SpringBoot集成 Swagger2
什么是Swagger?
swagger是一个在线文档工具,在前后端分离的情况下作用愈加突出,使用swagger我们可以针对我们在后端的接口做一个在线测试。
简单地使用swagger2只需要三步。
第一步,配置pom文件。在pom文件中引入swagger的相关依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.9.2</version> </dependency> <!-- 这里使用 swagger-bootstrap-ui 替代了原有丑陋的ui,下面两个依赖二选一 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.xiaoymin</groupId> <artifactId>swagger-bootstrap-ui</artifactId> <version>1.9.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.9.2</version> </dependency> |
如果使用swagger第三方ui:swagger-bootstrap-ui,访问url:http://localhost:8080/doc.html
如果使用springfox-swagger-ui,访问url:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.htm
第二步,构建swagger配置类,yml文件增加swagger:enable: true (注意格式)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 | import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;/** * swagger 配置 */@Slf4j@Configuration@EnableSwagger2public class SwaggerConfig { @Value("${swagger.enable}") private boolean enable; @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .enable(enable) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() ////扫描该包下面的API注解,接口使用@ApiIgnore,该接口就不会暴露在 swagger2 的页面下 .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("接口服务文档") .description("接口文档") .termsOfServiceUrl("https://home.cnblogs.com/u/wffzk")//这里配置的是服务网站,我写的是我的博客园站点~欢迎关注~ .version("1.0") .build(); }} |
第三步:通过注解来完成API文档,一般用前三个注解就可以,用在类 /方法 /参数上
1. @Api
