201521123059 《Java程序设计》第七周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结
以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结集合相关内容。
参考资料:
XMind
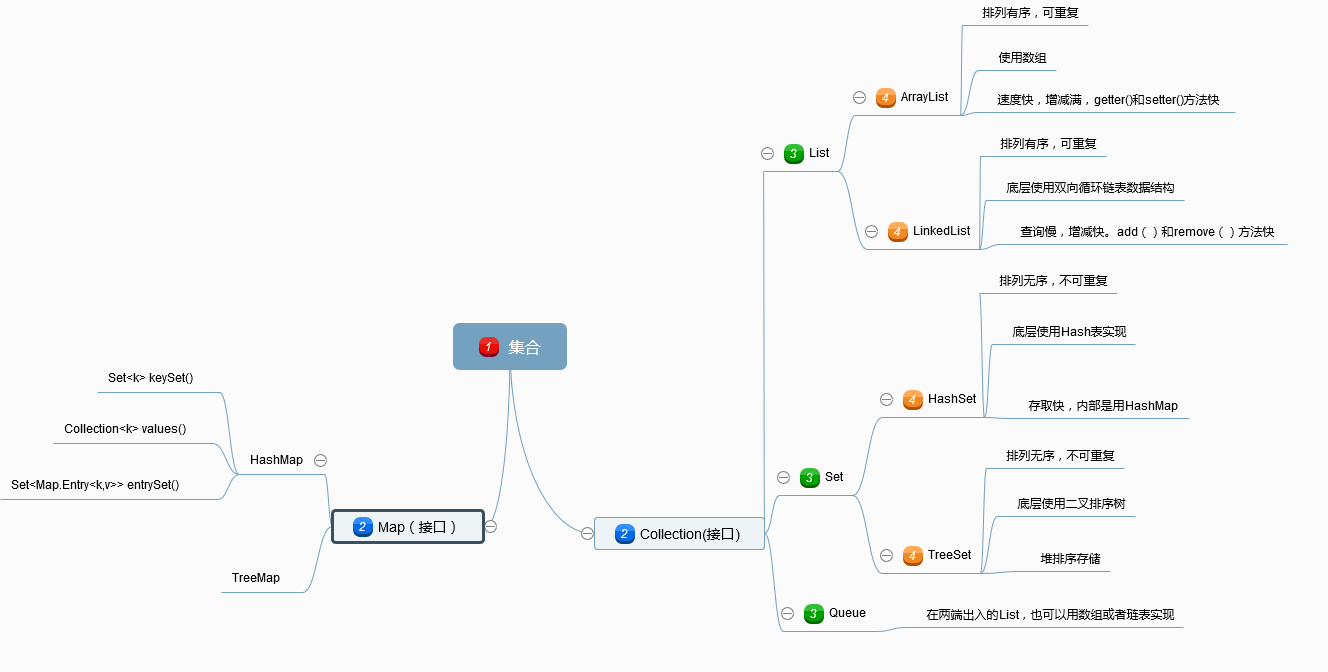
2. 书面作业
Q1: ArrayList代码分析
1.1 解释ArrayList的contains源代码
contains源代码如下:
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
解释:contains实现遍历ArrayList,indexOf函数返回值为序号,如果o为null则没有equals方法
1.2 解释E remove(int index)源代码
源代码如下:
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
解释:A:先检查要删除的位置如果超出List大小,就抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常。大概流程就是类似数组删除操作,删掉某个元素后,其位置之后的元素前移,最后再把size-1位置赋null让GC clear it。
1.3 结合1.1与1.2,回答ArrayList存储数据时需要考虑元素的类型吗?
答:不用考虑。因为ArrayList的参数是Object对象,而一切对象都是Object。
1.4 分析add源代码,回答当内部数组容量不够时,怎么办?
源代码如下:
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
解释:由以上代码分析在add函数里调用ensureCapacityInternal()来调整容量,如果容量超了则调用函数grow增加容量,在grow函数中建立一个新容量大小为oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)的容量
1.5 分析private void rangeCheck(int index)源代码,为什么该方法应该声明为private而不声明为public?
源代码如下:
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
答:因为不想外部使用这个方法。这样可以保证外部操作是容量不会越界而抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index))。
Q2:HashSet原理
2.1 将元素加入HashSet(散列集)中,其存储位置如何确定?需要调用那些方法?
