数据库之单表运用(建表、增删改查.备份还原)
一、进入数据库操作界面
1、mysql -u root -p 敲回车 ,输入密码 ,进入数据库操作界面
2、show databases 查看所有的数据(如果没有数据库:创建数据库 create database 库名称)
3、use 数据库名 使用数据库
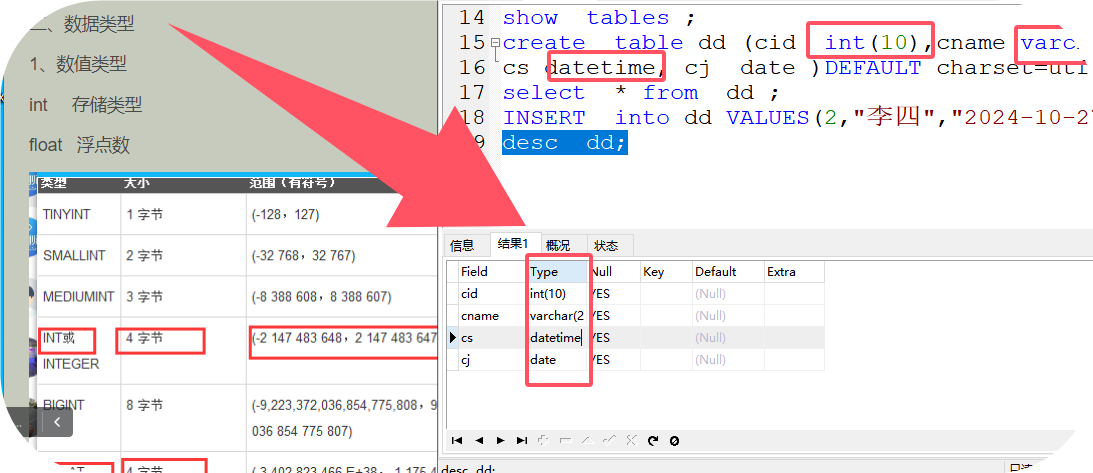
4、show tables 显示库中的所有表
5、建表语句
格式:create table 表名(字段名1 字符类型(字符长度),字段名2 字符类型(字符长度));
案例:create table aa(id int(10),name varchar(20));
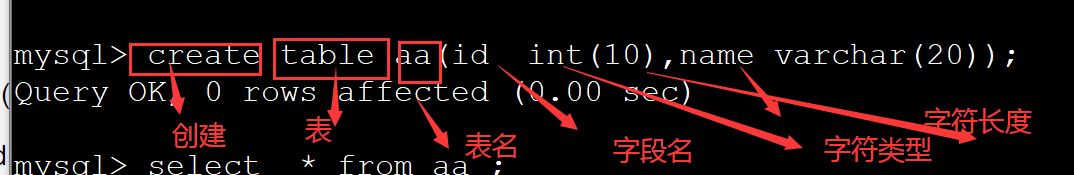
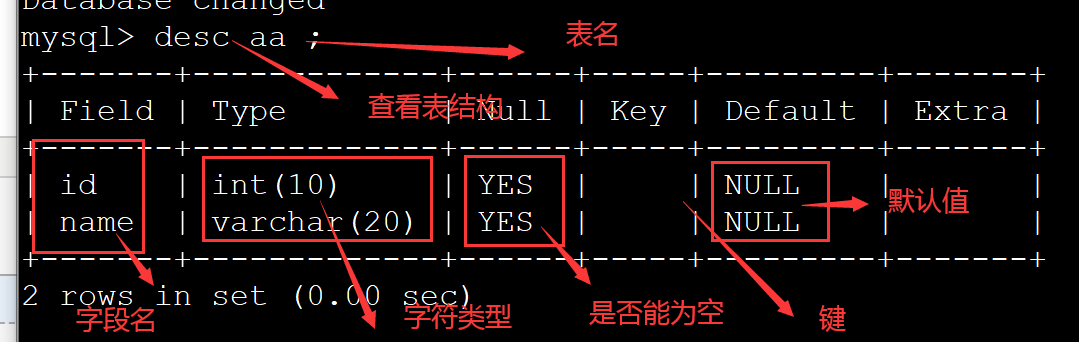
6、查看表结构:desc 表名
案例:
7、在navicat 中=点击库名=点击查询=新建查询===在新建查询中输入sql语句
8、插入数据:
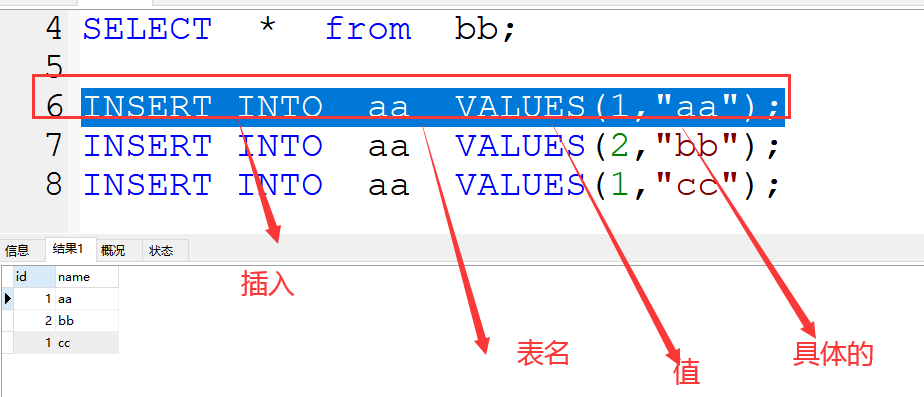
(1)插入方式一:
格式:INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES(值1,值2);
案例:INSERT INTO aa VALUES(1,"aa");
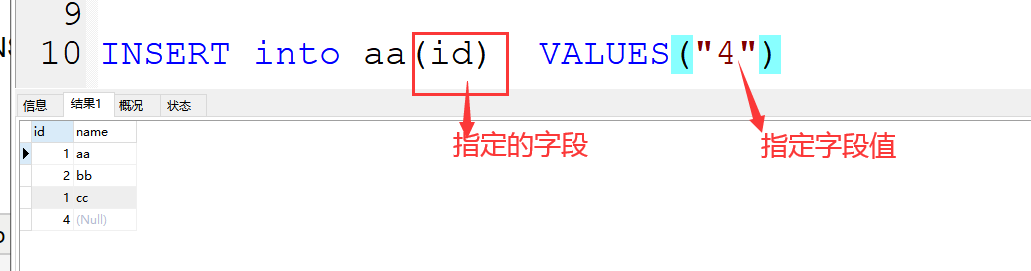
(2)插入方式二:(插入部分字段)
格式:INSERT into 表名(字段名) VALUES(字段值)
案例:INSERT into aa(id) VALUES("4")
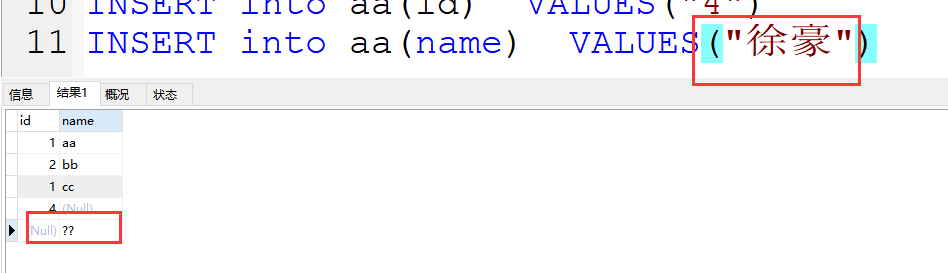