| 注解名称 | 注解属性 | 作用域 | 属性作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
@Api |
tags | 类 | 说明该类的作用 |
| value | 类 | 说明该类的作用 |
举个例子:
1 2 3 4 | @Api(value = "用户类控制器",tags="用户类控制器")public class UserController {...} |

2. @ApiOperation
| 注解名称 | 注解属性 | 作用域 | 属性作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
@ApiOperation() |
value | 方法 | 描述方法作用 |
| notes | 方法 | 提示内容 | |
| tags | 方法 | 分组 |
举个例子:
1 2 3 4 | @ApiOperation(value = "获取用户列表",notes = "获取用户列表")public List<User> get() { ... } |
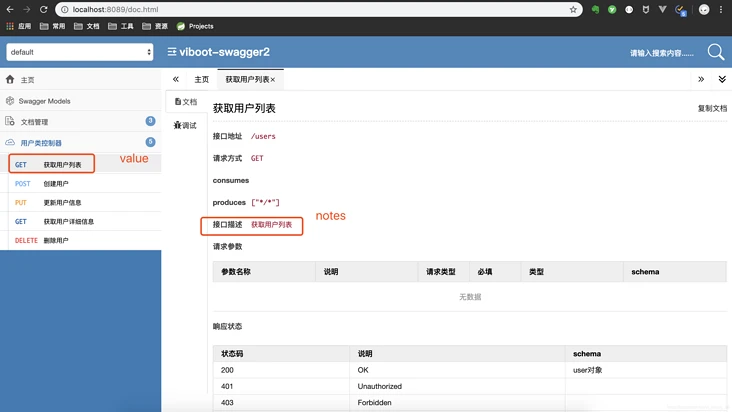
3. @ApiParam
| 注解名称 | 注解属性 | 作用域 | 属性作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
@ApiParam() |
name | 方法参数 | 参数名 |
| value | 方法参数 | 参数说明 | |
| required | 方法参数 | 是否必填 |
举个例子:
1 2 3 4 | @ApiOperation(value="获取用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来获取用户详细信息")public User get(@ApiParam(name="id",value="用户id",required=true) Long id) { return userService.getById(id);} |
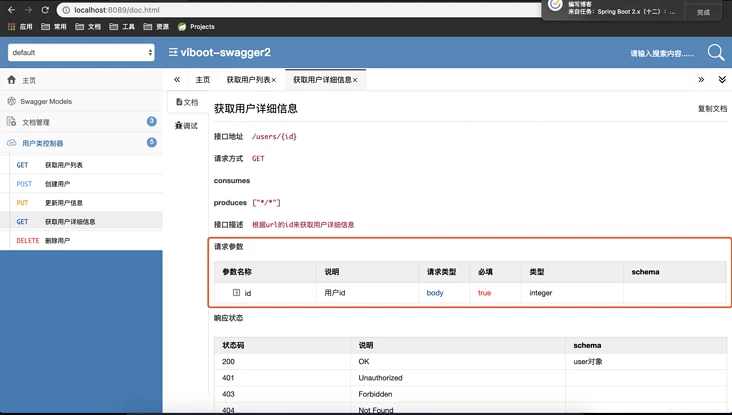
4. @ApiModel && @ApiModelProperty
| 注解名称 | 注解属性 | 作用域 | 属性作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
@ApiModel() |
value | 类 | 对象名 |
| description | 类 | 描述 | |
@ApiModelProperty() |
value | 方法 | 字段说明 |
| name | 方法 | 属性名 | |
| dataType | 方法 | 属性类型 | |
| required | 方法 | 是否必填 | |
| example | 方法 | 举例 | |
| hidden | 方法 | 隐藏 |
