Linux多线程开发(三)
Linux多线程开发(三)
线程概述
线程概述

线程和进程区别

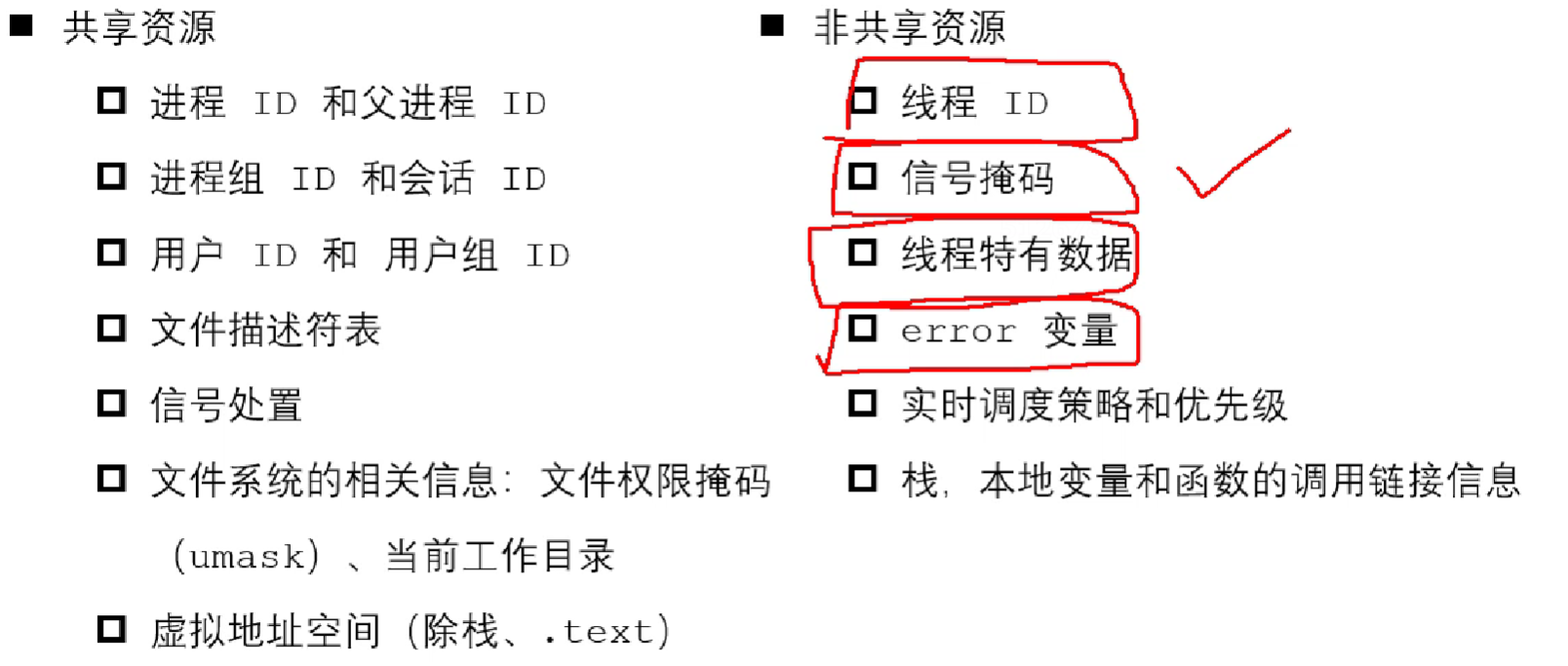
线程之间共享和非共享资源
NPTL

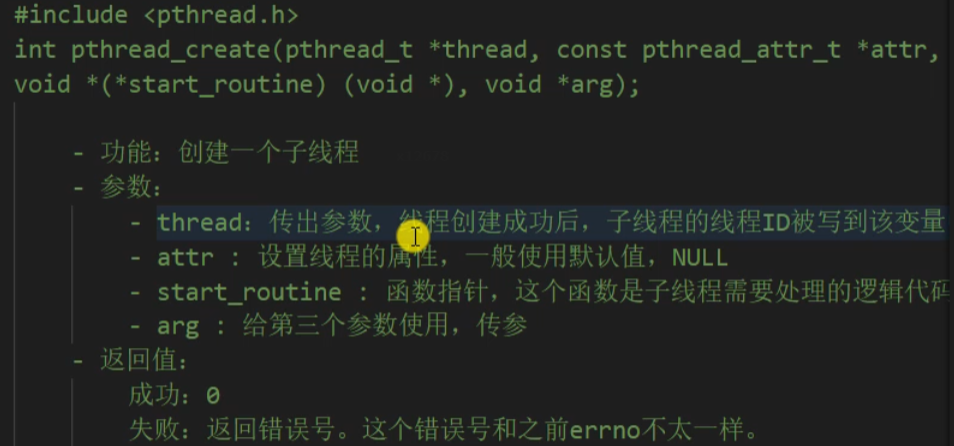
线程创建
代码
1 /* 2 一般情况下,main函数所在的线程我们称之为主线程(main线程),其余创建的线程 3 称之为子线程。 4 程序中默认只有一个进程,fork()函数调用,2进行 5 程序中默认只有一个线程,pthread_create()函数调用,2个线程。 6 7 #include <pthread.h> 8 int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, 9 void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg); 10 11 - 功能:创建一个子线程 12 - 参数: 13 - thread:传出参数,线程创建成功后,子线程的线程ID被写到该变量中。 14 - attr : 设置线程的属性,一般使用默认值,NULL 15 - start_routine : 函数指针,这个函数是子线程需要处理的逻辑代码 16 - arg : 给第三个参数使用,传参 17 - 返回值: 18 成功:0 19 失败:返回错误号。这个错误号和之前errno不太一样。 20 获取错误号的信息: char * strerror(int errnum); 21 22 */ 23 #include <stdio.h> 24 #include <pthread.h> 25 #include <string.h> 26 #include <unistd.h> 27 28 void * callback(void * arg) { 29 printf("child thread...\n"); 30 printf("arg value: %d\n", *(int *)arg); 31 return NULL; 32 } 33 34 int main() { 35 36 pthread_t tid; 37 38 int num = 10; 39 40 // 创建一个子线程 41 int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, (void *)&num); 42 43 if(ret != 0) { 44 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 45 printf("error : %s\n", errstr); 46 } 47 48 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 49 printf("%d\n", i); 50 } 51 52 sleep(1); 53 54 return 0; // exit(0); 55 }
终止线程

