Java方法(四)
设计方法原则:本意为功能块,是实现某个功能语句块的结合,设计方法时保持原子性(一个方法完成一个功能)
public class operator { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = add(1,3); System.out.println(sum); } //加法 public static int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; } }
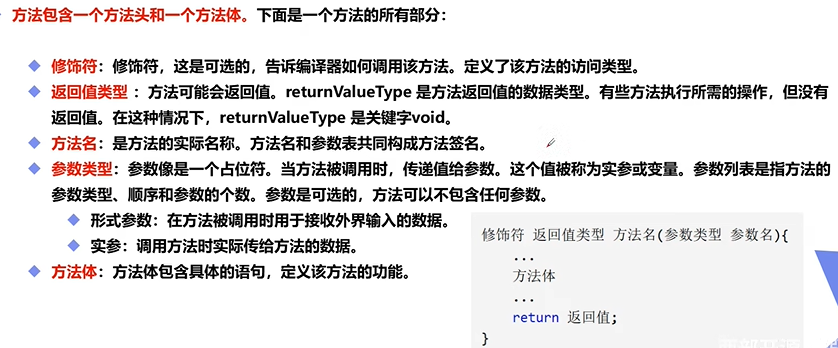
方法的定义以及调用
public class operator { public static void main(String[] args) { int str = str(2,4); System.out.println(str); } public static int str(int a,int b){ int result = 0; if (a==b){ System.out.println("a=b"); return 0; } if (a>b){ result = a; }else { result = b; } return result; } }
方法重载
public class operator { public static void main(String[] args) { double str = str(2.5,4.2); System.out.println(str); } public static int str(int a,int b){ int result = 0; if (a==b){ System.out.println("a=b"); return 0; } if (a>b){ result = a; }else { result = b; } return result; } public static double str(double a,double b){ double result = 0; if (a==b){ System.out.println("a=b"); return 0; } if (a>b){ result = a; }else { result = b; } return result; } }也可以通过强制转换进行重载方法

public class operator { public static void main(String[] args) { double sum = add(3.6,4.9); System.out.println(sum); } public static int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; } public static long add(long a,long b){ return a-b; } public static double add(double a,double b){ return a*b; } }
命令行传参
public class operator { public static void main(String[] args) { //args.length 数组长度 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { System.out.println("args[" + i + "]:" + args[i]); } } }//主要在于使用命令行进行编译,运行,重在路径名
可变参数(不定向参数,指定参数后加.....,只能放在最后)
public class operator { public static void main(String[] args) { printMax(12,43,56,73.3,21,1,9,5); printMax(new double[]{1,2,3}); } public static void printMax(double...numbers){ if (numbers.length==0){ System.out.println("No argument passed"); return; } double result = numbers[0]; for (int i = 1;i<numbers.length;i++){ if (numbers[i]>result){ result = numbers[i]; } } System.out.println("The max value is:"+result); } }
递归(自己调用自己,如计算阶乘)

public class jiabaoyu { public static void main(String[] args) { //阶层计算 System.out.println(f(5)); } public static int f(int n){ if (n==1){ return 1; }else { return n*f(n-1); } } }//边界条件;前阶段;返回阶段:[n*(n-1)];栈机制;适用于基数较少的运算




