文件查找locate和find
1.文件查找
在文件系统上查找符合条件的文件
文件查找:
非实时查找(数据库查找):locate
实时查找:find
2.locate
locate 查询系统上预建的文件索引数据库 /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db
索引的构建是在系统较为空闲时自动进行(周期性任务),执行updatedb可以更新数据库
索引构建过程需要遍历整个根文件系统,很消耗资源
locate和updatedb命令来自于mlocate包
工作特点: 查找速度快
模糊查找
非实时查找
搜索的是文件的全路径,不仅仅是文件名
可能只搜索用户具备读取和执行权限的目录
格式:
locate [OPTION]... [PATTERN]...
常用选项:
-i 不区分大小写的搜索 -n N 只列举前N个匹配项目 -r 使用基本正则表达式
范例:
#搜索名称或路径中包含“conf”的文件 locate conf #使用Regex来搜索以“.conf”结尾的文件 locate -r '\.conf$'
范例: locatedb创建数据库
[root@centos8 ~]#dnf -y install mlocate [root@centos8 ~]#locate conf locate: can not stat () `/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db': No such file or directory [root@centos8 ~]#updatedb [root@centos8 ~]#ll /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db -rw-r----- 1 root slocate 1041065 Jun 11 20:08 /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db [root@centos8 ~]#locate -n 3 conf /boot/config-4.18.0-147.el8.x86_64 /boot/grub2/i386-pc/configfile.mod /boot/loader/entries/5b85fc7444b240a992c42ce2a9f65db5-0-rescue.conf
范例: 文件新创建和删除,无法马上更新locate数据库
[root@centos8 ~]#touch test.log [root@centos8 ~]#locate test.log locate: can not stat () `/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db': No such file or directory [root@centos8 ~]#updatedb [root@centos8 ~]#locate test.log /root/test.log [root@centos8 ~]#touch test2.log [root@centos8 ~]#locate test2.log [root@centos8 ~]#updatedb [root@centos8 ~]#locate test2.log /root/test2.log [root@centos8 ~]#rm -f test2.log [root@centos8 ~]#locate test2.log /root/test2.log
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#locate -n 10 -ir '\.CONF$' /boot/loader/entries/5b85fc7444b240a992c42ce2a9f65db5-0-rescue.conf /boot/loader/entries/5b85fc7444b240a992c42ce2a9f65db5-4.18.0-147.el8.x86_64.conf /etc/autofs.conf /etc/autofs_ldap_auth.conf /etc/dracut.conf /etc/fuse.conf /etc/host.conf /etc/idmapd.conf /etc/kdump.conf /etc/krb5.conf