代码
1 /* 2 3 #include <pthread.h> 4 void pthread_exit(void *retval); 5 功能:终止一个线程,在哪个线程中调用,就表示终止哪个线程 6 参数: 7 retval:需要传递一个指针,作为一个返回值,可以在pthread_join()中获取到。 8 9 pthread_t pthread_self(void); 10 功能:获取当前的线程的线程ID 11 12 int pthread_equal(pthread_t t1, pthread_t t2); 13 功能:比较两个线程ID是否相等 14 不同的操作系统,pthread_t类型的实现不一样,有的是无符号的长整型,有的 15 是使用结构体去实现的。 16 */ 17 #include <stdio.h> 18 #include <pthread.h> 19 #include <string.h> 20 21 void * callback(void * arg) { 22 printf("child thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self()); 23 return NULL; // pthread_exit(NULL); 24 } 25 26 int main() { 27 28 // 创建一个子线程 29 pthread_t tid; 30 int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL); 31 32 if(ret != 0) { 33 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 34 printf("error : %s\n", errstr); 35 } 36 37 // 主线程 38 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 39 printf("%d\n", i); 40 } 41 42 printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid ,pthread_self()); 43 44 // 让主线程退出,当主线程退出时,不会影响其他正常运行的线程。 45 pthread_exit(NULL); 46 47 printf("main thread exit\n"); 48 49 return 0; // exit(0); 50 }
pthread_self当前进程的id
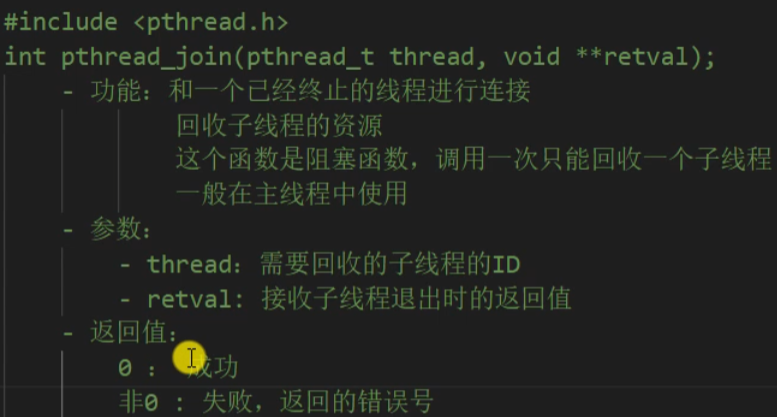
连接已终止的线程
代码
1 /* 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval); 4 - 功能:和一个已经终止的线程进行连接 5 回收子线程的资源 6 这个函数是阻塞函数,调用一次只能回收一个子线程 7 一般在主线程中使用 8 - 参数: 9 - thread:需要回收的子线程的ID 10 - retval: 接收子线程退出时的返回值 11 - 返回值: 12 0 : 成功 13 非0 : 失败,返回的错误号 14 */ 15 16 #include <stdio.h> 17 #include <pthread.h> 18 #include <string.h> 19 #include <unistd.h> 20 21 int value = 10; 22 23 void * callback(void * arg) { 24 printf("child thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self()); 25 // sleep(3); 26 // return NULL; 27 // int value = 10; // 局部变量 28 pthread_exit((void *)&value); // return (void *)&value; 29 } 30 31 int main() { 32 33 // 创建一个子线程 34 pthread_t tid; 35 int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL); 36 37 if(ret != 0) { 38 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 39 printf("error : %s\n", errstr); 40 } 41 42 // 主线程 43 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 44 printf("%d\n", i); 45 } 46 47 printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid ,pthread_self()); 48 49 // 主线程调用pthread_join()回收子线程的资源 50 int * thread_retval; 51 ret = pthread_join(tid, (void **)&thread_retval); 52 53 if(ret != 0) { 54 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 55 printf("error : %s\n", errstr); 56 } 57 58 printf("exit data : %d\n", *thread_retval); 59 60 printf("回收子线程资源成功!\n"); 61 62 // 让主线程退出,当主线程退出时,不会影响其他正常运行的线程。 63 pthread_exit(NULL); 64 65 return 0; 66 }
线程的分离
代码
1 /* 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread); 4 - 功能:分离一个线程。被分离的线程在终止的时候,会自动释放资源返回给系统。 5 1.不能多次分离,会产生不可预料的行为。 6 2.不能去连接一个已经分离的线程,会报错。 7 - 参数:需要分离的线程的ID 8 - 返回值: 9 成功:0 10 失败:返回错误号 11 */ 12 #include <stdio.h> 13 #include <pthread.h> 14 #include <string.h> 15 #include <unistd.h> 16 17 void * callback(void * arg) { 18 printf("chid thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self()); 19 return NULL; 20 } 21 22 int main() { 23 24 // 创建一个子线程 25 pthread_t tid; 26 27 int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL); 28 if(ret != 0) { 29 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 30 printf("error1 : %s\n", errstr); 31 } 32 33 // 输出主线程和子线程的id 34 printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self()); 35 36 // 设置子线程分离,子线程分离后,子线程结束时对应的资源就不需要主线程释放 37 ret = pthread_detach(tid); 38 if(ret != 0) { 39 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 40 printf("error2 : %s\n", errstr); 41 } 42 43 // 设置分离后,对分离的子线程进行连接 pthread_join() 44 // ret = pthread_join(tid, NULL); 45 // if(ret != 0) { 46 // char * errstr = strerror(ret); 47 // printf("error3 : %s\n", errstr); 48 // } 49 50 pthread_exit(NULL); 51 52 return 0; 53 }
线程操作