答:HashSet存储形式是链表实现。当加入一个新元素时,HashSet先调用该对象的hashCode()方法得到其hashCode值,而该HashCode值决定了该元素的存储位置。然后根据哈希码查找到对应的桶,如果桶中已有其他元素,则调用新元素的equals方法与已有元素进行比较;如果比较结果为假,则将新元素插入桶中如果比较结果为真,则用新的值替换旧的值。
Q3:ArrayListIntegerStack
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-1 ArrayListIntegerStack
**3.1 比较自己写的ArrayListIntegerStack与自己在题集jmu-Java-04-面向对象2-进阶-多态、接口与内部类中的题目5-3自定义接口ArrayIntegerStack,有什么不同?(不要出现大段代码) **
不同之处如下:
class ArrayIntegerStack implements IntegerStack {
private Integer[] stack;
private int num=0;
public ArrayIntegerStack(int n) {
this.setStack(new Integer[n]);
}
public class ArrayListIntegerStack implements IntegerStack {
private List<Integer> list;
public ArrayListIntegerStack(){
list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
**3.2 简单描述接口的好处. **
答:好处之一是一样的方法可以使用不同的接口实现,有些接口实现比较简单,有些比较复杂,具体要求应该按照题目的,可以提供多一种方式实现方法。
Q4:Stack and Queue
4.1 编写函数判断一个给定字符串是否是回文,一定要使用栈,但不能使用java的Stack类(具体原因自己搜索)。请粘贴你的代码,类名为Main你的学号。
public class Main201521123059 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=in.nextLine();
System.out.println(isHuiwen(str));
}
public static boolean isHuiwen(String text){
int length = text.length();
for(int i=0;i<length/2;i++){
if(text.charAt(i)!=text.charAt(length-i-1)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
4.2 题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-6 银行业务队列简单模拟。(不要出现大段代码)
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Queue<Integer> qA=new LinkedList<Integer>(),qB=new LinkedList<Integer>();
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) {
int x=in.nextInt();
if( x % 2==0 ) qB.add( x );
else qA.add( x );
}
while(!qA.isEmpty()||!qB.isEmpty()){
Integer a1=qA.poll();
if(a1!=null){
if(qA.isEmpty()&&qB.isEmpty())
System.out.print(a1);
else System.out.print(a1+" ");
}
Integer a2=qA.poll();
if(a2!=null){
if(qA.isEmpty()&&qB.isEmpty())
System.out.print(a2);
else System.out.print(a2+" ");
}
Integer b=qB.poll();
if(b!=null){
if(qA.isEmpty()&&qB.isEmpty())
System.out.print(b);
else System.out.print(b+" ");
}
}
}
解析:此题先建立两个队列,把输入尾号为偶数的顾客add(x)入qB中,奇数的add(x)入qA中,然后按顺序输出qA和qB的元素,即先是输出两个qA的元素在输出qB的一个元素,但是需要注意的是取对头元素用poll() ,因为poll() 获取并移除此列表的头(第一个元素)之后可以继续操作下一个元素。
Q5:统计文字中的单词数量并按单词的字母顺序排序后输出
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-2 统计文字中的单词数量并按单词的字母顺序排序后输出 (不要出现大段代码)
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Set<String>set=new TreeSet();
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNext()){
String str=in.next();
if(str.equals("!!!!!"))break;
set.add(str);
}
System.out.println(set.size());
if(set.size()<10)
for (String string : set) {
System.out.println(string);
}
else{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(set.toArray()[i]);
}
}
}
**5.1 实验总结 **
答:这道题目的关键是输入一堆单词然后把单词分出来还要按单词的字母顺序排序后输出,这样我们就可以用一个while(in.hasNext()),在循环里面set.add()可以分离出来单词,然后建立一个TreeSet(),因为TreeSet会默认帮我们排好序,然后我们输出就可以了。
Q6:选做:加分考察-统计文字中的单词数量并按出现次数排序
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-3 统计文字中的单词数量并按出现次数排序(不要出现大段代码 )
6.1 伪代码
6.2 实验总结*
Q7:面向对象设计大作业-改进
**7.1 完善图形界面(说明与上次作业相比增加与修改了些什么) **
**7.2 使用集合类改进大作业 **
参考资料:
JTable参考项目
3. 码云上代码提交记录及PTA实验总结
题目集:jmu-Java-05-集合
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图

3.2. PTA实验
编程(5-1, 5-2, 5-3(选做), 5-6)
实验总结已经在作业中体现,不用写。