3.find
find 是实时查找工具,通过遍历指定路径完成文件查找
工作特点:
查找速度略慢
精确查找
实时查找
查找条件丰富
可能只搜索用户具备读取和执行权限的目录
格式:
find [OPTION]... [查找路径] [查找条件] [处理动作]
查找路径:指定具体目标路径;默认为当前目录
查找条件:指定的查找标准,可以文件名、大小、类型、权限等标准进行;默认为找出指定路径下的所有文件
处理动作:对符合条件的文件做操作,默认输出至屏幕
4.find指定搜索目录层级
-maxdepth level 最大搜索目录深度,指定目录下的文件为第1级
-mindepth level 最小搜索目录深度
范例:
find /etc -maxdepth 2 -mindepth 2
5.find对每个目录先处理目录内的文件,再处理目录本身
-depth -d #warning: the -d option is deprecated; please use -depth instead, because the latter is a POSIX-compliant feature
范例:
[root@centos8 data]#tree /data/test /data/test ├── f1.txt ├── f2.txt └── test2 └── test3 ├── f3.txt └── f4.txt 4 directories, 2 files [root@centos8 data]#find /data/test /data/test /data/test/f1.txt /data/test/f2.txt /data/test/test2 /data/test/test2/test3 /data/test/test2/test3/f3.txt /data/test/test2/test3/f4.txt [root@centos8 data]#find /data/test -depth /data/test/f1.txt /data/test/f2.txt /data/test/test2/test3/f3.txt /data/test/test2/test3/f4.txt /data/test/test2/test3 /data/test/test2 /data/test
这个选项很快就淘汰了
6.find根据文件名和inode查找
-name "文件名称" #支持使用glob,如:*, ?, [], [^],通配符要加双引号引起来
-iname "文件名称" #不区分字母大小写
-inum n #按inode号查找
-samefile name #相同inode号的文件
-links n #链接数为n的文件
-regex “PATTERN” #以PATTERN匹配整个文件路径,而非文件名称
范例:
find -name snow.png find -iname snow.png find / -name ".txt" find /var –name "log*" [root@centos8 data]#find -regex ".*\.txt$" ./scripts/b.txt ./f1.txt
7.find根据属主、属组查找
-user USERNAME #查找属主为指定用户(UID)的文件 -group GRPNAME #查找属组为指定组(GID)的文件 -uid UserID #查找属主为指定的UID号的文件 -gid GroupID #查找属组为指定的GID号的文件 -nouser #查找没有属主的文件 -nogroup #查找没有属组的文件
8.find根据文件类型查找
-type TYPE
TYPE可以是以下形式:
f: 普通文件
d: 目录文件
l: 符号链接文件
s:套接字文件
b: 块设备文件
c: 字符设备文件
p: 管道文件
范例:
#查看/home的目录 find /home –type d -ls
9.find空文件或目录
-empty
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#find /app -type d -empty
