MyBatis基础使用三
MyBatis基础使用三
批量删除的基础用法
Sql基础语句
delete from user where id in(6,7)
接口处书写语句
//批量删除
void DeleteMoreUsers(@Param("ids") String ids);
映射文件
注意:这里只能使用**“{}与#{}的区别,请参考MyBatis基础使用一
<delete id="DeleteMoreUsers">
delete from user where id in (${ids})
</delete>
测试文件
@Test
public void DeleteMoreUsers(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.DeleteMoreUsers("4,7");
sqlSession.close();
}
添加用户信息并获取自增的主键
接口处书写语句
//添加用户信息并获取自增的主键
void AddUser(User user);
映射文件
useGeneratedKeys:表示当前添加功能使用自增的主键 useGeneratedKeys:参数只针对 insert 语句生效,默认为 false。当设置为 true 时,表示如果插入的表以自增列为主键,则允许 JDBC 支持自动生成主键,并可将自动生成的主键返回 keyProperty:将添加的数据的自增主键为实体类类型的参数的属性赋值 keyProperty:返回的主键信息存储到插入信息的对象所包含的属性中,即id
<insert id="AddUser" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" >
insert into user values (null,#{username},#{password},#{age},#{gender},#{email})
</insert>
测试文件
@Test
public void AddUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user =new User(null,"比起谷八幡","125810",20,"男","2978366481@qq.com");
mapper.AddUser(user);
System.out.println("id= "+user.getId());
sqlSession.close();
}
最后返回结果,即为插入数据自增的主键的值
处理字段名和属性名不一致的情况
- 为查询的字段设置别名,和属性名保持一致
<select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,age,gender from emp where emp_id=#{empId}>
emp_id 、emp_name 为sql表中的字段名,empId、empName为属性名
- 当字段符合MySQL的要求使用_,而属性符合java的要求使用驼峰。 此时可以在MyBatis的核心配置文件中设置一个全局配置,可以自动将下划线映射为驼峰 需要注意不能随便映射,这里必须符合下划线到驼峰的换名规则 emp_id:empId,emp_name:empName
这里通过在核心配置文件中配置setting,设置驼峰命名的别名
<!-- 将下划线映射为驼峰-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
-
使用resultMap自定义映射处理
-
resultMap:设置自定义的映射关系
-
id:唯一标识
-
type:处理映射关系的实体类类型
- 常用的标签:
- id:处理主键和实体类中属性的映射关系
- result:处理普通字段和实体类中属性的映射关系
- column:设置映射关系中的字段名,必须是sql查询出的某个字段
- property:设置映射关系中的属性的属性名,必须是处理的实体类类型中的属性
- association:处理多对一的映射关系(主要处理实体类类型的属性)
- 常用的标签:
-
通过一个简单的例子来熟悉一下resultMap的用法
首先,在接口中编写一个查询的方法
//根据查询数据
Emp SelectById(@Param("empId") int id);
在xml映射中编写sql查询语句
这里通过resultMap配置sql中的文段和实体类中的属性
<resultMap id="EmpResultMap" type="com.wfy.pojo.Emp">
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectById" resultMap="EmpResultMap">
select * from emp where emp_id=#{empId}
</select>
编写一个简单的测试类
@Test
public void SelectById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Emp emp = mapper.SelectById(1);
System.out.println(emp);
}
多对一的查询(多表查询)
通过三种不同的映射方式多对一的进行查询
- 级联方式处理
- association
- 分步查询(优点:可以实现延迟加载)
级联方式处理多对一的查询
这里通过映射文件进行举例说明:
<resultMap id="EmpAndDeptResultMap" type="Emp">
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"></result>
<!--级联方式-->
<result column="dept_id" property="dept.deptId"></result>
<result column="dept_name" property="dept.deptName"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectEmpAndDeptById" resultMap="EmpAndDeptResultMap">
select
emp.*,dept.*
from emp
left join dept
on emp.dept_id=dept.dept_id
where emp.emp_id =#{empId}
</select>
association的方式处理多对一的查询
association:处理多对一的映射关系(处理实体类类型的属性)
- property:设置需要处理映射关系的属性的属性名
- javaType:设置要处理的属性的类型
<resultMap id="EmpAndDeptResultMap" type="Emp">
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"></result>
<association property="dept" javaType="Dept">
<id column="dept_id" property="deptId"></id>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
分步查询的方式处理多对一的查询
一个表中嵌套其他的表,通过分步骤的查询
这里使用了两张表Emp和Dept
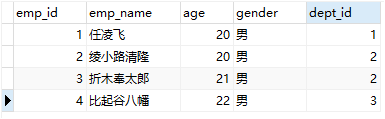
