C#反射机制
最近项目上使用到到反射,找到以前保留的一份文档,作者是李志伟,找不到原出处,在此表示感谢。
在这分享一下。
1.反射机制基础类
(1)反射机制的功能与介绍
审查元数据并收集关于它的类型信息的能力称为反射。元数据(编译以后的最基本数据单元)就是一大堆的表,当编译程序集或者模块时,编译器会创建一个类定义表,一个字段定义表,和一个方法定义表等。System.reflection命名空间包含的几个类,允许用户解析这些元数据表的代码:
System.Reflection.Assembly:表示一个程序集。
System.Reflection.Module:在模块上执行反射。
System.Type:表示各种类型。
System.Reflection.MethodBase:提供有关方法和构造函数的信息。
System.Reflection.MethodInfo:发现方法的属性并提供对方法元数据的访问。
System.Reflection.MemberInfo:获取或访问有关成员属性。
System.Reflection.FieldInfo:发现字段属性并提供对字段元数据的访问权。
System.Reflection.PropertyInfo:发现或访问属性(Property)的属性(Attribute)。
System.Reflection.EventInfo:发现事件的属性并提供对事件元数据的访问权。
System.Reflection.ConstructorInfo:发现或访问类构造函数的属性。
(2)反射层次模型图
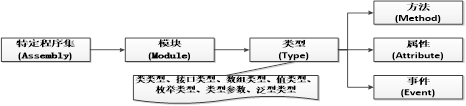
(3)Assembly类获取程序及信息
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Assembly assem = Assembly.Load("mscorlib");//加载系统程序集
PrintInfo(assem);//输出程序集相关信息
assem = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"F:\System.Data.SQLite.dll");//或使用LoadFile()方法
PrintInfo(assem);//输出程序集相关信息
assem = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();//获取当前执行代码的程序集
PrintInfo(assem);//输出程序集相关信息
Console.Read();
}
//输出程序集相关信息
static void PrintInfo(Assembly assem)
{
Console.WriteLine("程序集全名:" + assem.FullName);
Console.WriteLine("程序集的版本:" + assem.GetName().Version);
Console.WriteLine("程序集初始位置:" + assem.CodeBase);
Console.WriteLine("程序集位置:" + assem.Location);
Console.WriteLine("程序集入口:" + assem.EntryPoint);
Type[] types = assem.GetTypes();//得到该程序集里所有的类型
Console.WriteLine("程序集下包含的类型数:" + types.Length);
//foreach (var item in types)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("类:" + item.Name);//输出类型名
//}
Console.WriteLine("============================\n");
}
}
(4)Module类获取程序集模块信息
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load("mscorlib");//加载程序集
Module module = assembly.GetModule("CommonLanguageRuntimeLibrary");//得到指定模块
Console.WriteLine("模块名:"+module.Name);
Type[] types = module.FindTypes(Module.FilterTypeName, "Assembly*");
foreach (var item in types)
{
Console.WriteLine("类名:" + item.Name);//输出类型名
}
Console.Read();
}
}
(5)Type类获取类型的信息
class Myclass
{
private int Id;
public string Name;
public void Method(int i) { }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type type = typeof(Myclass);
Console.WriteLine("类型名:" + type.Name);
Console.WriteLine("类全名:" + type.FullName);
Console.WriteLine("命名空间名:" + type.Namespace);
Console.WriteLine("程序集名:" + type.Assembly);
Console.WriteLine("模块名:" + type.Module);
Console.WriteLine("基类名:" + type.BaseType);
Console.WriteLine("是否类:" + type.IsClass);
Console.WriteLine("类的公共成员:");
MemberInfo[] memberInfos = type.GetMembers();//得到所有公共成员
foreach (var item in memberInfos)
{
Console.WriteLine("成员类型:" + item.MemberType + "\t成员:" + item);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
(6)利用反射调用方法
class Myclass
{
public Myclass()
{
Console.WriteLine("创建Myclass对象!");
}
public void Method(int i)
{
Console.WriteLine("输出值:" + i);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type t = typeof(Myclass);//得到类型
object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);//创建类型的实例
Console.WriteLine("已创建Myclass对象:" + o);
MethodInfo method = t.GetMethod("Method");//获得实例的方法
method.Invoke(o, new object[] { 100 });//调用方法
Console.Read();
}
}
2.特性(Attribute)
(1)Attribute介绍
Attributes是一种新的描述信息,我们既可以使用attributes来定义设计信息(例如:帮助文件,文档的URL),还可以用attributes定义运行时信息(例如,使XML中的元素与类的成员字段关联起来)。我们也可以用attributes来创建一个“自描述”的组件。
(2)示例
class Program
{
[Obsolete("已过时的方法!", true)]//把true改成false就可以编译通过
static void OldMethod() { }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
OldMethod();//调用过时的方法
Console.Read();
}
}
在该实例中我们用到了“Obsolete”Attribute,它标记了一个不该再被使用的语言元素(这里的元素为方法),该属性的第一个参数是string类型,它解释为什么该元素被荒弃,以及我们该使用什么元素来代替它。实际中,我们可以书写任何其它文本来代替这段文本。第二个参数是告诉编译器把依然使用这被标识的元素视为一种错误,这就意味着编译器会因此而产生一个警告。
3.自定义特性
(1)自定义特性说明
自定义的Attribute类都派生于System.Attribute类。
(2)示例
//自定义的Attribute类命名为XXXAttribute
