进程的前后执行和并发执行
1.信号发送kill
1)kill:内部命令,可用来向进程发送控制信号,以实现对进程的管理,每个信号对应一个数字,信号名称以SIG开头,不分大小写。
2)显示当前系统可用信号:
- kill -l
- trap -l
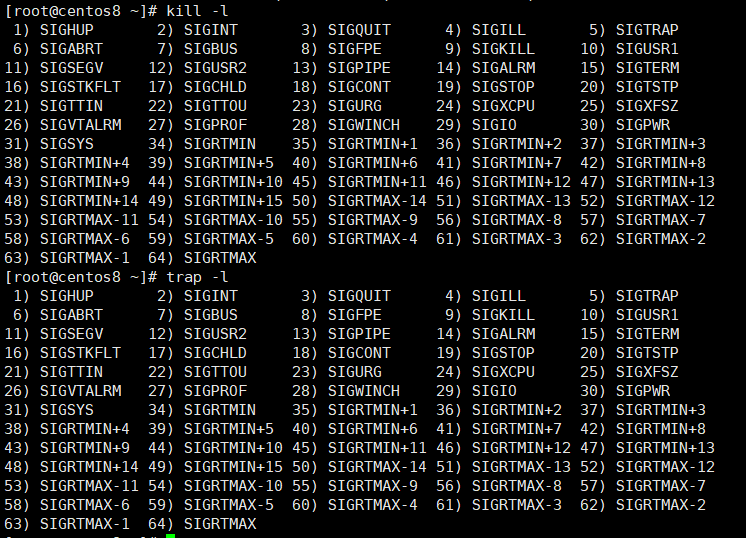
3)常用信号
范例:发送信号重读配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | [root@centos8 ~]# yum -y install httpd[root@centos8 ~]# systemctl start httpd[root@centos8 ~]# echo '<h1>weilian<h1>' > /var/www/html/index.html[root@centos8 ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html <h1>weilian<h1>[root@centos8 ~]# ss -ntlState Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 5 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:* LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:631 [::]:* LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6010 [::]:* [root@centos8 ~]# mkdir /data/html/[root@centos8 ~]# echo '<h1>N64<h1>' > /data/html/index.html[root@centos8 ~]# cat /data/html/index.html<h1>N64<h1>[root@centos8 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf [root@centos8 ~]# ps aux | grep httpd[root@centos8 ~]# kill -1 3843[root@centos8 ~]# ps aux | grep http |
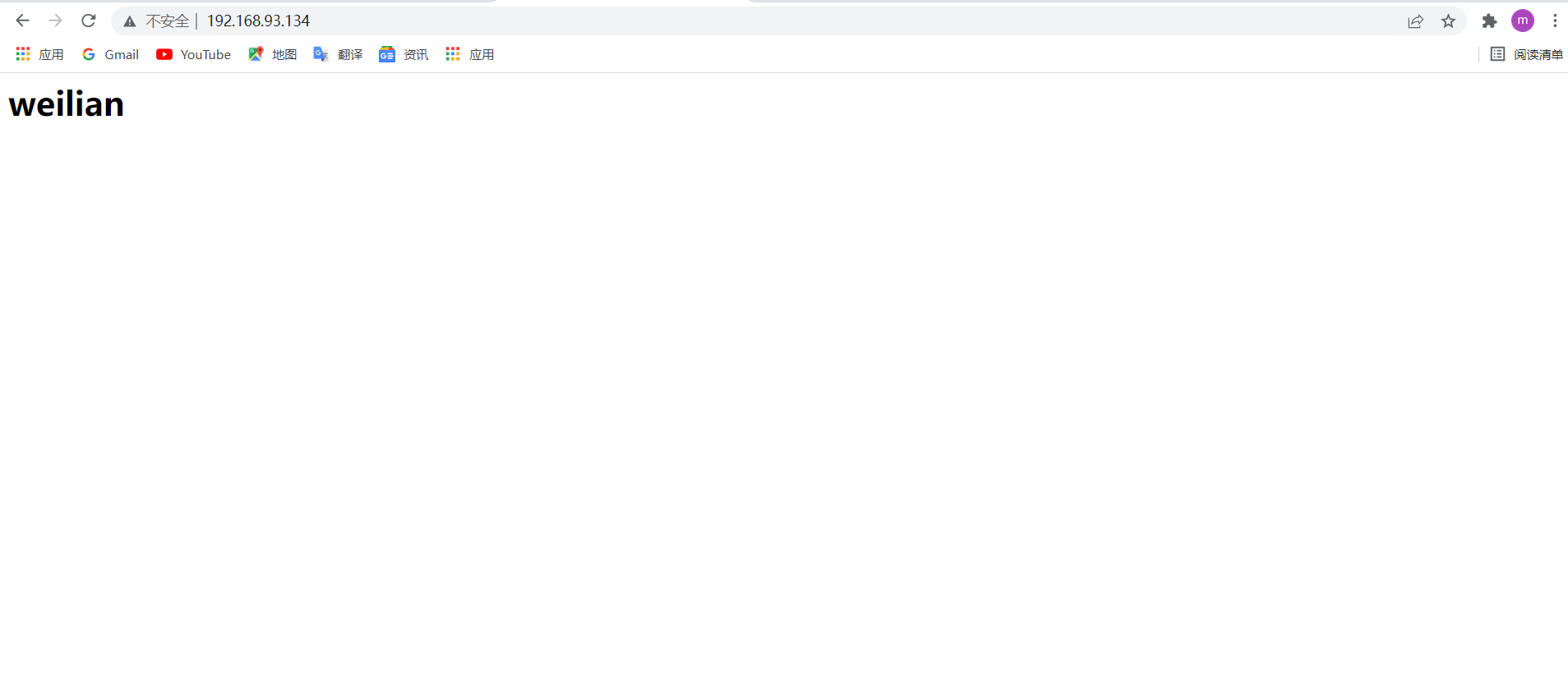

4)向进程发送信号
按PID:
kill pid
例:
kill -1 pid
按名称:killall来自于psmisc包
killall [-SINGNAL] comm...