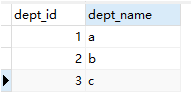
通过在两个不同的接口和映射文件中编写,通过association进行连接
EmpMapper接口:
//通过分步查询查询员工以及所对应的部门信息的第一步
Emp SelectEmpAndDeptByStepOne(@Param("empId") int id);
DeptMapper接口:
// 通过分步查询员工以及所对应的部门信息的第二步
Dept SelectEmpAndDeptByStepTwo(@Param("deptId") int id);
EmpMapper的映射文件:
核心配置文件中配置延迟加载:
<settings>
<!--开启延迟加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 按需加载,默认设置为false;若设置为true则表示不管需不需要都全部加载sql语句-->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
<resultMap id="EmpAndDeptByStepResultMap" type="Emp">
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"></result>
<!--association
property:设置需要处理映射关系的属性的属性名
select:设置分步查询的sql的唯一标识 ==说白了就是现属性的属性值有哪一个sql查询而来
column:将查询出的某个字段作为分步查询的sql的条件
fetchType:在开启了延迟加载的环境中,通过该属性设置当前的分步查询是否使用延迟加载
fetchType="eager(立即加载)/lazy(延迟加载)"
-->
<association property="dept" fetchType="eager"
select="com.wfy.mapper.DeptMapper.SelectEmpAndDeptByStepTwo"
column="dept_id">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectEmpAndDeptByStepOne" resultMap="EmpAndDeptByStepResultMap">
select * from emp where emp_id=#{empId}
</select>
DeptMapper的映射文件:
<select id="SelectEmpAndDeptByStepTwo" resultType="com.wfy.pojo.Dept">
select * from dept where dept_id=#{deptId}
</select>
测试文件:
@Test
public void SelectEmpAndDeptByStep(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Emp emp = mapper.SelectEmpAndDeptByStepOne(1);
System.out.println(emp);
}
一对多的查询(多表查询)
通过两种不同的映射方式一对多的进行查询
Collection的方式处理一对多的查询方式
collection:处理一对多的映射关系(处理集合类型的属性)
映射文件中的设置
- ofType: 设置集合类型的属性中存储的数据的类型
<resultMap id="DeptResultMap" type="Dept">
<id column="dept_id" property="deptId"></id>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName"></result>
<!--
ofType:设置集合类型的属性中存储的数据的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="Emp">
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"></result>
<result column="age" property="age"></result>
<result column="gender" property="gender"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectDeptAndEmpById" resultMap="DeptResultMap">
select *
from dept
left join emp
on dept.dept_id = emp.dept_id
where dept.dept_id=#{deptId}
</select>
分步查询
通过以dept_id为条件进行分布查询
通过案例展示:
DeptMapper:
//分步查询,根据id查询部门信息为第一步
Dept SelectDeptAndEmpByStepOne(@Param("deptId")int id);
EmpMapper:
//通过分步查询查询部门信息以及部门中所对应的员工信息
List<Emp> SelectDeptAndEmpByStepTwo(@Param("deptId") int id);
DeptMapper的映射文件:
<resultMap id="DeptAndEmpResultMap" type="Dept">
<id column="dept_id" property="deptId"></id>
<id column="dept_name" property="deptName"></id>
<collection property="emps"
select="com.wfy.mapper.EmpMapper.SelectDeptAndEmpByStepTwo"
column="dept_id">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectDeptAndEmpByStepOne" resultMap="DeptAndEmpResultMap">
select * from dept where dept_id=#{deptId}
</select>
EmpMapper的映射文件:
<resultMap id="EmpResultMap" type="com.wfy.pojo.Emp">
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectDeptAndEmpByStepTwo" resultMap="EmpResultMap">
select * from emp where dept_id=#{deptId}
</select>
测试案例:
@Test
public void SelectDeptAndEmpByStep(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSession();
DeptMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DeptMapper.class);
Dept dept = mapper.SelectDeptAndEmpByStepOne(2);
System.out.println(dept);
sqlSession.close();
}
注意:处理表中的连接对象,多对一对应对象,一对多对应集合



