【实验结论】
1、二分查找
设N个整数有序(由小到大)存放在一维数组中。编写函数binarySearch(),实现使用二分查找算法在一维数组中 查找特定整数item。如果找到,返回item在数组元素中的下标;如果item不在数组中,则返回-1。
实现方式1:形参是数组,实参是数组名,使用数组元素直接访问方式实现
程序源码:

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 const int N=5; 3 int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item); 4 int main() { 5 int a[N]={2,4,17,23,45}; 6 int i,index, key; 7 8 printf("数组a中的数据:\n"); 9 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 10 printf("%d ",a[i]); 11 printf("\n"); 12 13 printf("输入待查找的数据项: "); 14 scanf("%d", &key); 15 16 // 调用函数binarySearch()在数组a中查找指定数据项item,并返回查找结果给index 17 18 index=binarySearch(a,N,key); 19 if(index>=0) 20 printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d\n", key, index); 21 else 22 printf("%d不在数组中\n", key); 23 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item) { 28 int low, high, mid; 29 30 low = 0; 31 high = n-1; 32 33 while(low <= high) { 34 mid = (low+high)/2; 35 36 if (item == x[mid]) 37 return mid; 38 else if(item < x[mid]) 39 high = mid - 1; 40 else 41 low = mid + 1; 42 } 43 44 return -1; 45 }
运行结果截图:

实现方式2:形参是指针变量,实参是数组名,使用指针变量间接访问方式实现
程序源码:

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 const int N=5; 3 int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item); 4 int main() { 5 int a[N]={2,6,13,21,30}; 6 int i,index, key; 7 8 printf("数组a中的数据:\n"); 9 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 10 printf("%d ",a[i]); 11 printf("\n"); 12 13 printf("输入待查找的数据项: "); 14 scanf("%d", &key); 15 16 // 调用函数binarySearch()在数组a中查找指定数据项item,并返回查找结果 17 18 index=binarySearch(a,N,key); 19 if(index>=0) 20 printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d\n", key, index); 21 else 22 printf("%d不在数组中\n", key); 23 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item) { 28 int low, high, mid; 29 30 low = 0; 31 high = n-1; 32 33 while(low <= high) { 34 mid = (low+high)/2; 35 36 if (item == *(x+mid)) 37 return mid; 38 else if(item < *(x+mid)) 39 high = mid - 1; 40 else 41 low = mid + 1; 42 } 43 44 return -1; 45 }
运行结果截图:

2、选择法排序
使用选择法对字符串按字典序排序
程序源码:

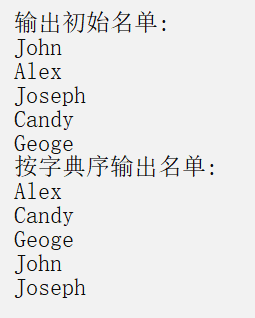
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 void selectSort(char str[][20], int n ); // 函数声明,形参str是二维数组名 4 int main() { 5 char name[][20] = {"John", "Alex", "Joseph", "Candy", "Geoge"}; 6 int i; 7 8 printf("输出初始名单:\n"); 9 for(i=0; i<5; i++) 10 printf("%s\n", name[i]); 11 12 selectSort(name, 5); // 调用选择法对name数组中的字符串排序 13 14 printf("按字典序输出名单:\n"); 15 for(i=0; i<5; i++) 16 printf("%s\n", name[i]); 17 18 return 0; 19 } 20 21 // 函数定义 22 // 函数功能描述:使用选择法对二维数组str中的n个字符串按字典序排序 23 void selectSort(char str[][20], int n) { 24 int i, j, k; 25 char temp[20]; 26 for(i=0; i<n-1; i++) { 27 k = i; // k用于记录当前最小元素的下标 28 29 for(j=i+1; j<n; j++) 30 if (strcmp(str[j],str[k])<0) 31 k = j; // 如果str[j]比当前最小元素还要小,就更新k,确保它总是存放最小元素的下标 32 33 if(k != i) { // 找到最小元素后,交换str[i]和str[k] 34 strcpy(temp,str[i]); 35 strcpy(str[i],str[k]); 36 strcpy(str[k],temp); 37 } 38 } 39 40 }
运行结果截图:
【实验总结与体会】
实验内容1:二分查找算法
数组名作为参数 vs. 指针变量作为参数,在形参、实参写法,以及函数实现中数组元素表示的差异 :
|
|
形参写法 |
实参写法 |
数组元素的表示 |
|
数组名作为参数 |
int x[] |
Sum(a,b) |
a[i] |
|
指针变量作为参数 |
int *p1、int *p2 |
Swap(pa,pb) |
P[1]、*(p+1) |
实验内容2:选择法排序
使用选择法对字符串排序时注意事项 :
(1)字符串的比较和赋值,不能直接使用关系运算符和赋值运算符,要借助字符串处理函数。
如本题中的①字符串比较函数strcmp(字符串1,字符串2):
函数功能:比较两个字符串的大小,返回一个整数值。
若函数值为0,则字符串1与字符串2相等;
若函数值大于0,则字符串1大于字符串2;
若函数值小于0,则字符串1小于字符串2。
②字符串的赋值/拷贝函数strcpy(字符数组,字符串):
函数功能:将字符串复制到字符数组中。如果字符串的长度小于数组的长度,其余部分用'\0'填补。
返回处理完的字符串。
另:使用字符串处理函数必须包含头文件<string.h>
(2)数组名作为变量的引用,对二维数组str[][20]行地址的理解。
(3)编写子函数selectSort时,对局部变量i、j边界值的控制。
实验内容3:使用指针变量对字符串进行处理
注意事项总结:
(1)用指针进行字符串复制操作时,要在串结尾处写入结束符'\0'。
(2)串复制时,串s的长度应大于串t;串连接时,串s的长度应大于等于串s与串t长度之和。
互评博客页面地址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/holya/
https://www.cnblogs.com/yy-Siri/