例:
[root@centos8 ~]# pidof bash 3350 2945 868 [root@centos8 ~]# killall bash [root@centos8 ~]# pidof bash 3350 868
按模式:pkill
例:
[root@centos8 ~]# su - wang [wang@centos8 ~]$ tail -f /etc/passwd [root@centos8 ~]# pgrep -u wang -l 34444 bash 34484 tail [root@centos8 ~]# pkill -u wang [root@centos8 ~]# pgrep -u wang -l 34444 bash
5)
简单来说,0信号就是检查一个进程是否正常
例:
[root@centos8 ~]# ping 192.168.93.133 [root@centos8 ~]# kill -0 35053 [root@centos8 ~]# echo $? 0
如果为0,表示正常,如果不为零,表示不正常
以后再生产中,会用其进行健康性检查,当然,此方式有局限性,当进程处于停止或僵尸状态,此方式仍认为是健康的
2.作业管理
1)前台作业:通过终端启动,且启动后一直占据终端后台作业,可通过终端启动,但启动后进入后台运行(释放终端)
例:
1 2 | [root@centos8 ~]# ping 192.168.93.133 &[root@centos8 ~]# killall -2 ping |
范例:将后台停止进程变为运行用bg或kill -18
[root@centos8 ~]# ping 192.168.93.133 按ctrl+z将其置为后台停止,只对前台起作用 [root@centos8 ~]# jobs #查看作业编号 [root@centos8 ~]# bg 1 #将其恢复为后台运行/kill -18 %1
范例:将后台运行变为后台用kill -19
[root@centos8 ~]# ping 192.168.93.133 & [root@centos8 ~]# jobs [root@centos8 ~]# kill -19 %2
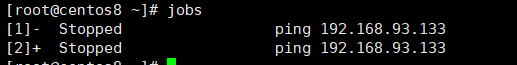
范例:将后台恢复为前台fg
[root@centos8 ~]# fg 1 [root@centos8 ~]# fg 2 [root@centos8 ~]# jobs [root@centos8 ~]#
2)
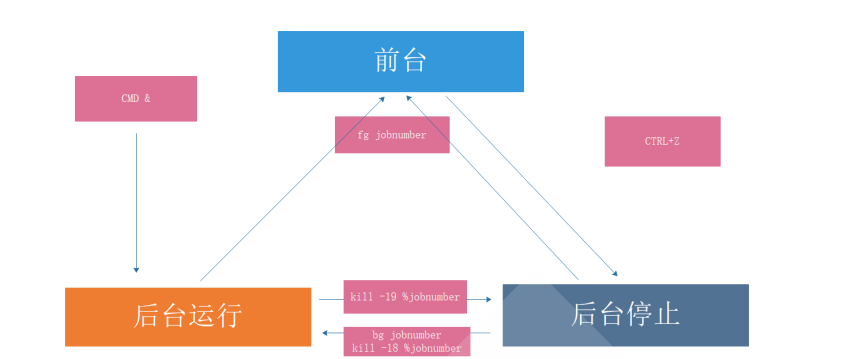
3.并行
利用后台执行,实现并行功能,即同时运行多个进程,提高效率