(3)插入的中文字符变成?号
解决方案:
在建表时的语句后面添加:
default charset=utf8;
案例:create table cc(cid int(5),cname char(20))DEFAULT charset=utf8;
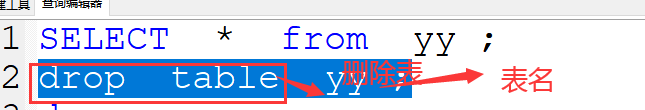
9、删除表格
drop table 表名
案例:drop table yy ;
二、数据类型
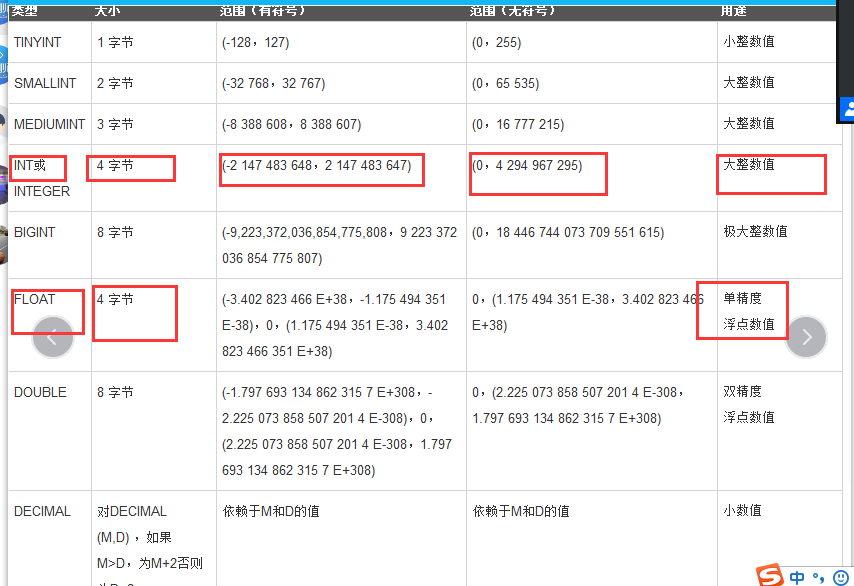
1、数值类型
int 存储类型
float 浮点数
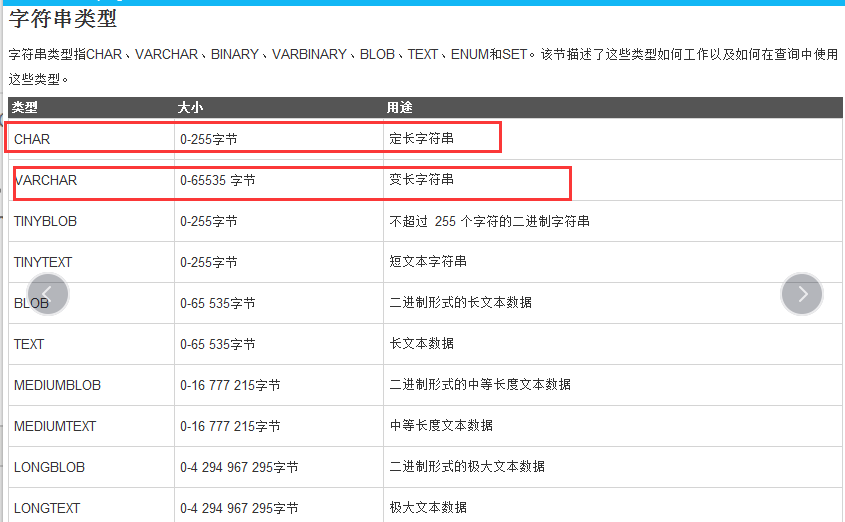
2、字符类型
char
varchar
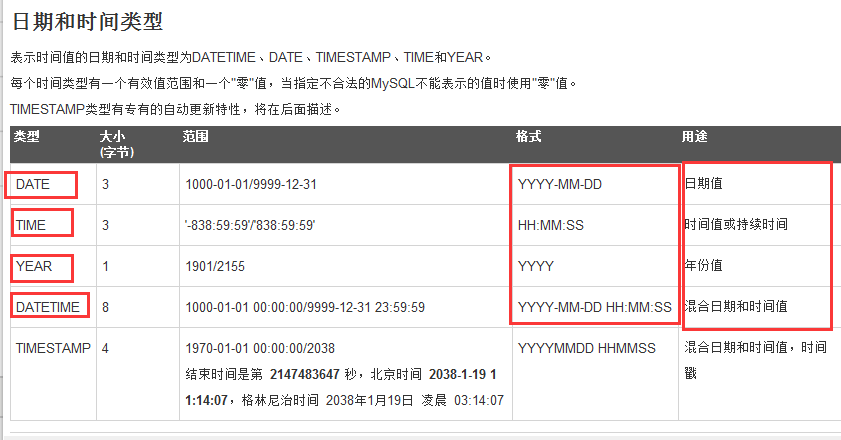
3、时间类型
date
time
datetime
year
约束:约束用于对表中字段进行限制,保证表中数据的正确性和唯一性
1、primary key 主键约束
非空,唯一,用于唯一标识的记录,类似身份证。
一个表中只用一个主键

2、not null 非空约束
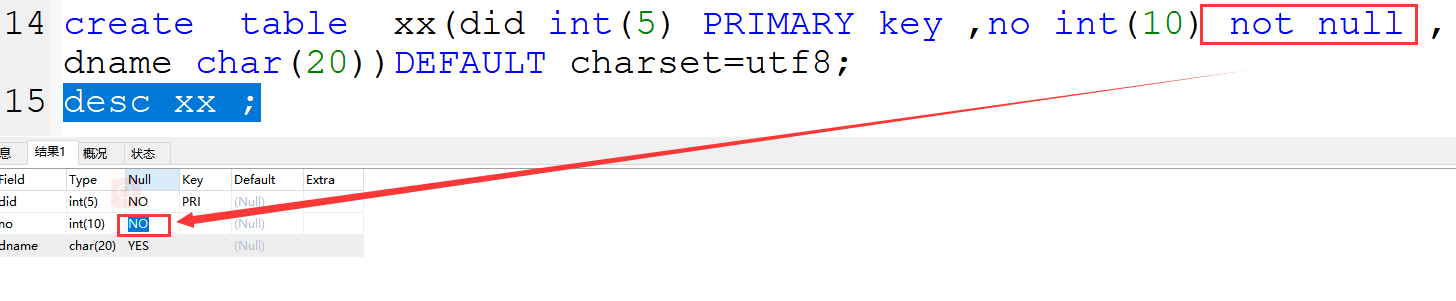
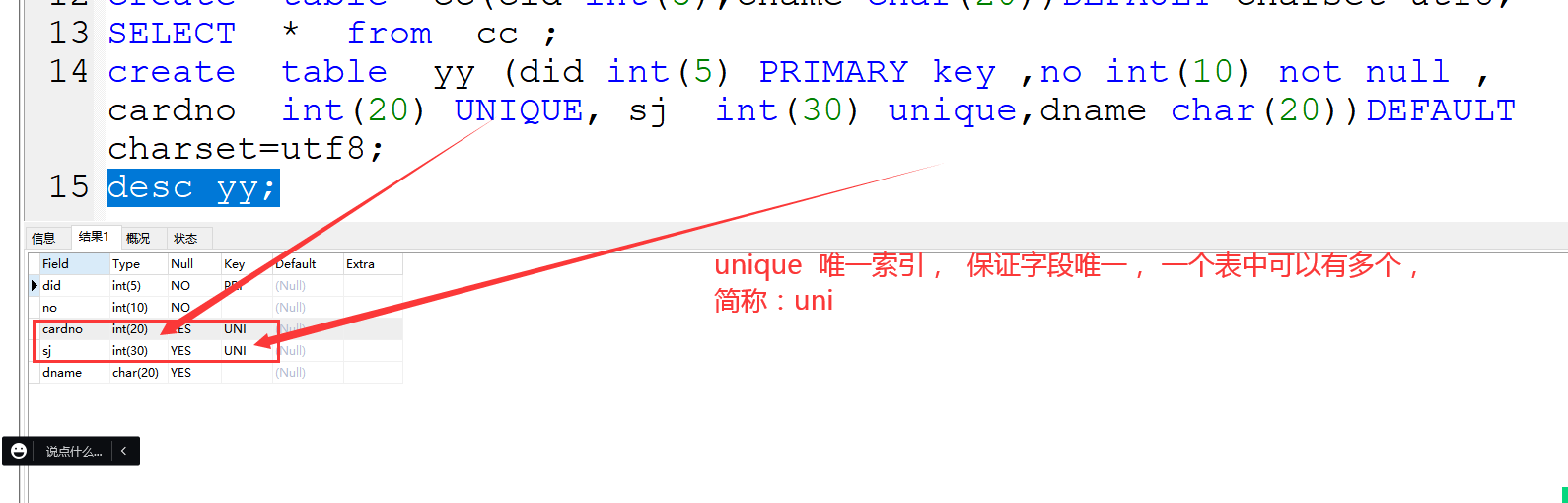
3、unique 唯一索引
保证字段值具有唯一性,并且能为空,一个表中可以有多个唯一索引
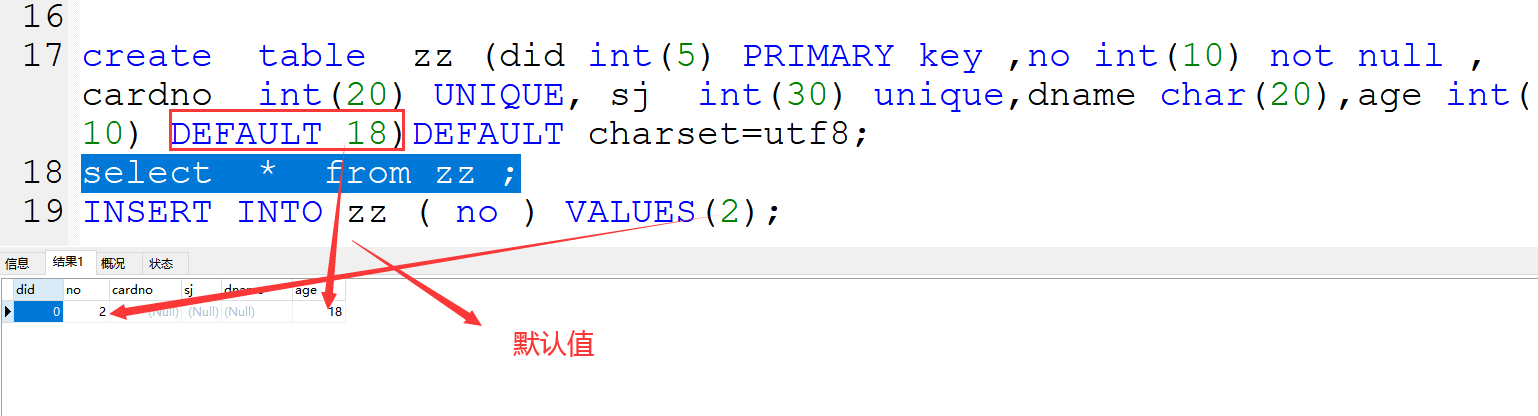
4、default 默认值约束
定义:默认给字段指定默认值
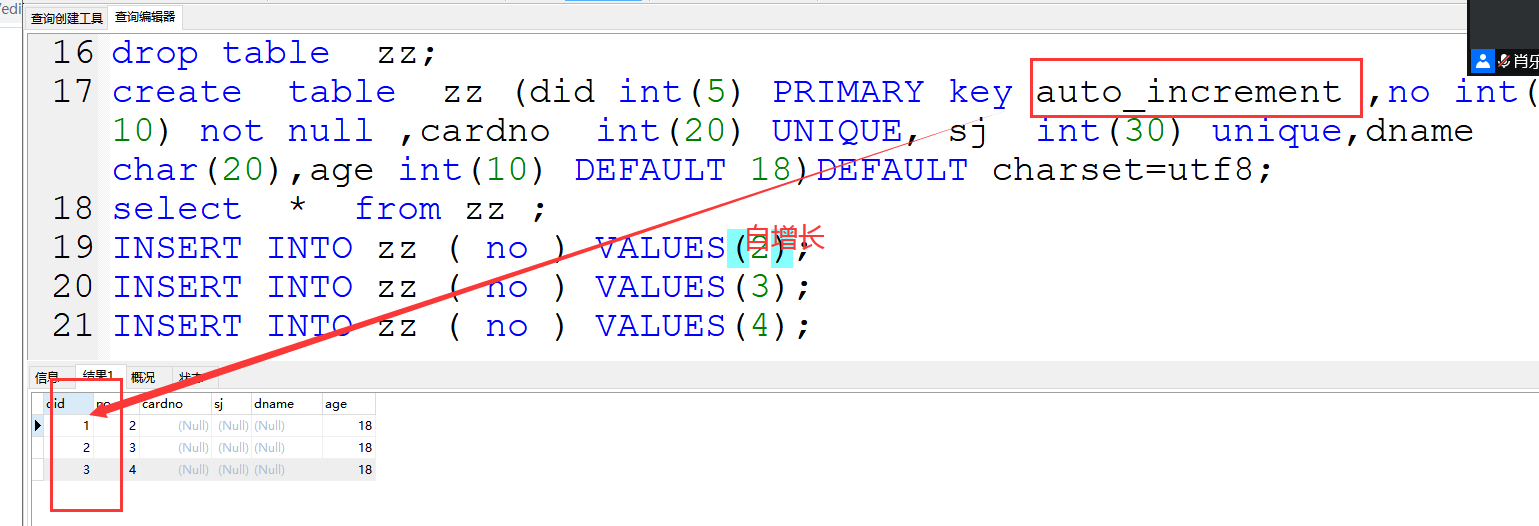
5、auto_increment 自增长约束(一般都是和主键同时使用)