线程取消
pthread_cancel:取消线程或者是让线程终止
是遇到终止点才取消,没遇到终止点不取消。
代码
1 /* 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread); 4 - 功能:取消线程(让线程终止) 5 取消某个线程,可以终止某个线程的运行, 6 但是并不是立马终止,而是当子线程执行到一个取消点,线程才会终止。 7 取消点:系统规定好的一些系统调用,我们可以粗略的理解为从用户区到内核区的切换,这个位置称之为取消点。 8 */ 9 10 #include <stdio.h> 11 #include <pthread.h> 12 #include <string.h> 13 #include <unistd.h> 14 15 void * callback(void * arg) { 16 printf("chid thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self()); 17 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 18 printf("child : %d\n", i); 19 } 20 return NULL; 21 } 22 23 int main() { 24 25 // 创建一个子线程 26 pthread_t tid; 27 28 int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL); 29 if(ret != 0) { 30 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 31 printf("error1 : %s\n", errstr); 32 } 33 34 // 取消线程 35 pthread_cancel(tid); 36 37 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 38 printf("%d\n", i); 39 } 40 41 // 输出主线程和子线程的id 42 printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self()); 43 44 45 pthread_exit(NULL); 46 47 return 0; 48 }
线程属性

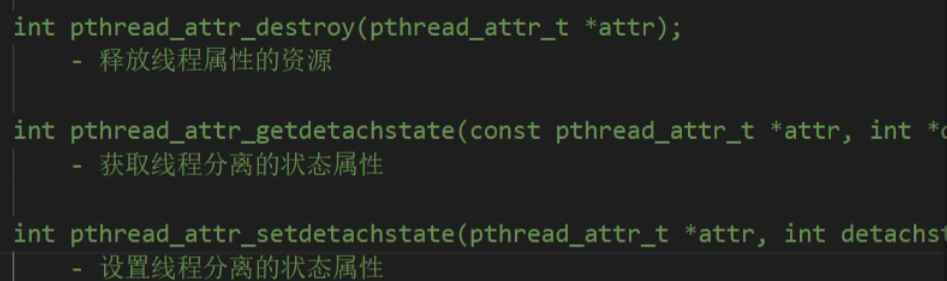
代码
1 /* 2 int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *attr); 3 - 初始化线程属性变量 4 5 int pthread_attr_destroy(pthread_attr_t *attr); 6 - 释放线程属性的资源 7 8 int pthread_attr_getdetachstate(const pthread_attr_t *attr, int *detachstate); 9 - 获取线程分离的状态属性 10 11 int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate); 12 - 设置线程分离的状态属性 13 */ 14 15 #include <stdio.h> 16 #include <pthread.h> 17 #include <string.h> 18 #include <unistd.h> 19 20 void * callback(void * arg) { 21 printf("chid thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self()); 22 return NULL; 23 } 24 25 int main() { 26 27 // 创建一个线程属性变量 28 pthread_attr_t attr; 29 // 初始化属性变量 30 pthread_attr_init(&attr); 31 32 // 设置属性 33 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); 34 35 // 创建一个子线程 36 pthread_t tid; 37 38 int ret = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, callback, NULL); 39 if(ret != 0) { 40 char * errstr = strerror(ret); 41 printf("error1 : %s\n", errstr); 42 } 43 44 // 获取线程的栈的大小 45 size_t size; 46 pthread_attr_getstacksize(&attr, &size); 47 printf("thread stack size : %ld\n", size); 48 49 // 输出主线程和子线程的id 50 printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self()); 51 52 // 释放线程属性资源 53 pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); 54 55 pthread_exit(NULL); 56 57 return 0; 58 }
线程同步

代码
1 /* 2 使用多线程实现买票的案例。 3 有3个窗口,一共是100张票。 4 */ 5 6 #include <stdio.h> 7 #include <pthread.h> 8 #include <unistd.h> 9 10 // 全局变量,所有的线程都共享这一份资源。 11 int tickets = 100; 12 13 void * sellticket(void * arg) { 14 // 卖票 15 while(tickets > 0) { 16 usleep(6000); 17 printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets); 18 tickets--; 19 } 20 return NULL; 21 } 22 23 int main() { 24 25 // 创建3个子线程 26 pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; 27 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 28 pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 29 pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 30 31 // 回收子线程的资源,阻塞 32 pthread_join(tid1, NULL); 33 pthread_join(tid2, NULL); 34 pthread_join(tid3, NULL); 35 36 // 设置线程分离。 37 // pthread_detach(tid1); 38 // pthread_detach(tid2); 39 // pthread_detach(tid3); 40 41 pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出主线程 42 43 return 0; 44 }
注意:分离后join,会报错。
usleep(3000):3000微秒。
互斥锁
互斥量