举个例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | @ApiModel(value="user对象",description="用户对象user")public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户ID",example = "1000001",hidden=true) private Long id; @ApiModelProperty(value="用户名",required = true,dataType = "String") private String userName; @ApiModelProperty(value = "密码") private String password;} |
5. @ApiImplicitParam && @ApiImplicitParams
@ApiImplicitParam`可以单个用于方法之上,多个参数的话可以把`@ApiImplicitParam`放到`@ApiImplicitParams`中,这里只罗列`@ApiImplicitParam`的属性:
| 注解名称 | 注解属性 | 作用域 | 属性作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
@ApiImplicitParam() |
value | 方法 | 参数说明 |
| name | 方法 | 参数名 | |
| dataType | 方法 | 数据类型 | |
| paramType | 方法 | 参数类型 | |
| example | 方法 | 举例 |
举个例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户实体user", required = true, dataType = "User") }) public void put(User user) { userService.updateById(user); } |
这里需要注意一点,我们并没有在注解中写图中圈中的两个参数,这个是去读取了我们刚刚为User类的注解,并将用户名设置为必填!
6.@ApiResposne && @ApiResponses
| 注解名称 | 注解属性 | 作用域 | 属性作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
@ApiResponse() |
response | 方法 | 返回类 |
| code | 方法 | 返回码 | |
| message | 方法 | 返回信息 | |
| examples | 方法 | 例子 |
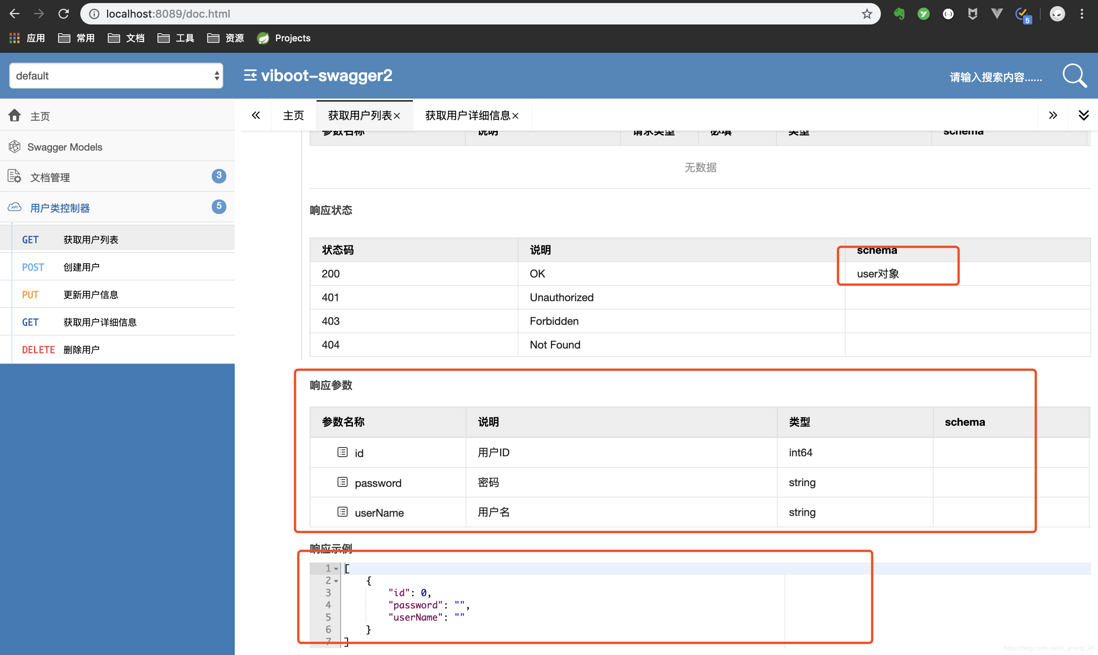 最后再聊聊这个UI
最后再聊聊这个UI
先贴几张spring-fox的ui(正是我们所熟知的那一套)
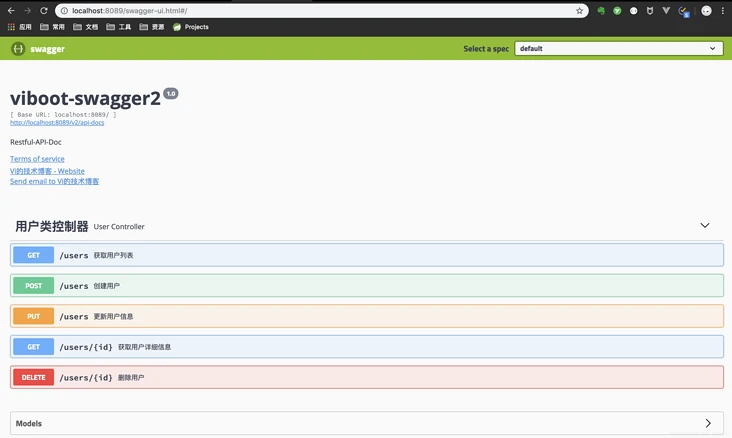
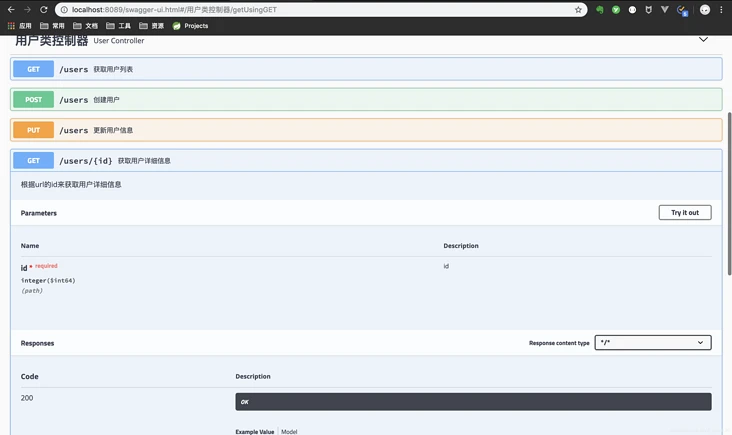
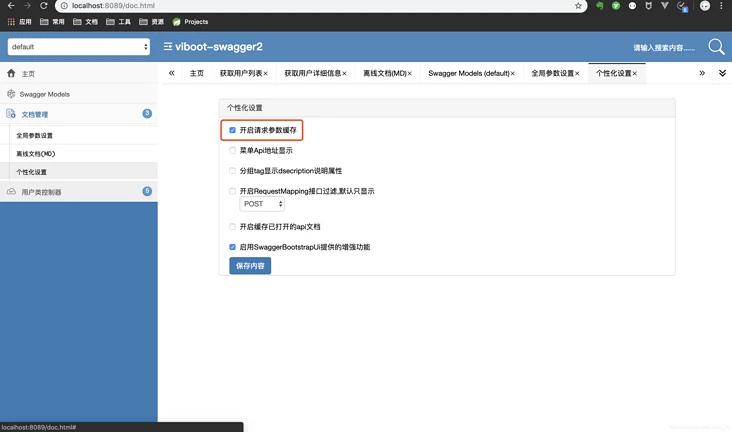
看到这里,大家对于这两套UI的选择应该有个答案了,当然bootstrap风格的ui不仅好看,还有各种强大的功能~
1.导出md文档

2.参数缓存


 最后再聊聊这个UI
最后再聊聊这个UI

【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· Vue3状态管理终极指南:Pinia保姆级教程