作用:在整数类型,字段默认值从1开始自增
(1)一般和主键约束一起使用,主要针对id
(2)每插入一条数据,就是在字段上自动+1,
===================
表结构的操作:
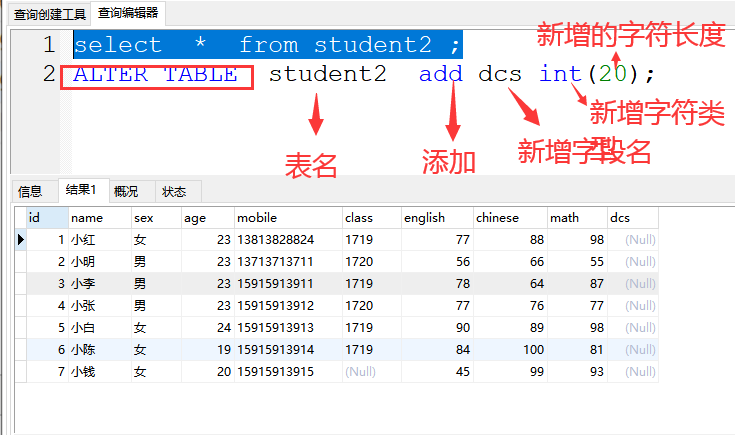
2、add 添加字段
格式:ALTER TABLE 表名 add 字段名 字符类型(字符长度);
案例:ALTER TABLE student2 add dcs int(20);
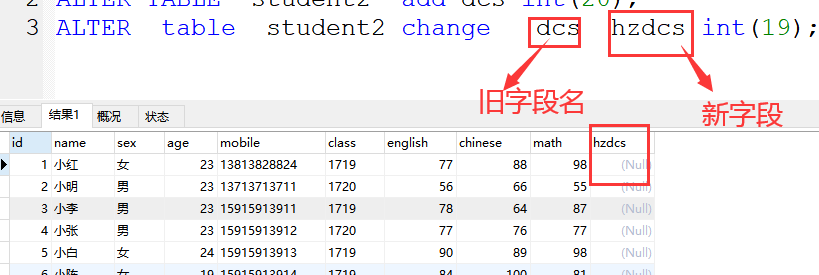
3、change 修改字段
格式:ALTER TABLE 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 字符类型(字符长度);
案例:ALTER table student2 change dcs hzdcs int(19);
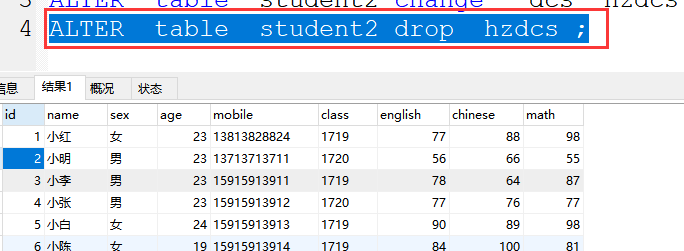
4、 drop 删除字段
格式:ALTER table 表名 drop 字段名 ;
案例:ALTER table student2 drop hzdcs ;
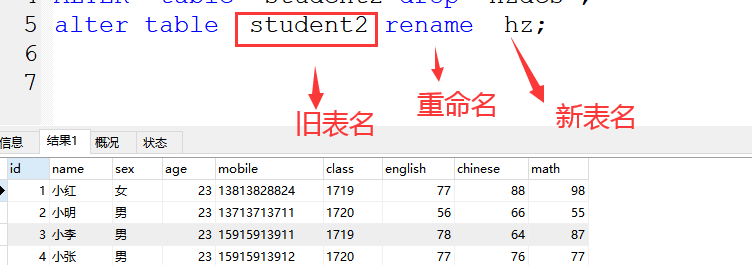
5、rename 修改表名
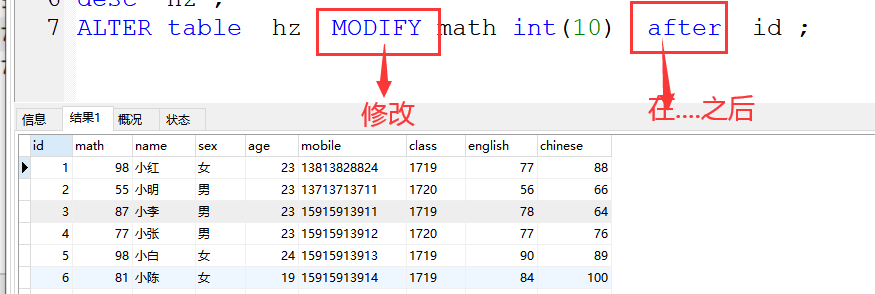
6、modify after 字段的调换
格式:ALTER table 表格 MODIFY 变动的字段 字段类型(字段长度) after 指定字段 ;
案例:ALTER table hz MODIFY math int(10) after id ;
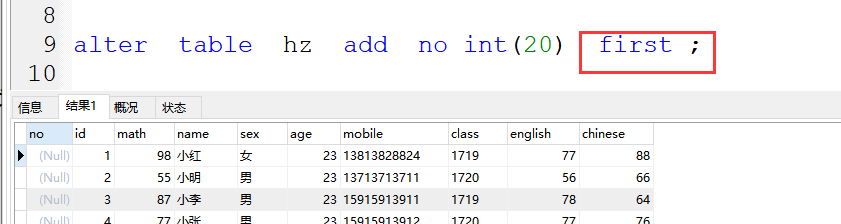