1)法一:
cat all.sh f1.sh& f2.sh& f3.sh&
2)法二:
(f1.sh&);(f2.sh&);(f3.sh&)
3)法三:
f1.sh&f2.sh&f3.sh&
后台执行,终端一关就停了
4.断开终端,使程序持续运行
1)screen
[root@centos8 ~]# yum -y install screen [root@centos8 ~]# screen [root@centos8 ~]# ping 192.168.93.133 #关闭终端 [root@centos8 ~]# ps aux | grep ping root 2570 0.0 0.1 388700 1348 tty2 Sl+ 20:21 0:00 /usr/libexec/gsd-housekeeping root 36388 0.0 0.2 32460 2300 pts/2 S+ 22:40 0:00 ping 192.168.93.133 root 36400 0.0 0.1 12136 1104 pts/0 R+ 22:41 0:00 grep --color=auto ping [root@centos8 ~]# kill -9 36388 [root@centos8 ~]# ps aux | grep ping root 2570 0.0 0.1 388700 1348 tty2 Sl+ 20:21 0:00 /usr/libexec/gsd-housekeeping root 36413 0.0 0.1 12136 1140 pts/0 R+ 22:41 0:00 grep --color=auto ping [root@centos8 ~]#
2)nohub
例:
[root@centos8 ~]# nohub ping 192.168.93.133 #他会把执行结果全都放在一个名叫 nohub.out的文件里。所以我们进行修改 [root@centos8 ~]#nohup ping 192.168.93.133 &> /dev/null & [root@centos8 ~]#ps aux | grep ping #关闭终端 [root@centos8 ~]#ps aux | grep ping [root@centos8 ~]#killall ping
范例:并行执行测试
[root@centos8 ~]# vim scan_host
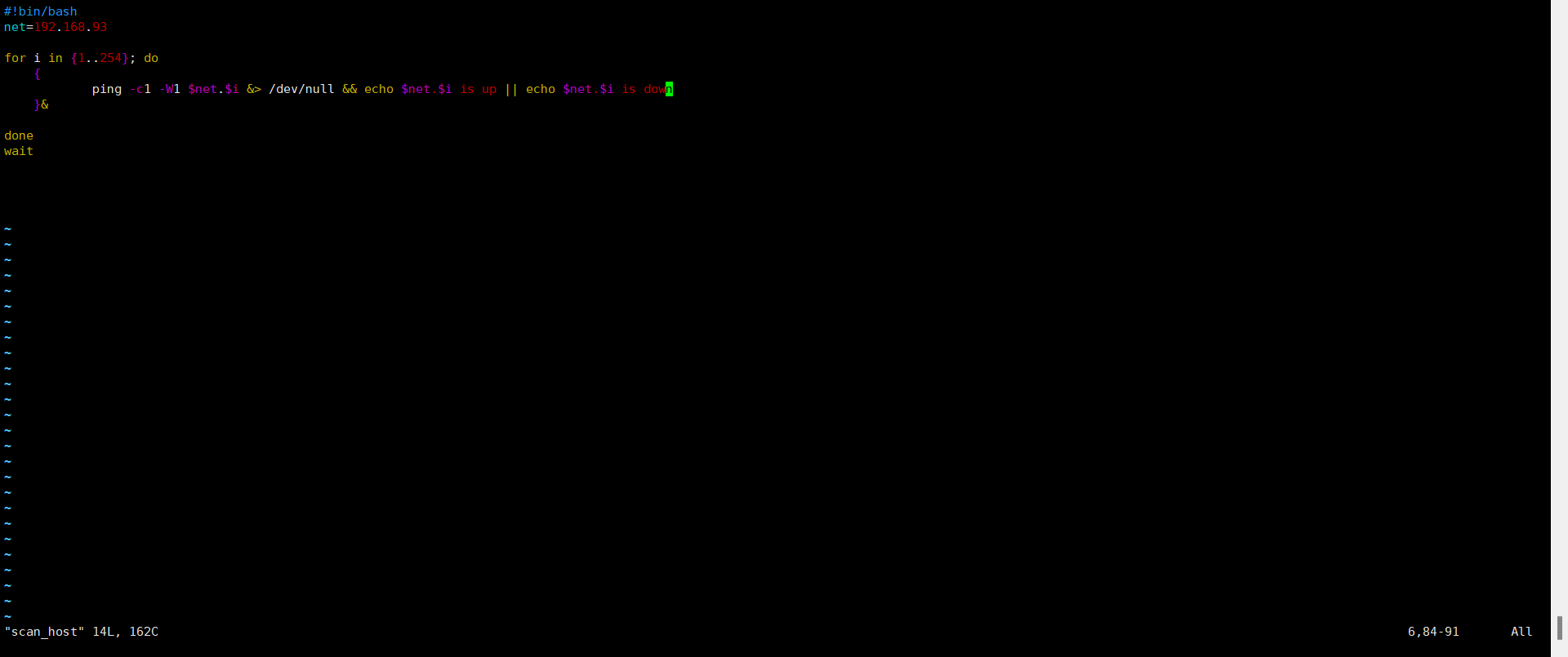
记录于2022-3-16-23:14 weilan





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话