class HelpAttribute : Attribute
{
private String description;
public HelpAttribute(String Descrition_in)
{
this.description = Descrition_in;
}
public String Description
{
get { return description; }
}
}
class Program
{
[Help("自定义特性")]//使用是不需要写“Attribute”后缀
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Read();
}
}
注意:按惯例我们是用”Attribute“作为attribute类名的后缀,然而,当我们当我们把attribute绑定到某语言元素时,是不包含“Attribute“后缀的。编译器首先在System.Attribute 的继承类中查找该attribute,如果没有找到,编译器会把“Attribute“追加到该attribute的名字后面,然后查找它。
(3)AttributeUsage类的使用
AttributeUsage类是另一预定义类(Attribute类本身用System.AttributeUsage类来标记),它将帮助我们控制我们自定义Attribute类的用法,这就是,我们能为自定义的Attribute类定义Attributes属性。它描述了一个自定义Attribute类能被怎样使用。
AttributeUsage提供三个属性,我们能将它们放置到我们的自定义Attribute类上。
AllowMultiple属性:该值指示能否为一个程序元素指定多个指示属性实例。
Inherited属性:该值指示指示的属性能否由派生类和重写成员继承。
ValidOn属性:获取一组值,这组值标识指示的属性可应用到的程序元素。此属性是AttributeTargets类型的枚举,可取如下值:
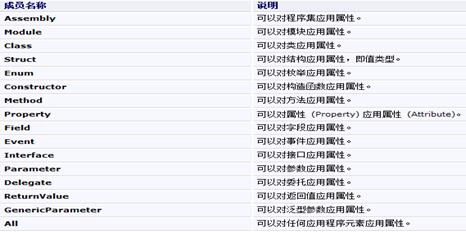
使用示例:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = false)]
class HelpAttribute : Attribute
{
private String description;
public HelpAttribute(String Descrition_in)
{
this.description = Descrition_in;
}
public String Description
{
get { return description; }
}
}
class Program
{
[Help("自定义特性")]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Read();
}
}
(4)可选参数与命名参数
可选参数是Attribute类构造函数的参数。它是强制的,必须在每次在Attribute绑定至某语言元素时提供一个值。而另一方面,命名参数倒是真正的可选参数,不是在Attribute构造函数的参数。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = false)]
class HelpAttribute : Attribute
{
private string _description;//可选参数
public string _name;//命名参数
public HelpAttribute(string description)
{
Console.WriteLine("HelpAttribute特性被创建!");
this._description = description;
}
public string Description
{
get { return _description; }
}
public string Name
{
get { return _name; }
set//命名参数,必须要有set方法
{
Console.WriteLine("属性:" + value);
_name = value;
}
}
}
class Program
{
[Help("自定义特性", Name = "李志伟")]//同时使用可选参数与命名参数
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Read();
}
}
(5)Attributes标识符
假设,我们想把HelpAttribute绑定到整个assembly(程序集)。第一个问题是我们要把HelpAttribute放在哪儿才能让编译器确定该Attribute是绑定至整个assembly呢?考虑另一种情况,我们想把Attribute绑定至一个方法的返回类型上,怎样才能让编译器确定我们是把Attribute绑定至方法的返回类型上,而不是整个方法呢?
为了解决诸如此类的含糊问题,我们使用Attribute标识符,有了它的帮助,我们就可以确切地申明我们把attribute 绑定至哪一个语言元素。例如:[assembly: Help("类上的自定义特性", Name = "lizhiwei")]这个在HelpAttribute前的assembly标识符确切地告诉编译器,该Attribute被绑定至整个assembly(程序集)。可能的标识符有:assembly、module、type、method、property、event、field、param、return。
(6)通过反射获取Attributes
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = false)]
class HelpAttribute : Attribute
{
private string _description;//可选参数
private string _name;//命名参数
public HelpAttribute(string description)
{
Console.WriteLine("====HelpAttribute特性被创建!====");
this._description = description;
}
public string Description
{
get { return _description; }
}
public string Name
{
get { return _name; }
set//命名参数,必须要有set方法
{
Console.WriteLine("====属性:" + value + "====");
_name = value;
}
}
}
//使用了自定义特性的测试类
[Help("类上的自定义特性", Name = "lizhiwei")]
class TestClass
{
[Help("方法上的自定义特性", Name = "李志伟1")]
[Help("方法上的自定义特性", Name = "李志伟2")]
public void TestMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("===========测试方法===========");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type t = typeof(TestClass);
//获取类上的自定义特性
object[] obis = t.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(HelpAttribute), false);
HelpAttribute attribute = obis[0] as HelpAttribute;
Console.WriteLine("\n" + attribute.Description + "--" + attribute.Name + "\n");
//获取方法上的自定义特性
MethodInfo method = t.GetMethod("TestMethod");
object[] methods = method.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(HelpAttribute), false);
foreach (HelpAttribute help in methods)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n" + help.Description + "--" + help.Name + "\n");
}
Console.Read();
}
}


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步