向量容器vector操作
1.向量容器vector
1.1 vector说明
- 进行vector操作前应添加头文件#include<vector>;
- vector是向量类型,可以容纳许多类型的数据,因此也被称为容器;
- 可以理解为动态数组,是封装好了的类,可以在运行阶段设置长度;
- 具有数组的快速索引方式;
- 可以插入和删除元素。
1.2 建议使用场景
- 开始就知道元素的数量;
- 对数据的索引和随机访问频繁;
- 插入和删除大多数在尾端。
1.3 vector初始化
使用格式:vector<数据类型> 变量名
常用的方式有如下几种:
- 方式1:
/* 定义一个整型向量(大小没有指定,可以动态的向里面添加删除) */ vector<int> a
- 方式2:
/* 定义具有10个整型元素的向量(尖括号为元素类型名,它可以是任何合法的数据类型),不具有初值,其值不确定 */ vector<int> a(10);
- 方式3:
/* 定义具有10个整型元素的向量,且给出的每个元素初值为1 */ vector<int> a(10,1);
1.4 常用操作
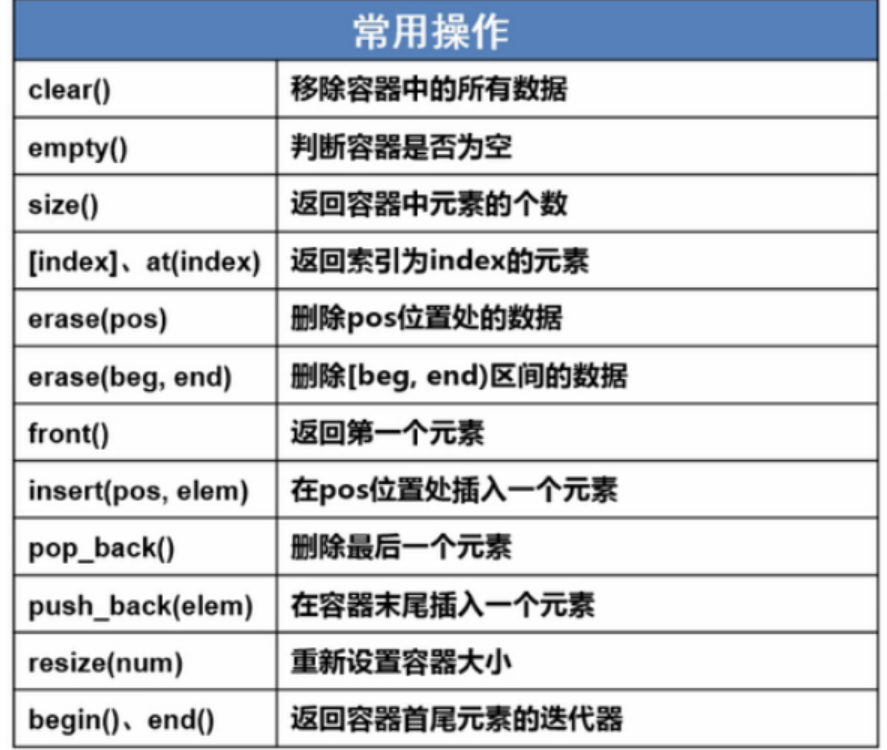
1.5 用例
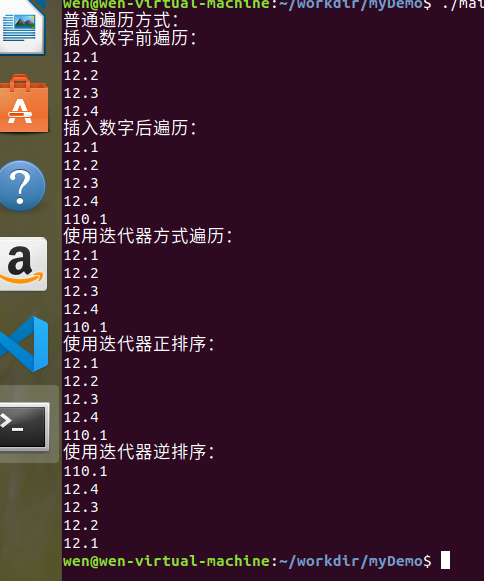
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int main() { int i; /*定义一个double类型的向量容器,不指定容器的大小 */ vector<double> vectorDouble = {12.1, 12.2, 12.3, 12.4}; cout<<"普通遍历方式:"<<endl; cout<<"插入数字前遍历:"<<endl; /* 遍历容器中的成员 */ for(i = 0; i < vectorDouble.size(); i++) { cout<<vectorDouble[i]<<endl; } /* 向容器中插入数字 */ vectorDouble.push_back(110.1); cout<<"插入数字后遍历:"<<endl; /* 遍历容器中的成员 */ for(i = 0; i < vectorDouble.size(); i++) { cout<<vectorDouble[i]<<endl; } /* 集合通用的遍历方法:使用迭代器 iterator */ vector<double>::iterator it; cout<<"使用迭代器方式遍历:"<<endl; /* 遍历容器中的成员 */ for(it = vectorDouble.begin(); it != vectorDouble.end(); ++it) { cout<<*it<<endl; } cout<<"使用迭代器正排序:"<<endl; /*正 排序 */ sort(vectorDouble.begin(), vectorDouble.end()); /* 遍历容器中的成员 */ for(it = vectorDouble.begin(); it != vectorDouble.end(); ++it) { cout<<*it<<endl; } cout<<"使用迭代器逆排序:"<<endl; /* 逆排序*/ reverse(vectorDouble.begin(), vectorDouble.end()); /* 遍历容器中的成员 */ for(it = vectorDouble.begin(); it != vectorDouble.end(); ++it) { cout<<*it<<endl; } return 0; }
程序运行结果显示:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号