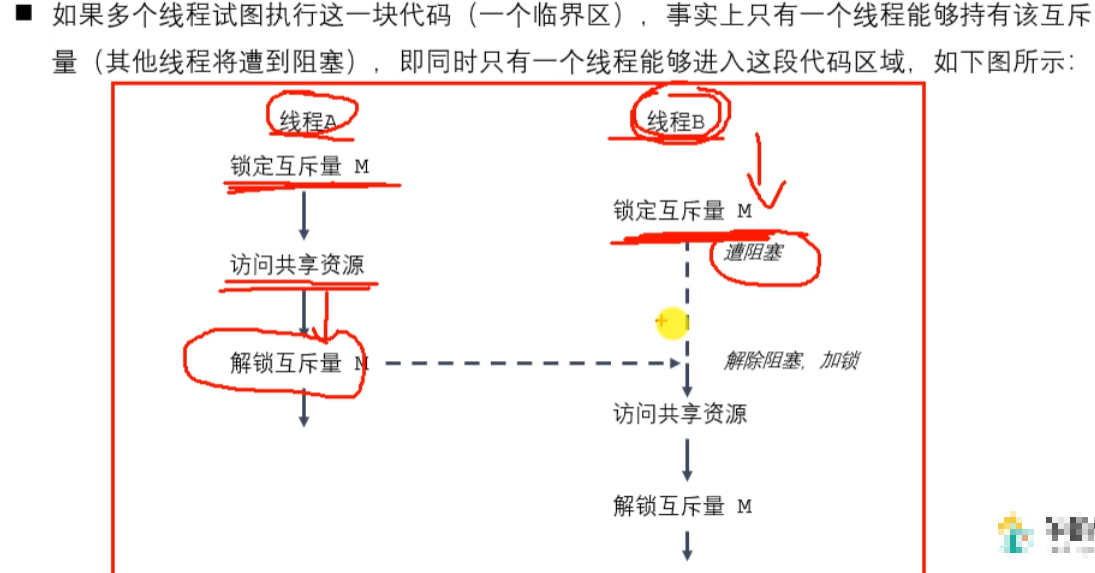
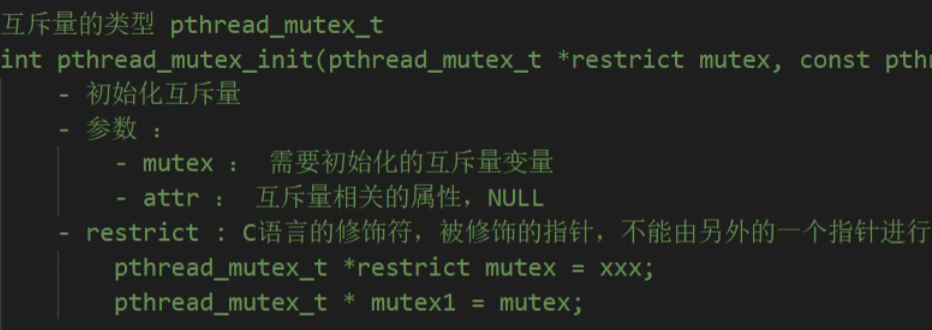

