加一个data model entity set
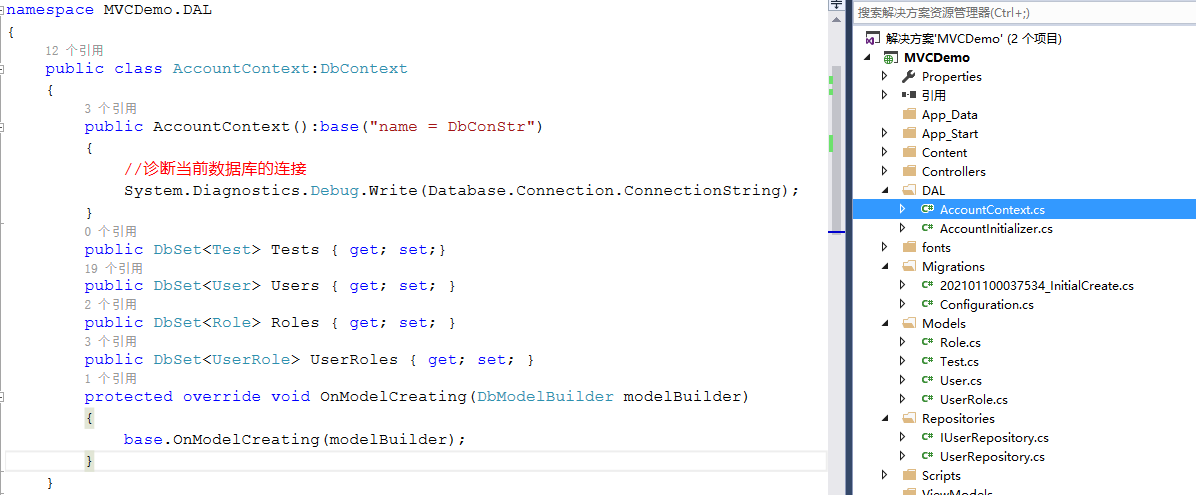
执行add-migration AddTestTable和update-database, 完成数据库表的添加。


去数据库中检查,发现已经多了Test这张表了。
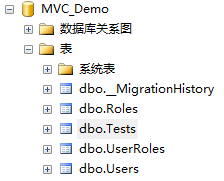
再检查命令add-migration AddTestTable新产生的配置文件 : 202101100807257_AddTestTable.cs
namespace MVCDemo.Migrations { using System; using System.Data.Entity.Migrations; public partial class AddTestTable : DbMigration { public override void Up() { CreateTable( "dbo.Tests", c => new { ID = c.Int(nullable: false, identity: true), TestName = c.String(), }) .PrimaryKey(t => t.ID); } public override void Down() { DropTable("dbo.Tests"); } } }
大家现在应该能充分理解到add-migration时产生的文件的作用了吧。
总结
本次我们主要讲解了数据库迁移/升级的问题。
主要分为 启用迁移(enable-migrations) 和 执行迁移(add-migration, update-database) 两大步骤。
启用迁移:产生迁移相关文件夹Migrations和文件夹中相关的配置文件。
执行迁移:产生相关的迁移更改文件并执行更改。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号