LR模型
本章首先阐述Logistic回归的定义,然后介绍一些最优化算法,其中包括基本的梯度上升法和一个改进的随机梯度上升法,这些最优化算法将用于分类器的 训练。最后给出一个Logistic回归的实例,预测一匹病马是否能被治愈。
5.1 基于Logistic回归和Sigmoid函数的分类
5.2 基于最优化方法的最佳回归系数确定
5.2.1 梯度上升法 梯度上升法基于的思想是:要找到某函数的最大值,最好的方法就是沿着函数的梯度方向探寻。
import numpy as np
from numpy import * def loadDataSet():#读取文本文件 dataMat = [];labelMat = [] fr = open('D:/02-ipynb/code-机器学习实战/machinelearninginaction/Ch05/testSet.txt') for line in fr.readlines(): lineArr = line.strip().split() dataMat.append([1.0,float(lineArr[0]),float(lineArr[1])])#每行前两个值是X1,X2,把X0设置为1 labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2]))#第三个值是数据对应的类别标签 return dataMat,labelMat def sigmoid(inX): return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-inX)) def gradAscent(dataMatIn,classLabels):#dataMaxIn是一个2维数组,100x3的矩阵 dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn)#将输入数据转换成Numpy矩阵 labelMat = np.mat(classLabels).transpose()#labelMat是类别标签,1x100行向量,转置为列向量 m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix)#得到矩阵大小 alpha = 0.001#参数,移动步长 maxCycles = 500#迭代次数 weights = np.ones((n,1)) for k in range(maxCycles):#循环迭代完成后,将返回训练好的回归系数 #矩阵运算 h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights)#h是一个列向量,100x3 * 3x1 = 100x1 error = (labelMat - h) weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose()* error return weights
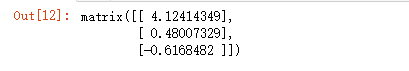
dataArr,labelMat = loadDataSet() weights = gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat) weights
"""上面已经解出了一组回归系数,它确定了不同类别数据之间的分割线。 5.2.3 分析数据:画出决策边界""" #5.2 画出数据集和Logistic回归最佳拟合直线的函数 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def plotBestFit(wei): weights = wei dataMat,labelMat = loadDataSet() dataArr = np.array(dataMat) n = np.shape(dataArr)[0] xcord1 = [] ycord1 = [] xcord2 = [] ycord2 = [] for i in range(n): if int(labelMat[i]) == 1: xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]) ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2]) else: xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]) ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2]) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1,s=30,c = 'red',marker='s') ax.scatter(xcord2,ycord2,s=30,c='green') x = arange(-3.0,3.0,0.1) y = ((-weights[0]-weights[1]*x)/weights[2]).T ax.plot(x,y) plt.xlabel('X1') plt.ylabel('X2') plt.show()
plotBestFit(weights)
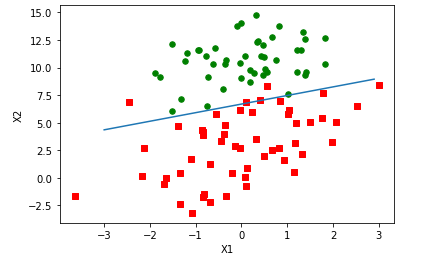
尽管例子简单且数据集很小,但这个方法却需要大量的计算(300次乘法),因此对该算法稍作改进。
5.2.4 训练算法:随机梯度上升
梯度上升算法在每次更新回归系数时都需要遍历整个数据集,如果有数十亿样本和成千上万的特征,那么该方法的计算复杂度就太高了。 一种改进方法是一次仅用一个样本点来更新回归系数,该方法称为随机梯度上升算法。
"""5-3 随机梯度上升算法 变量h和误差error都是向量; 没有矩阵的转换过程,所有变量的数据类型都是Numpy数组""" def stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix,classLabels): m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix) alpha = 0.01 weights = np.ones(n) for i in range(m): h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weights)) error = classLabels[i] - h weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[i] return weights
dataArr,labelMat = loadDataSet() weights = stocGradAscent0(np.array(dataArr),labelMat) plotBestFit(weights)
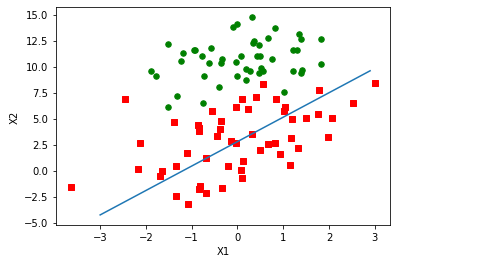
拟合出来的直线效果还不错,但不如上图完美。这里的分类器错分了三分之一的样本。
