js数据结构与算法--双向链表的实现
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据节点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,双向链表中的任意一个节点开始,都可以很方便的访问它的前驱节点和后继节点。
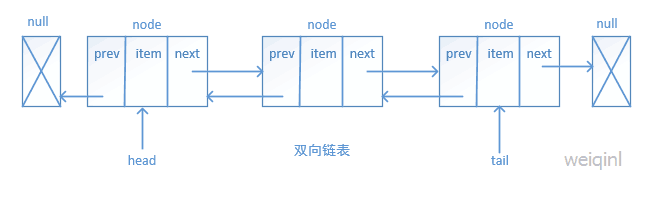
双向链表的实现
linkednode.js ,里面使用了类的继承extends,使用了super函数。
/**
* 链表节点,链表中的项,链表中的节点
*/
export class Node {
constructor(element, next = null) {
this.element = element // 链表中节点的值
this.next = next // 指向列表中下一个节点项的指针
}
}
export class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element, next = null, prev = null) {
super(element, next)
this.prev = prev
}
}
doublyLinkedList.js 双向链表类,实现了各个功能,功能说明,都在代码注释中
import {
DoublyNode
} from './linkednode'
/**
* 双向链表类
*/
export class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
/**
* 链表长度
*/
this.length = 0
/**
* 头指针
*/
this.head = null
/**
* 尾指针
*/
this.tail = null
}
/**
* 在链表末尾添加元素
* @param {*} element 需要插入的元素
*/
append(element) {
let node = new DoublyNode(element)
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
this.tail.next = node
node.prev = this.tail
this.tail = node
}
this.length++
return true
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入元素
* @param {Int32Array} position 指定位子
* @param {*} element 需要插入的元素
*/
insert(position, element) {
// 检查越界值
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
// 实例化一个双向链表的节点
let node = new DoublyNode(element)
// 赋初始值
let current = this.head
let previous
let index = 0 // 位置索引
if (position === 0) { // 在第一个位子添加
if (!this.head) { // 链表无数据的时候,将head和tail都指向新元素
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else { // 链表有数据的时候, head node current
node.next = current
current.prev = node
this.head = node
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 添加到最后一项 current node
current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
} else { // 在列表中间位置添加
// 新链表的节点原型是: previous <---> node <---> current
while (index++ < position) { // 位置索引递增到指定点之前,找出前后两个节点
previous = current // 当前节点设置为新链表中要插入的节点的前一个元素。
current = current.next // 当前节点之后的元素设置为新链表中要插入的节点的当前元素
}
node.next = current
previous.next = node
current.prev = node
node.prev = previous
}
this.length++ // 更新列表的长度
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入元素
* 在链表头,在链表尾,在链表前半段,在链表后半段
* @param {Int32Array} position 指定位置
* @param {*} element 需要插入的元素
*/
insert_up(position, element) {
let node = new DoublyNode(element)
let previous
let current = this.head
if (position > -1 && position <= this.length) {
if (position === 0) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
node.next = current
current.prev = node
this.head = node
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
} else if (position < this.length / 2) { // 目标在链表前半段
let index = 0
// 0 1 2 [] 3 4 5
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = node
node.next = current
node.prev = previous
current.prev = node
} else { // 目标在链表的后半段
// 0 1 2 3 4 | 5 6 [] 7 8 9
let index = this.length
current = this.tail
while (index-- > position) {
previous = current.prev
current = current
}
previous.next = node
node.next = current
node.prev = previous
current.prev = node
}
this.length++
return true
} else {
// 如果超出范围,直接添加到链表末尾
let current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
this.length++
return true
}
}
/**
* 从任意位置移除元素,返回移除的元素
* 从头部,从尾部,从链表的前半段,从链表的后半段
* @param {*} position 位置索引
*/
removeAt(position) {
let current = this.head // 当前项
let previous // 前一项
let index = 0 // 索引
// 越界检查
if (position > -1 && position < this.length) {
if (position === 0) { // 第一项
this.head = current.next
// 如果是最后一项要删除,将tail置为null,此时head也为null
// 如果非最后一项,则将this.head.prev置为null
if (this.length === 1) { // 只有一项的情况,更新tail
this.tail = null
} else {
this.head.prev = null // 将首项的prev置空 或者 current.next.prev = null
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) { // 最后一项
current = this.tail
previous = current.prev
this.tail = previous
this.tail.next = null
} else if (position <= this.length / 2) { // 索引在链表前半段,分开计算,提升性能
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 将previous与current下一项连起来---跳过current
previous.next = current.next
current.next.prev = previous
} else { // 索引在链表后半段
index = this.length - 1
current = this.tail
while (index-- > position) {
previous = current
current = current.prev
}
// 将previous与current的上一项连起来--跳过current
previous.prev = current.prev
current.prev.next = previous
}
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
// 超出链表安全长度,链表有数据,则删除末尾元素
if (typeof position === 'number' && this.length > 0) {
let current = this.tail
this.tail = current.prev
this.tail.next = null
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
return null
}
}
}
/**
* 从列表中移除一项
* 先找出元素的索引项,再根据索引移除元素
* @param {*} element 列表中的元素
*/
remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element)
return this.removeAt(index)
}
/**
* 返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
* @param {*} element 元素
*/
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0 // 计算位置数
while (current) {
if (element === current.element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
/**
* 判断是否为空链表
* 空链表返回true,非空(链表长度大于0)返回false
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0
}
/**
* 返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似
*/
size() {
return this.length
}
/**
* 获取链表的表头节点
*/
getHead() {
return this.head
}
/**
* 获取链表的尾节点
*/
getTail() {
return this.tail
}
/**
* 输出元素的值
*/
toString() {
let current = this.head
let string = 'null'
while (current) {
string += "<--->" + current.element + (current.next ? '' : '<--->null')
current = current.next
}
return string
}
}
思考
双向链表与单项链表的比较:
-
双向链表可以双向遍历。从头到尾,或者从尾到头
-
双向链表可以访问一个特定节点的下一个或者前一个元素,而单链表只能访问下一个元素。
-
双向链表内存占用比单链表的多
链表还有一个双向循环链表,在需要用到的时候,考虑它们各自的不同,选择合适的链表来操作。
感谢您的认真阅读,更多内容请查看:
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/weiqinl
个人主页http://weiqinl.com
github: weiqinl
简书:weiqinl
您的留言讨论是对博主最大的支持!
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/weiqinl
个人主页http://weiqinl.com
github: weiqinl
简书:weiqinl
您的留言讨论是对博主最大的支持!
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。