代码
1 /* 2 互斥量的类型 pthread_mutex_t 3 int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr); 4 - 初始化互斥量 5 - 参数 : 6 - mutex : 需要初始化的互斥量变量 7 - attr : 互斥量相关的属性,NULL 8 - restrict : C语言的修饰符,被修饰的指针,不能由另外的一个指针进行操作。 9 pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex = xxx; 10 pthread_mutex_t * mutex1 = mutex; 11 12 int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); 13 - 释放互斥量的资源 14 15 int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); 16 - 加锁,阻塞的,如果有一个线程加锁了,那么其他的线程只能阻塞等待 17 18 int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); 19 - 尝试加锁,如果加锁失败,不会阻塞,会直接返回。 20 21 int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); 22 - 解锁 23 */ 24 #include <stdio.h> 25 #include <pthread.h> 26 #include <unistd.h> 27 28 // 全局变量,所有的线程都共享这一份资源。 29 int tickets = 1000; 30 31 // 创建一个互斥量 32 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 33 34 void * sellticket(void * arg) { 35 36 // 卖票 37 while(1) { 38 39 // 加锁 40 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 41 42 if(tickets > 0) { 43 usleep(6000); 44 printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets); 45 tickets--; 46 }else { 47 // 解锁 48 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 49 break; 50 } 51 52 // 解锁 53 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 54 } 55 56 57 58 return NULL; 59 } 60 61 int main() { 62 63 // 初始化互斥量 64 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 65 66 // 创建3个子线程 67 pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; 68 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 69 pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 70 pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 71 72 // 回收子线程的资源,阻塞 73 pthread_join(tid1, NULL); 74 pthread_join(tid2, NULL); 75 pthread_join(tid3, NULL); 76 77 pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出主线程 78 79 // 释放互斥量资源 80 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); 81 82 return 0; 83 }
死锁
死锁

代码
deadlock.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 5 // 全局变量,所有的线程都共享这一份资源。 6 int tickets = 1000; 7 8 // 创建一个互斥量 9 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 10 11 void * sellticket(void * arg) { 12 13 // 卖票 14 while(1) { 15 16 // 加锁 17 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 18 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 19 20 if(tickets > 0) { 21 usleep(6000); 22 printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets); 23 tickets--; 24 }else { 25 // 解锁 26 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 27 break; 28 } 29 30 // 解锁 31 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 32 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 33 } 34 35 return NULL; 36 } 37 38 int main() { 39 40 // 初始化互斥量 41 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 42 43 // 创建3个子线程 44 pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; 45 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 46 pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 47 pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL); 48 49 // 回收子线程的资源,阻塞 50 pthread_join(tid1, NULL); 51 pthread_join(tid2, NULL); 52 pthread_join(tid3, NULL); 53 54 pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出主线程 55 56 // 释放互斥量资源 57 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); 58 59 return 0; 60 }
deadlock1.c(多线程多锁造成的死锁场景)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 5 // 创建2个互斥量 6 pthread_mutex_t mutex1, mutex2; 7 8 void * workA(void * arg) { 9 10 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1); 11 sleep(1); 12 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2); 13 14 printf("workA....\n"); 15 16 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2); 17 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1); 18 return NULL; 19 } 20 21 22 void * workB(void * arg) { 23 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2); 24 sleep(1); 25 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1); 26 27 printf("workB....\n"); 28 29 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1); 30 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2); 31 32 return NULL; 33 } 34 35 int main() { 36 37 // 初始化互斥量 38 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL); 39 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex2, NULL); 40 41 // 创建2个子线程 42 pthread_t tid1, tid2; 43 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, workA, NULL); 44 pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, workB, NULL); 45 46 // 回收子线程资源 47 pthread_join(tid1, NULL); 48 pthread_join(tid2, NULL); 49 50 // 释放互斥量资源 51 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1); 52 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex2); 53 54 return 0; 55 }
读写锁


代码
1 /* 2 读写锁的类型 pthread_rwlock_t 3 int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr); 4 int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); 5 int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); 6 int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); 7 int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); 8 int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); 9 int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); 10 11 案例:8个线程操作同一个全局变量。 12 3个线程不定时写这个全局变量,5个线程不定时的读这个全局变量 13 */ 14 15 #include <stdio.h> 16 #include <pthread.h> 17 #include <unistd.h> 18 19 // 创建一个共享数据 20 int num = 1; 21 // pthread_mutex_t mutex; 22 pthread_rwlock_t rwlock; 23 24 void * writeNum(void * arg) { 25 26 while(1) { 27 pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock); 28 num++; 29 printf("++write, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num); 30 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); 31 usleep(100); 32 } 33 34 return NULL; 35 } 36 37 void * readNum(void * arg) { 38 39 while(1) { 40 pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock); 41 printf("===read, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num); 42 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); 43 usleep(100); 44 } 45 46 return NULL; 47 } 48 49 int main() { 50 51 pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL); 52 53 // 创建3个写线程,5个读线程 54 pthread_t wtids[3], rtids[5]; 55 for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 56 pthread_create(&wtids[i], NULL, writeNum, NULL); 57 } 58 59 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 60 pthread_create(&rtids[i], NULL, readNum, NULL); 61 } 62 63 // 设置线程分离 64 for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 65 pthread_detach(wtids[i]); 66 } 67 68 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 69 pthread_detach(rtids[i]); 70 } 71 72 pthread_exit(NULL); 73 74 pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock); 75 76 return 0; 77 }
生产者和消费者模型
该模型采用链表结构实现。