10.find组合条件
与:-a ,默认多个条件是与关系 或:-o 非:-not !
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#find /etc/ -type d -o -type l |wc -l 307 [root@centos8 ~]#find /etc/ -type d -o -type l -ls |wc -l 101 [root@centos8 ~]#find /etc/ \( -type d -o -type l \) -ls |wc -l 307
下图助于理解
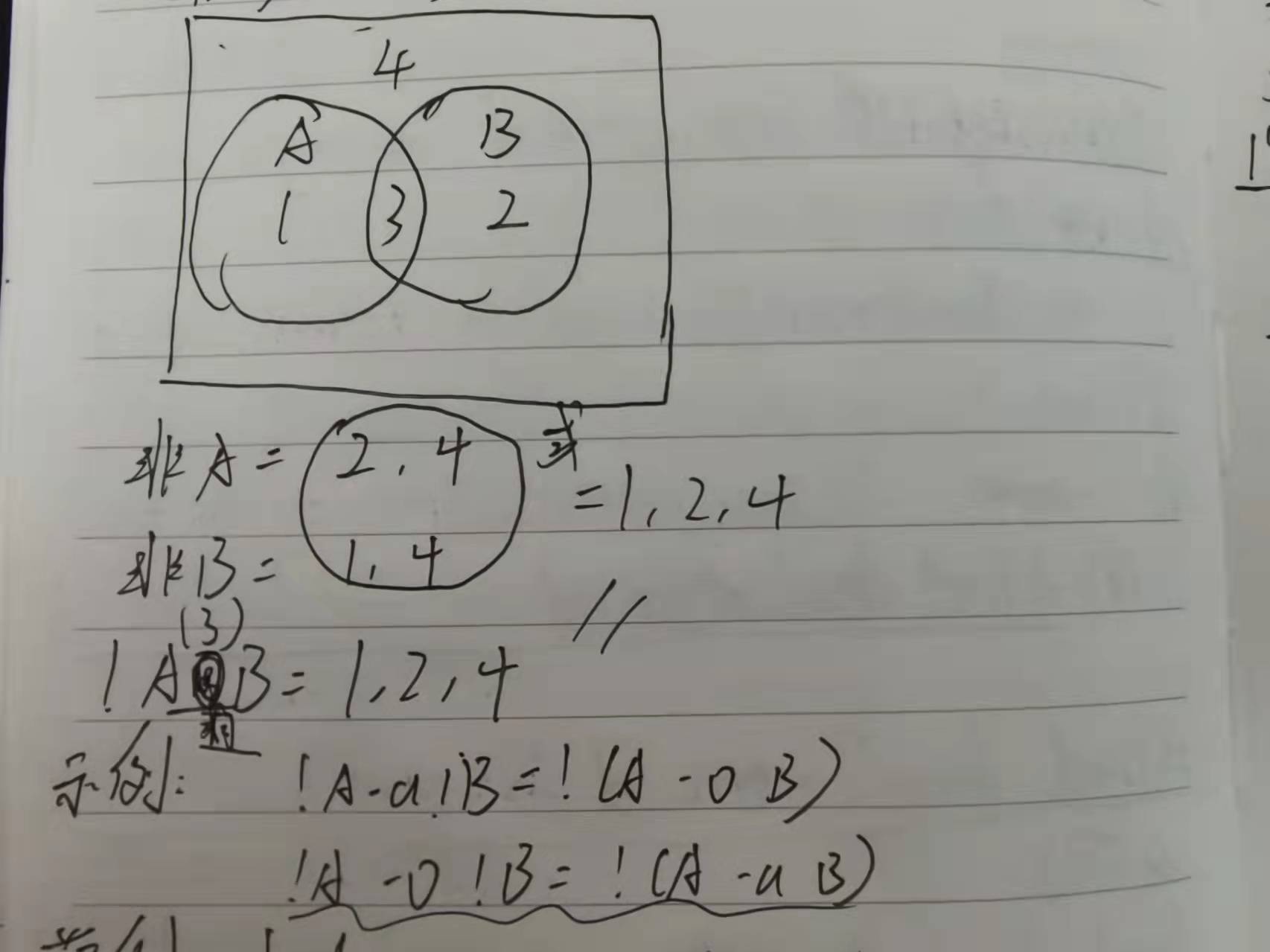
德·摩根定律:
♥(非 A) 或 (非 B) = 非(A 且 B)
♥(非 A) 且 (非 B) = 非(A 或 B)
示例:
!A -a !B = !(A -o B)
!A -o !B = !(A -a B)
范例:
ind -user joe -group joe find -user joe -not -group joe find -user joe -o -user jane find -not \( -user joe -o -user jane \) find / -user joe -o -uid 500
范例:
[root@centos8 data]#find ! \( -type d -a -empty \)| wc -l 56 [root@centos8 data]#find ! -type d -o ! -empty |wc -l 56 [mage@centos8 data]$find ! -user wang ! -user mage . ./script40 ./script40/backup ./script40/backup/args.sh ./script40/backup/chook_rabbit.sh ./script40/backup/disk_check.sh ./script40/backup/ping.sh ./script40/backup/systeminfo.sh ./script40/backup/test_read.sh ./script40/backup/test.sh ./script40/if_bmi.sh ./script40/case_yesorno.sh ./script40/case_yesorno2.sh ./script40/b.txt ./f1.txt ./test ./test/f1.txt.link ./f1.txtlink ./test2
[root@centos8 home]#ll total 0 drwx------. 2 mage mage 62 Jan 16 17:53 mage drwx------. 2 wang wang 62 Jan 16 10:43 wang drwx------ 2 xiaoming xiaoming 62 Apr 6 09:51 xiaoming [root@centos8 home]#find ! \( -user wang -o -user mage \) . ./xiaoming ./xiaoming/.bash_logout ./xiaoming/.bash_profile ./xiaoming/.bashrc [root@centos8 home]#find ! -user wang -a ! -user mage . ./xiaoming ./xiaoming/.bash_logout ./xiaoming/.bash_profile ./xiaoming/.bashrc
#找出/tmp目录下,属主不是root,且文件名不以f开头的文件 find /tmp \( -not -user root -a -not -name 'f*' \) -ls find /tmp -not \( -user root -o -name 'f*' \) –ls
11.find排除目录
范例:
#查找/etc/下,除/etc/security目录的其它所有.conf后缀的文件
find /etc -path '/etc/security' -a -prune -o -name "*.conf"
