mysql系列——常用关键字详解(五)
1.查询语句关键字顺序
select 字段们 from 表1 join 表2 on 条件 where 条件 and 条件 group by 字段们
having 分组后的条件 order by 字段们 排序方式 limit 分页 ;(排序方式在limit之前,默认asc)
2.常用关键字及基本用法
1、distinct关键字
1 2 | 显示没有重复记录的商品名称,商品价格列表select distinct ware_name,price from t_ware; |
2、使用计算列
1 2 | 查询所有商品价格提高20%后的价格select ware_id,ware_name,price*1.2 from t_ware; |
3、as:给列起别名
1 2 3 4 | 不省略asselect ware_id,ware_name,price*1.2 price_raise from t_ware;省略asselect ware_id,ware_name,price*1.2 as price_raise from t_ware; |
4、使用逻辑表达式 and or not
1 2 | or 显示商品类别编号为6或7的商品select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where category_id=6 or category_id=7; |
1 2 | not 显示商品价格不大于100的商品select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where not price>100; |
1 2 | and 显示商品价格大于100且商品类别编号为5的商品select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where price>100 and category_id = 5; |
5、使用between关键字
1 2 | 显示商品价格在200元至1000元之间的商品(留心一下,是半开区间还是封闭区间?)select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where price between 200 and 1000; |
6、in、not in查询
1 2 | 显示商品类别为5,6,7且价格不小于200元的商品select ware_id,ware_name,price,category_id from t_ware where category_id in (5,6,7) and price>=200; |
7、使用like子句进行模糊查询
1 2 3 4 5 | %(百分号)表示0到n个任意字符select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where ware_name like '%纯棉%';_(下划线)表示单个的任意字符select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where ware_name like '%长袖_恤%'; |
8、limit 筛选数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | 给定两个参数时,第一个参数指定第一个返回记录行的偏移量,第二个参数指定返回记录行的最大数目select * from user limit 5,10; // 检索记录行 6-15如果只给定一个参数,它表示返回最大的记录行数目,换句话说,limit n 等价于 limit 0,n。 select * from user limit 5; //检索前5个记录行当 limit和offset组合使用时,limit后面只能有一个参数,表示要取的数量,offset表示要跳过的数量 。 select * from user limit 3 offset 1; |
9、case when 的基本使用。 深入了解https://www.cnblogs.com/wffzk/p/13141052.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | select name '英雄', (此处name 后面as省略) case name when '德莱文' then '斧子' when '盖伦' then '大宝剑' when '暗夜猎手' then '弩' else '无' end '装备' (此处end后面as省略) from user_info; |
10、转义字符escape的使用
1 | select ware_id,ware_name,price from t_ware where ware_name like '%\%%' escape '\'; |
11、使用group by
1 2 | 统计每个二级类别下有多少商品,以及商品总价值select w.category_id,wc.category_name,count(w.ware_id),sum(w.price) from t_ware w left join t_ware_category wc on w.category_id=wc.category_id group by w.category_id,wc.category_name; |
12、使用having对结果进行筛选
1 2 | 查询user表查询每一个班级中年龄大于20,性别为男的人数select count(*)as '大于20岁人数',classid from user where sex='男' group by classid,age having age>20 ; |
13、使用order by 排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 | 默认升序select * from t_ware_category where parent_id = 0 order by ware_id ;升序(由小到大)select * from t_ware_category where parent_id = 0 order by ware_id asc;降序(由大到小)select * from t_ware_category where parent_id = 0 order by ware_id desc ; |
14、常用统计函数
1 2 3 4 5 | sum():返回一个数字列或计算列的总和 select sum(price) from t_ware;avg():对一个数字列或计算列球平均值min():返回一个数字列或一个数字表达式的最小值max():返回一个数字列或一个数字表达式的最大值account():返回满足select语句中指定的条件的记录值 |
15、is null、is not null(null值专用查询)
null值存在的坑:查询运算符、like、between…and…、in、not in对null值查询不起作用
mysql为提供了查询空值的语法:is null、is not null。
1 | select 列名 from 表名 where 列 is null;<br>select 列名 from 表名 where 列 is not null; |
经典面试题 下面2个sql查询结果一样吗?
1 2 3 | select * from students;select * from students where name like '%'; |
结果分为两种情况:
- 当name没有null值时,返回的结果一样;
- 当name有null值时,第2个查询不出name为null的记录。
关键字知识拓展:
in 和 exists的区别:
in常用于where表达式中,其作用是查询某个范围内的数据。not in与in作用相反
in列表的值类型必须一致或兼容;in列表中不支持通配符
in()适合B表比A表数据小的情况;exists()适合B表比A表数据大的情况
select * from A where id in(select id from B)
select a.* from A a where exists(select 1 from B b where a.id=b.id)
where 和 having 的区别:
where用于分组前,满足where条件后才会进行分组中,having用于分组后,满足分组后的条件才会被查询出
where不能对聚合函数进行判断,having可以对聚合函数进行判断
group by 和 order by的区别:
group by:就是将一个“数据集”划分成若干个“小区域”,然后针对若干个“小区域”进行数据处理。
order by:用来对数据库的一组数据进行排序,可以是多个字段 desc:降序 asc:升序(默认)
原始表:
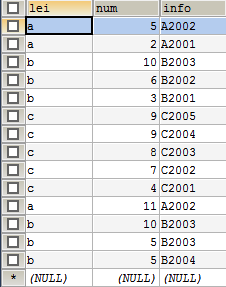
(1)group by 和聚合函数一起使用
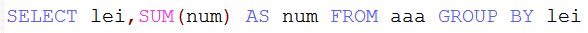
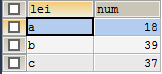
(2)group by 和order by连用
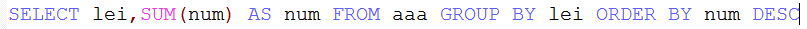
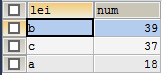
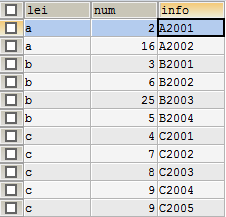
(3)按几个条件分组,如下按照lei和info进行分组
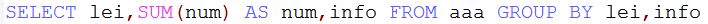




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· Vue3状态管理终极指南:Pinia保姆级教程