代码
1 /* 2 生产者消费者模型(粗略的版本) 3 */ 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <pthread.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <unistd.h> 8 9 // 创建一个互斥量 10 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 11 12 struct Node{ 13 int num; 14 struct Node *next; 15 }; 16 17 // 头结点 18 struct Node * head = NULL; 19 20 void * producer(void * arg) { 21 22 // 不断的创建新的节点,添加到链表中 23 while(1) { 24 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 25 struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 26 newNode->next = head; 27 head = newNode; 28 newNode->num = rand() % 1000; 29 printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self()); 30 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 31 usleep(100); 32 } 33 34 return NULL; 35 } 36 37 void * customer(void * arg) { 38 39 while(1) { 40 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 41 // 保存头结点的指针 42 struct Node * tmp = head; 43 44 // 判断是否有数据 45 if(head != NULL) { 46 // 有数据 47 head = head->next; 48 printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self()); 49 free(tmp); 50 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 51 usleep(100); 52 } else { 53 // 没有数据 54 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 55 } 56 } 57 return NULL; 58 } 59 60 int main() { 61 62 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 63 64 // 创建5个生产者线程,和5个消费者线程 65 pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5]; 66 67 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 68 pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL); 69 pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL); 70 } 71 72 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 73 pthread_detach(ptids[i]); 74 pthread_detach(ctids[i]); 75 } 76 77 while(1) { 78 sleep(10); 79 } 80 81 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); 82 83 pthread_exit(NULL); 84 85 return 0; 86 }
条件变量

注意:解决线程同步的方法有互斥锁和读写锁,条件变量不是锁,条件变量不用来解决线程同步的问题。
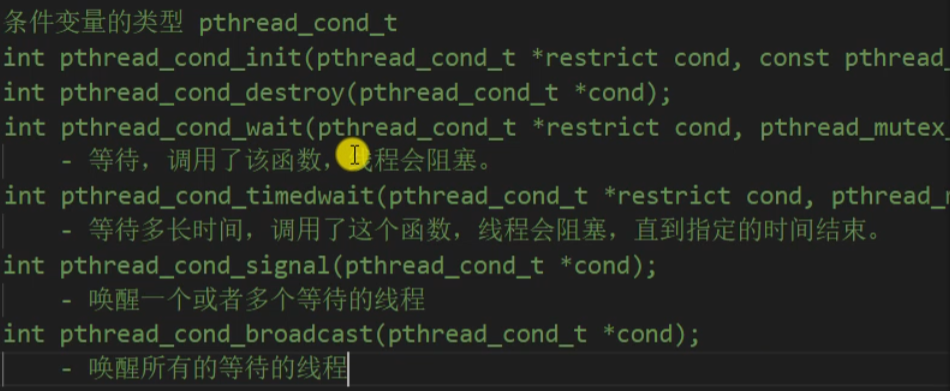
代码
1 /* 2 条件变量的类型 pthread_cond_t 3 int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr); 4 int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond); 5 int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex); 6 - 等待,调用了该函数,线程会阻塞。 7 int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime); 8 - 等待多长时间,调用了这个函数,线程会阻塞,直到指定的时间结束。 9 int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond); 10 - 唤醒一个或者多个等待的线程 11 int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond); 12 - 唤醒所有的等待的线程 13 */ 14 #include <stdio.h> 15 #include <pthread.h> 16 #include <stdlib.h> 17 #include <unistd.h> 18 19 // 创建一个互斥量 20 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 21 // 创建条件变量 22 pthread_cond_t cond; 23 24 struct Node{ 25 int num; 26 struct Node *next; 27 }; 28 29 // 头结点 30 struct Node * head = NULL; 31 32 void * producer(void * arg) { 33 34 // 不断的创建新的节点,添加到链表中 35 while(1) { 36 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 37 struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 38 newNode->next = head; 39 head = newNode; 40 newNode->num = rand() % 1000; 41 printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self()); 42 43 // 只要生产了一个,就通知消费者消费 44 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); 45 46 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 47 usleep(100); 48 } 49 50 return NULL; 51 } 52 53 void * customer(void * arg) { 54 55 while(1) { 56 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 57 // 保存头结点的指针 58 struct Node * tmp = head; 59 // 判断是否有数据 60 if(head != NULL) { 61 // 有数据 62 head = head->next; 63 printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self()); 64 free(tmp); 65 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 66 usleep(100); 67 } else { 68 // 没有数据,需要等待 69 // 当这个函数调用阻塞的时候,会对互斥锁进行解锁,当不阻塞的,继续向下执行,会重新加锁。 70 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); 71 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 72 } 73 } 74 return NULL; 75 } 76 77 int main() { 78 79 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 80 pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); 81 82 // 创建5个生产者线程,和5个消费者线程 83 pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5]; 84 85 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 86 pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL); 87 pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL); 88 } 89 90 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 91 pthread_detach(ptids[i]); 92 pthread_detach(ctids[i]); 93 } 94 95 while(1) { 96 sleep(10); 97 } 98 99 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); 100 pthread_cond_destroy(&cond); 101 102 pthread_exit(NULL); 103 104 return 0; 105 }
信号量(信号灯)
注意:单独使用信号量不能让线程安全,需要配合使用互斥锁才能保证线程的安全。
信号量的类型