7、first 添加字段到第一位
格式:alter table 表名 add 表字段 字符类型(字符长度) first ;
案例:alter table hz add no int(20) first ;
=========================================
数据库汇中:增、删、改、查
一、查询语句:
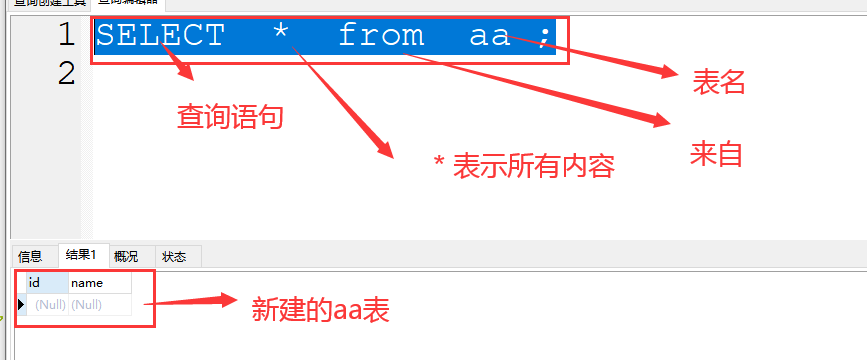
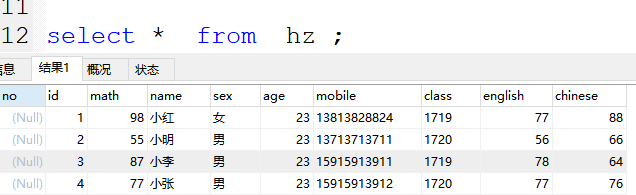
(1)查询一个表中的所有数据
格式:select * from 表名 ; * 表示所有的字段
案例:select * from hz ;
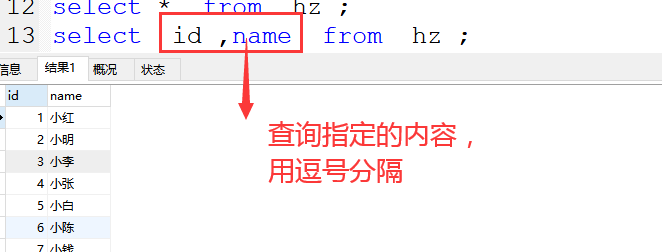
(2)查询部分字段(多个字段用,分割)
格式:select 字段1,字段2 from hz ;
案例:select id,name from hz ;
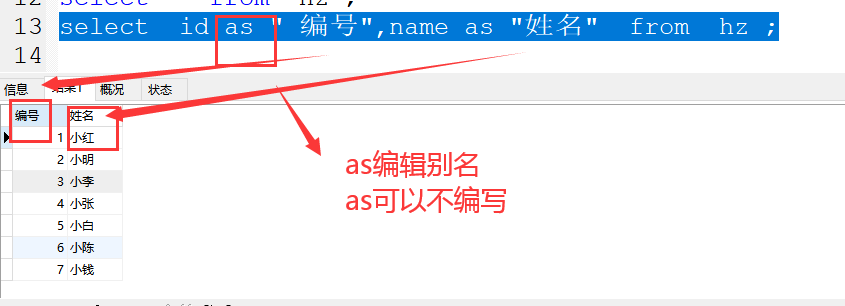
(3)查询字段可以通过as 取别名
案例1( as写,):
select id as " 编号",name as "姓名" from hz ;
案例2(可以省略 as不写):
select id " 编号",name "姓名" from hz ;
(4)指定条件查询内容:where +条件
条件1:比较运算:>,<,=,!=,<>,>=,<=
条件2:and ,or ,between ....and ,in , is not null
案例1:= 等于
select id ,name from hz where id=1;
案例2:> 大于
select id ,name from hz where id>1;