#查找/etc/下,除/etc/security和/etc/systemd,/etc/dbus-1三个目录的所有.conf后缀的文件
find /etc \( -path "/etc/security" -o -path "/etc/systemd" -o -path "/etc/dbus1" \) -a -prune -o -name "*.conf"
#排除/proc和/sys目录
find / \( -path "/sys" -o -path "/proc" \) -a -prune -o -type f -a -mmin -1
12.find根据文件大小来查找
size [+|-]#UNIT #常用单位:k, M, G,c(byte),注意大小写敏感 #UNIT: #表示(#-1, #],如:6k 表示(5k,6k] -#UNIT #表示[0,#-1],如:-6k 表示[0,5k] +#UNIT #表示(#,∞),如:+6k 表示(6k,∞)
范例:
find / -size +10G [root@centos8 ~]#find / -size +10G /proc/kcore find: ‘/proc/25229/task/25229/fd/6’: No such file or directory find: ‘/proc/25229/task/25229/fdinfo/6’: No such file or directory find: ‘/proc/25229/fd/5’: No such file or directory find: ‘/proc/25229/fdinfo/5’: No such file or directory [root@centos8 ~]#ll -h /proc/kcore -r-------- 1 root root 128T Dec 14 2020 /proc/kcore [root@centos8 ~]#du -sh /proc/kcore 0 /proc/kcore
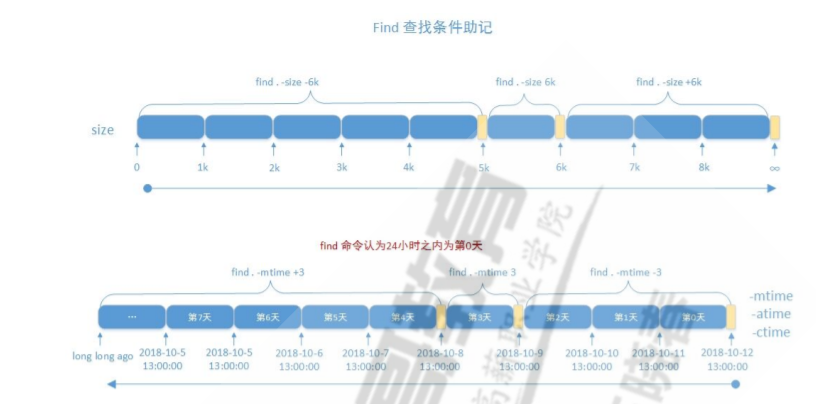
13.find根据时间戳
#以“天”为单位 -atime [+|-]# # #表示[#,#+1) +# #表示[#+1,∞] -# #表示[0,#) -mtime -ctime #以“分钟”为单位 -amin -mmin -cmin
14.find根据权限查找
-perm [/|-]MODE MODE #精确权限匹配 /MODE #任何一类(u,g,o)对象的权限中只要能一位匹配即可,或关系,+ 从CentOS 7开始淘汰 -MODE #每一类对象都必须同时拥有指定权限,与关系 0 表示不关注
说明:
find -perm 755 会匹配权限模式恰好是755的文件
只要当任意人有写权限时,find -perm /222就会匹配
只有当每个人都有写权限时,find -perm -222才会匹配
只有当其它人(other)有写权限时,find -perm -002才会匹配
15.find处理动作
-print:默认的处理动作,显示至屏幕 -ls:类似于对查找到的文件执行"ls -dils"命令格式输出 -fls file:查找到的所有文件的长格式信息保存至指定文件中,相当于 -ls > file -delete:删除查找到的文件,慎用! -ok COMMAND {} \; 对查找到的每个文件执行由COMMAND指定的命令,对于每个文件执行命令之前,都会 交互式要求用户确认 -exec COMMAND {} \; 对查找到的每个文件执行由COMMAND指定的命令 {}: 用于引用查找到的文件名称自身
范例:
#备份配置文件,添加.orig这个扩展名 find -name ".conf" -exec cp {} {}.orig \; #提示删除存在时间超过3天以上的joe的临时文件 find /tmp -ctime +3 -user joe -ok rm {} \; #在主目录中寻找可被其它用户写入的文件 find ~ -perm -002 -exec chmod o-w {} \; #查找/data下的权限为644,后缀为sh的普通文件,增加执行权限 find /data –type f -perm 644 -name "*.sh" –exec chmod 755 {} \;
2022-2-2 23:30