代码
1 /* 2 信号量的类型 sem_t 3 int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value); 4 - 初始化信号量 5 - 参数: 6 - sem : 信号量变量的地址 7 - pshared : 0 用在线程间 ,非0 用在进程间 8 - value : 信号量中的值 9 10 int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem); 11 - 释放资源 12 13 int sem_wait(sem_t *sem); 14 - 对信号量加锁,调用一次对信号量的值-1,如果值为0,就阻塞 15 16 int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem); 17 18 int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout); 19 int sem_post(sem_t *sem); 20 - 对信号量解锁,调用一次对信号量的值+1 21 22 int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *sval); 23 24 sem_t psem; 25 sem_t csem; 26 init(psem, 0, 8); 27 init(csem, 0, 0); 28 29 producer() { 30 sem_wait(&psem); 31 sem_post(&csem) 32 } 33 34 customer() { 35 sem_wait(&csem); 36 sem_post(&psem) 37 } 38 39 */ 40 41 #include <stdio.h> 42 #include <pthread.h> 43 #include <stdlib.h> 44 #include <unistd.h> 45 #include <semaphore.h> 46 47 // 创建一个互斥量 48 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 49 // 创建两个信号量 50 sem_t psem; 51 sem_t csem; 52 53 struct Node{ 54 int num; 55 struct Node *next; 56 }; 57 58 // 头结点 59 struct Node * head = NULL; 60 61 void * producer(void * arg) { 62 63 // 不断的创建新的节点,添加到链表中 64 while(1) { 65 sem_wait(&psem); 66 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 67 struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 68 newNode->next = head; 69 head = newNode; 70 newNode->num = rand() % 1000; 71 printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self()); 72 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 73 sem_post(&csem); 74 } 75 76 return NULL; 77 } 78 79 void * customer(void * arg) { 80 81 while(1) { 82 sem_wait(&csem); 83 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 84 // 保存头结点的指针 85 struct Node * tmp = head; 86 head = head->next; 87 printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self()); 88 free(tmp); 89 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 90 sem_post(&psem); 91 92 } 93 return NULL; 94 } 95 96 int main() { 97 98 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); 99 sem_init(&psem, 0, 8); 100 sem_init(&csem, 0, 0); 101 102 // 创建5个生产者线程,和5个消费者线程 103 pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5]; 104 105 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 106 pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL); 107 pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL); 108 } 109 110 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 111 pthread_detach(ptids[i]); 112 pthread_detach(ctids[i]); 113 } 114 115 while(1) { 116 sleep(10); 117 } 118 119 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); 120 121 pthread_exit(NULL); 122 123 return 0; 124 }
雪儿言



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号