常见的字符串操作
字符串(String),是由零个或多个字符组成的有限串行。一般记为 (
(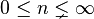 )。它是编程语言中表示文本的数据类型。
)。它是编程语言中表示文本的数据类型。
通常以串的整体作为操作对象,如:在串中查找某个子串、求取一个子串、在串的某个位置上插入一个子串以及删除一个子串等。
两个字符串相等的充要条件是:长度相等,并且各个对应位置上的字符都相等。
设p、q是两个串,求q在p中首次出现的位置的运算叫做模式匹配。
串的两种最基本的存储方式是顺序存储方式和链接存储方式。
 将整形转换为字符串
将整形转换为字符串
//************************************ // Method: ItoA // Description: Transfer an int to a string // Access: public // Returns: void // Qualifier: // Parameter: int n // Parameter: char * str //************************************ void ItoA(int n, char *str) { char num[256]; int k = n, i; if (n<0) k = -n; for(i=0; k>0; i++) { num[i] = k%10 + '0'; k /= 10; } if(n<0) num[i] = '-'; else --i; int j; for(j=0;i>=0;j++,i--) { str[j] = num[i]; } str[j] ='\0'; }
 将字符串转换为整形
将字符串转换为整形
//************************************ // Method: AtoI // Description: Transfer a string to a long integer // Access: public // Returns: void // Qualifier: // Parameter: long * n // Parameter: char * str //************************************ void AtoI(long *n, char* str) { if(str == NULL) throw "error"; bool sign = false; if(*str == '-') { str++; sign = true; } else if (*str == '+') { str++; } *n = 0; while(*str) { if(*str >= '0' && *str <='9') { *n =(*n)*10 + ((*str) - '0') ; str++; } else { throw "error"; } } if(sign == true){(*n) = -(*n);} }
 字符串循环移位
字符串循环移位
//************************************ // Method: LoopMove // Description: Move the chars from the string recurrently // Access: public // Returns: void // Qualifier: // Parameter: char * pStr // Parameter: int steps: The steps to be moved //************************************ void LoopMove(char* pStr, int steps) { if (pStr == NULL) { throw "error"; } int len = strlen(pStr); if (steps%len != 0) { char* snippet = new char[len]; strcpy(snippet, pStr + len - steps%len); *(pStr + len - steps%len) = '\0'; strcpy(snippet + steps%len, pStr); strcpy(pStr, snippet); } }
 字符串拷贝
字符串拷贝
//************************************ // Method: strCpy // Description: Copy string from source to destination // Access: public // Returns: char*: Start address of the destination string // Qualifier: // Parameter: const char * Src: Source string // Parameter: char * Dst: Destination string //************************************ char* strCpy(const char* Src, char* Dst) { if(Src == NULL || Dst == NULL) throw "error"; char* DstCpy = Dst; while((*Dst++ = *Src++) != '\0'); return DstCpy; }
 字符串匹配
字符串匹配
//************************************ // Method: FindSubStr // FullName: Locate substring. Returns a pointer to the first occurrence of str2 in str1, or a null pointer if str2 is not part of str1. The matching process does not include the terminating null-characters. // Access: public // Returns: const char*: A pointer to the first occurrence in str1 of any of the entire sequence of characters specified in str2, or a null pointer if the sequence is not present in str1. // Qualifier: // Parameter: const char * str1: C string to be scanned. // Parameter: const char * str2: C string containing the sequence of characters to match. //************************************ const char* FindSubStr(const char* str1, const char*str2) { if (str1 == NULL || str2 == NULL) { throw "error"; } int len1 = 0; int len2 = 0; const char*p = str1; while(*p++) len1++; p = str2; while(*p++) len2++; if (len1 < len2) { return NULL; } int i = 0; for (;i <= len1 - len2;i++) { int j = 0; while(*(str2 + j)) { if(*(str1 + i + j) == *(str2 + j)) { j++; } else { break; } } if (j == len2) { return (str1 + i); } } return NULL; }
 语句单词顺序反转
语句单词顺序反转
//************************************ // Method: InverseSentence // FullName: Inverse a Sentence which is ended with a '.', while keep the order of each word // Access: public // Returns: void // Qualifier: // Parameter: char * str // Parameter: char * res //************************************ void InverseSentence(char* str, char* res) { int len = strlen(str); int i = len - 1; int cnt = 0;//number of letter which is not space int cnt_s = 0;//number of letter which is space for (;i >= 0;i--) { if (*(str + i) != ' ' && *(str + i) != '.') { cnt++; if (i == 0 || *(str + i - 1) == ' ' || *(str + i - 1) == '.') { memcpy(res + len - i - cnt, str + i, cnt); cnt = 0; } } else { cnt_s++; if (*(str + i - 1) != ' ' && *(str + i - 1) != '.') { memcpy(res + len - i - cnt_s, str + i, cnt_s); cnt_s = 0; } } } *(res + len) = '\0'; //move the dot to the end memcpy(res, res + 1, len - 1); *(res + len - 1) = '.'; *(res + len) = '\0'; }