案例3:<小于
select id ,name from hz where id<2;
案例4:<=小于等于
select id ,name from hz where id<=2;
案例5:>=大于等于
select id ,name from hz where id>=2;
(6)!=不等于
案例6:select id ,name from hz where id != 2;
(7)<>不等于
select id ,name from hz where id <> 2;
================================
(8)and 同时满足条件
案例8; and 是同时满足多个条件
select id ,name,math from hz where id > 2 and math>90;
(9)or 只要满足其中一个条件 就显示
select id ,name,math from hz where id > 6 or math>90;
(10)between....and 在什么范围之间
案例:select * from hz where id BETWEEN 3 and 6 ;
备注:包含了本身,
(11)in 在一组数据中选择(在数据汇总匹配)
案例:select * from hz where id in (1,3,8)
(12)not in 不在一组数据中选
案例:select * from hz where id NOT in (1,3,8)
(13)is null 为空的数据
select * from hz where class is null;
(14)is not nu 不为空的数据
select * from hz where class is not null;
=================================================
order by 排序
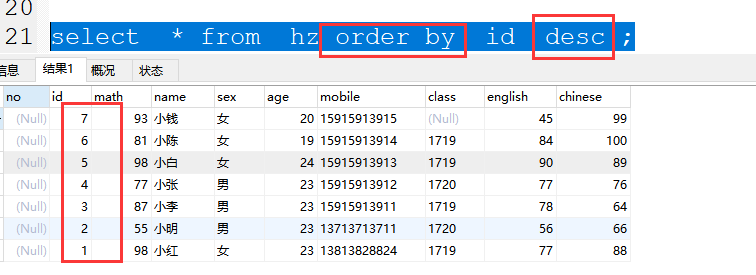
(1)降序 (大到小)
order by desc
案例:select * from hz order by id desc ;
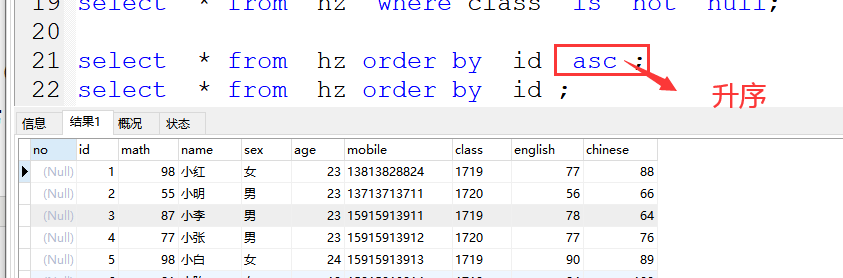
(2)升序(小到大)
order by (asc) 可不写
案例:
select * from hz order by id asc ;
select * from hz order by id ;
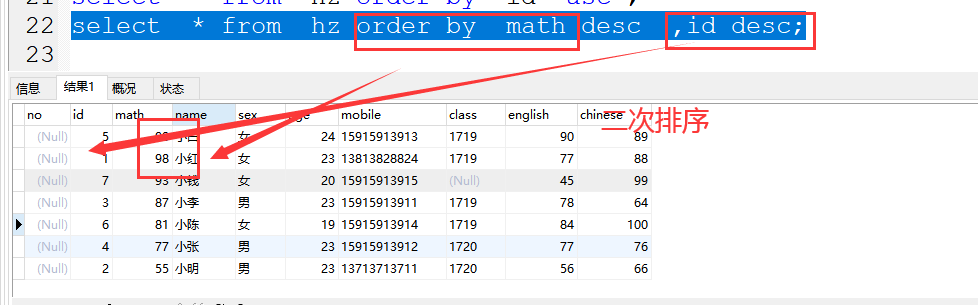
(3)二次排序
案例:select * from hz order by math desc ,id desc;
=====================
**like 模糊匹配查询
%:表示匹配1个字符或多个字符
_ : 下滑线表示一个字符
案例1:匹配xx开头的数据
select * from hz where math like "7%"; # 匹配7开头的数据
案例2:匹配xx结尾数据
select * from hz where math like "%7"; #匹配7结尾的数据
案例3:匹配含有xx结尾数据
select * from hz where math like "%7%"; #匹配含有7的数据
案例4:匹配指定位数的数据
select * from hz where math like "7_"; #匹配具体位数的数据
=====================
limit (索引位,步长) 显示指定的数据,限制;
根据索引位置来取值,从0开始,一个表第一行的索引就是0,第二行就是1
select * from hz limit 2; #表示取两行数据, 2 表示步长
select * from hz limit 1,2;#表示从索引1开始取二行,2表示步长2行
select * from hz limit 4,3 ;# 表示从索引4开始取值,第五行开始,取三行,
=====================
sql 聚合函数:
max 最大数
案例1:select max(math) from hz ;
min最小数
案例2:select min(math) from hz ;
avg 平均值
案例3:select avg(math) from hz ;
sum 求和
案例4:select sum(math) from hz ;
count 统计
案例5:select count(math) from hz ;
distinct 去重
案例6:select DISTINCT(math) from hz ;
==================
group by ....... having
group by 是分组,一般不会单独使用,通常和聚合函数组合使用
案例1:分组
select sum(math),class from hz group by class ;
案例2:分组 在条件 having
(1)select sum(math) s,class from hz group by class having s>200 ;
(2)select sum(math) ,class from hz group by class having sum(math)>200 ;
注意:having 一般接在group by 后面
==================
改:update ......set......