"""改进的随机梯度上升算法""" def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix,classLabels,numIter=150): m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix) weights = np.ones(n) for j in range(numIter): dataIndex = list(range(m)) for i in range(m): alpha = 4/(1.0+j+i)+0.01#alpha每次迭代时需要调整 randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#随机选取更新 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights)) error = classLabels[randIndex] - h weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex] del(dataIndex[randIndex]) return weights dataArr,labelMat = loadDataSet() weights = stocGradAscent1(np.array(dataArr),labelMat) plotBestFit(weights)
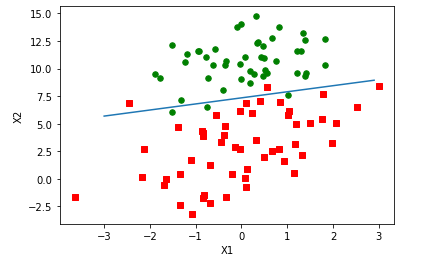
#默认迭代次数是150,可以通过stocGradAscent()的第三个参数来进行修改 weights = stocGradAscent1(np.array(dataArr),labelMat,500) plotBestFit(weights)
5.3.1 准备数据:处理数据中的缺失值
使用可用特征的均值来填补缺失值;
使用特殊值来填补缺失值,如-1;
忽略有缺失值的样本;
使用相似样本的均值填补缺失值;
使用另外的机器学习算法预测缺失值;
回归系数的更新公式:
weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex];
如果dataMatrix的某特征值对应值为0,那么该特征的系数将不做更新:
weights = weights;
另外,由于sigmoid(0) = 0.5,即它对结果的预测不具有任何倾向性,因此上述做法也不会对误差造成任何影响。基于上述原因,将缺失值用0代替即可以保留现有数据,也不需要对优化算法进行修改。此外,该数据集中的特征取值一般不为0,因此在某种意义上来说它也满足“特殊值”这个要求。
预处理中要做的第二件事是,如果在测试数据集中发现了一条数据的类别标签已经缺失,简单的做法就是将该条数据丢弃。这是因为类别标签与特征不同,很难确定采用某个合适的值来替换。采用Logistic回归进行分类时这种做法是合理的,而如果采用类似KNN的方法就可能不太行。
"""测试算法:用Logistic回归进行分类 5-5 Logistic回归分类函数""" def classifyVector(inX,weights):#以回归系数和特征向量作为输入来计算对应的Sigmoid值 prob = sigmoid(sum(inX*weights)) if prob > 0.5: return 1.0 else: return 0.0 def colicTest(): frTrain = open('D:/02-ipynb/code-机器学习实战/machinelearninginaction/Ch05/horseColicTraining.txt') frTest = open('D:/02-ipynb/code-机器学习实战/machinelearninginaction/Ch05/horseColicTest.txt') trainingSet = [] trainingLabels = [] for line in frTrain.readlines(): currLine = line.strip().split('\t') lineArr = [] for i in range(21): lineArr.append(float(currLine[i])) trainingSet.append(lineArr) trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21])) trainWeights = stocGradAscent1(np.array(trainingSet),trainingLabels,500)#计算回归系数向量 errorCount = 0 numTestVec = 0.0 for line in frTest.readlines(): numTestVec += 1.0 currLine = line.strip().split('\t') lineArr = [] for i in range(21): lineArr.append(float(currLine[i])) if int(classifyVector(np.array(lineArr),trainWeights)) != int(currLine[21]): errorCount += 1 errorRate = (float(errorCount)/numTestVec) print("the error rate of this test is: %f" % errorRate) return errorRate def multiTest():#调用函数colicTest()10次并求结果的平均值 numTests = 10 errorSum = 0.0 for k in range(numTests): errorSum += colicTest() print("after %d iterations the average error rate is: %f" %(numTests,errorSum/float(numTests)))
multiTest()
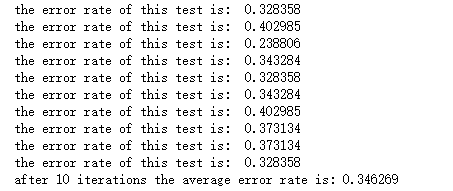
从上面的结果来看,10次迭代之后的平均错误率为34%。如果调整colicTest()中的迭代次数和stocGradAscent1()中的步长,平均错误率可以降到20%左右。
本章小结
Logistic回归的目的是寻找一个非线性函数Sigmiod的最佳拟合参数,求解过程可以由最优化算法来完成。在最优化算法中,最常用的就是梯度上升算法,而梯度上升算法又可以简化为随机梯度上升算法。
随机梯度上升算法与梯度上升算法的效果相当,但占用更少的计算资源。此外,随机梯度上升是一个在线算法,它可以在新数据到来时就完成参数更新,而不需要重新读取整个数据集来进行批处理运算。
机器学习的一个重要问题是如何处理缺失数据。这个问题没有标准答案,取决于实际应用中的需求,现有一种解决方案,每种方案都各有优缺点。
下一章将介绍与Logistic回归类似的另一种分类算法:支持向量机,它被认为是目前最好的现成的算法之一。