格式:update 表名 set 字段名=新值 where条件;
案例:update hz set id=1 where id=9;
==================
删除:
(1)delete
格式:DELETE from 表名 where 条件;
DELETE from hz where id=1;
(2)truncate 快速删除数据
格式:truncate 表名 ;
案例:truncate ff ;
(3)drop 删除
格式:drop table 表名
案例:drop table emp ;
drop >truncate> delete
==================
单行注释:ctrl +/
取消注释:shift+ctrl+/
多行注释:选中多行 ,ctrl +/
取消注释:选中多行 shift+ctrl+/
备份:
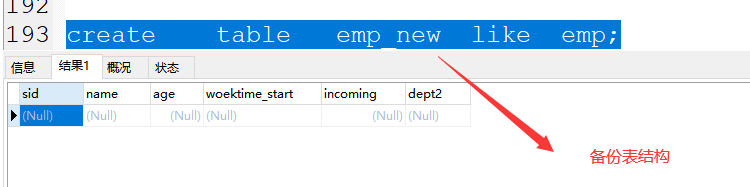
(1)备份表结构:
格式:create table 新表名 like 旧表名;
create table emp_new like emp;
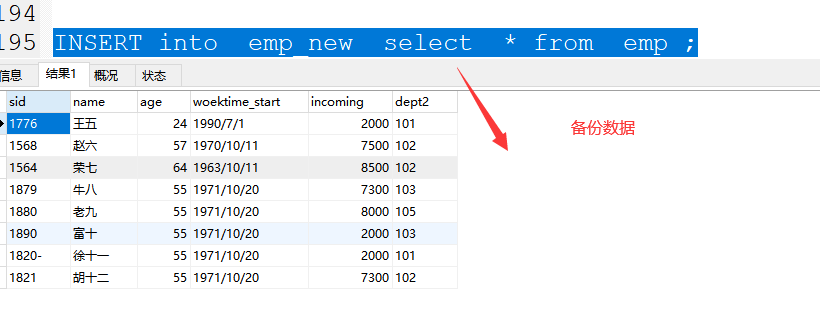
(2)备份表数据
格式:insert into 新表结构 select * from 旧表有数据 ;
案例:INSERT into emp_new select * from emp ;
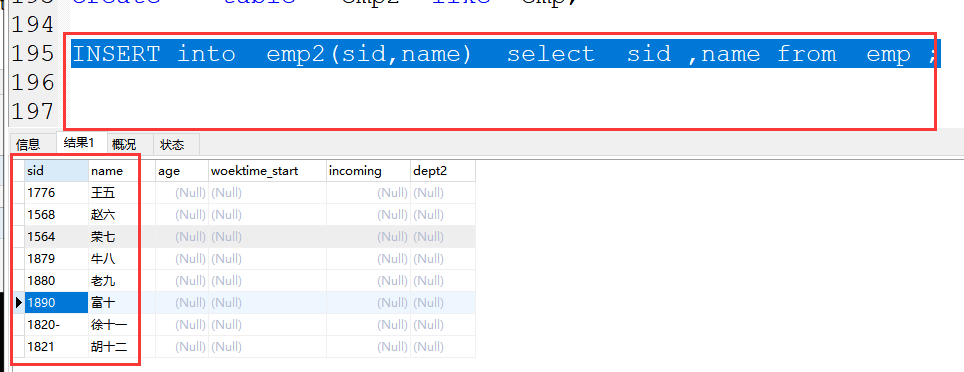
(3)备份部分数据
格式:insert into 表名(字段1,字段2) select 字段1,字段2 from 旧表 ;
案例:INSERT into emp2(sid,name) select sid ,name from emp ;
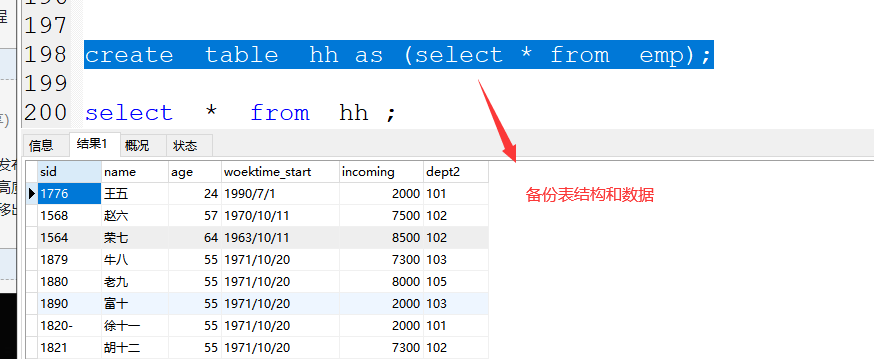
(4)备份表结构和数据
格式:create table 新表 as (select * from 原表);
案例:create table hh as (select * from emp);
=========================================================================
在linux 中:
备份:
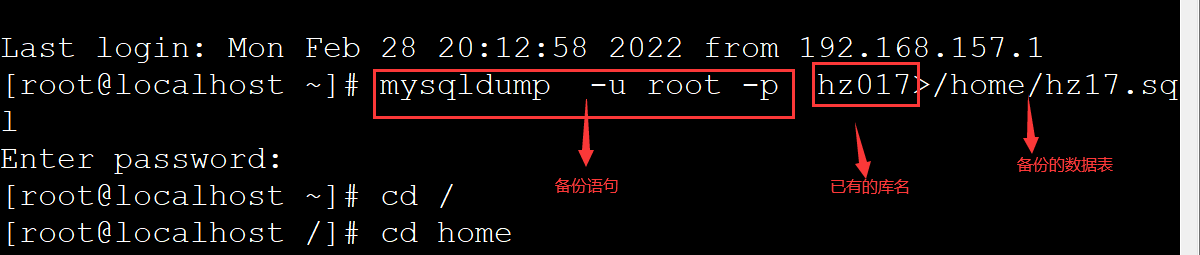
格式:mysqldump -u root -p 原库>新sql脚本名
案例:mysqldump -u root -p hz017>/home/hz17.sql
还原:
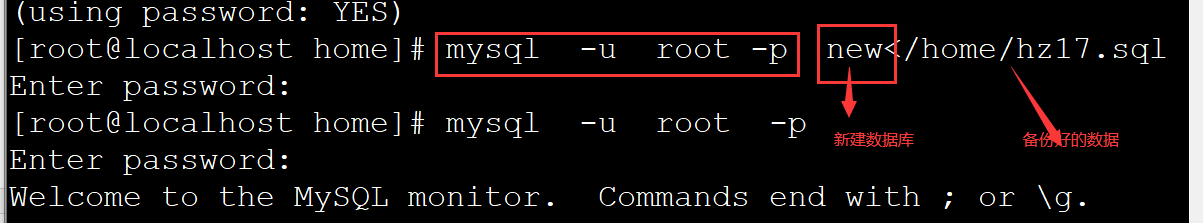
格式:mysql -u root -p 新库<备份好的脚本
案例:mysql -u root -p new</home/hz17.sql





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构