学习Python必刷的100道经典练习题,没练等于白学
习题一:
打印两数之和:

1 num1 = 45 2 num2 = 2 3 4 sum = num1 + num2 5 6 print(f"{num1}+{num2}={sum}"
习题二:
数字的阶乘:比如6的阶乘:6x5x4x3x2x1,3的阶乘3x2x1

1 def jiecheng(number): 2 result = 1 3 4 while number>1: 5 result *= number 6 number -= 1 7 return result 8 9 10 11 print('jiecheng 6 =',jiecheng(6)) 12 print('jiecheng 3 =',jiecheng(3)) 13 print('jiecheng 100 =',jiecheng(100))
习题三:
算圆的面积:

1 import math 2 3 def compute_area_of_circle(r): 4 return round(math.pi * r * r,2) 5 6 print("area of 2 is:",compute_area_of_circle(2))
习题四;
区间内的所有素数:输入开始和结束数字,打印区间内所有素数,比如,输入11和25,打印11-25直接所有素数,包括25.
素数,如果数字只能被1和自己整除就是素数,否则不是素数,比如3室素数,4不是。

1 def panduan(number): 2 '''判断一个数是否为素数''' 3 if number in [1,2]: 4 return True 5 for i in range(2,number): 6 if number % i == 0: 7 return False 8 return True 9 10 11 12 def sushu(begin,end): 13 '''获取一个区间数据''' 14 for number in range(begin,end + 1): 15 if panduan(number): 16 print(f"{number} is a prime") 17 18 19 sushu(11,25)
习题五:
求前N个数字的平方和,比如5的平方和,1的平方+2的平方+3的平方+4的平方+5的平方
方法一:

1 def pingfang(number): 2 result = 0 3 while number >= 1: 4 result += number * number 5 number -= 1 6 return result 7 8 9 print(pingfang(5))
方法二:

1 def pingfang(number): 2 result = 0 3 for i in range(1,number + 1): 4 result += i * i 5 return result 6 7 8 print(pingfang(5))
习题六:
计算列表数字的和,比如input列表[1,2,3,4]说是列表[17,5,3,5]
方法一:

1 def list_sum(list_name): 2 sum = 0 3 for i in range(len(list_name)): 4 sum += list_name[i] 5 return sum 6 7 8 9 list1 = [1,2,3,4] 10 list2 = [17,5,3,5] 11 12 print("list1 sum is:",list_sum(list1)) 13 print("list2 sum is:",list_sum(list2))
方法二:

1 def list_sum(list_name): 2 sum = 0 3 for i in list_name: 4 sum += i 5 return sum 6 7 8 9 list1 = [1,2,3,4] 10 list2 = [17,5,3,5] 11 12 print("list1 sum is:",list_sum(list1)) 13 print("list2 sum is:",list_sum(list2))
习题七:
计算数字范围内所有偶数
输入开始和结束值,不包含结束值,得到所有偶数,偶数,能被数字2整除的整数,是2的倍数,
比如4-15直接的偶数
方法一

1 def calc_integer(begin,end): 2 result = [] 3 for i in range(begin,end): 4 if i % 2 == 0: 5 result.append(i) 6 return result 7 8 print(calc_integer(4,15))
方法二,采用列表推导式

1 begin = 4 2 end = 15 3 date = [result for result in range(begin,end) if result % 2 ==0] 4 print(date)
习题八:
移除列表中多个元素,比如
输入原始列表:[3,5,7,9,11,13]
移除原始:[7,11]
返回:[3,5,9,13]

1 def remove_list(lista,listb): 2 for i in listb: 3 if i in lista: 4 lista.remove(i) 5 else: 6 pass 7 8 print(lista) 9 10 11 list1 = [3,5,7,9,11,13] 12 list2 = [7,11,15] 13 14 15 remove_list(list1,list2)
习题九:
对列表元素进行去重,
输入,包含重复元素的原始列表:[10,20,30,10,20]
返回:[10,20,30]
方法一:

1 def update_list(list_name): 2 update_list = [] 3 for i in list_name: 4 if i not in update_list: 5 update_list.append(i) 6 return update_list 7 8 9 list1 = [10,20,30,10,20] 10 print(f"yuanshi list is {list1},update list is ",update_list(list1))
方法二:

1 list1 = [10,20,30,10,20] 2 3 print(f"yuanshi list is {list1},update list is ",list(set(list1)))
习题十:
怎样对简单列表元素排序:
怎样对简单列表排序?
简单列表:元素类型不是复合类型(列表、元素、字典)
形式1:[20,50,10,40,30]
形式2:['bb','ee','aa','dd','cc']
知识点:
怎样原地排序?怎样不改变原列表排序?
怎样指定是升序还是降序排序?

1 list1 = [20,50,10,40,30] 2 #这种情况对list1内存进行了改变, 3 list1.sort() 4 5 print(f"list1 is {list1}")
不改变原始列表

1 list1 = [20,50,10,40,30] 2 #增加reverse参数,是将数据进行降序 3 list2 = sorted(list1,reverse=True) 4 5 print(f"list1 is {list1}") 6 print(f"list2 is {list2}")
习题十一
怎样实现学生成绩排序
学生成绩数据格式:复杂列表,元素是字典或是元组:
[
{'sno':101,'sname':"小张",'sgrade':88},
{'sno':102,'sname':"小王",'sgrade':77},
{'sno':103,'sname':"小李",'sgrade':99},
{'sno':104,'sname':"小赵",'sgrade':66}
]

1 students = [ 2 {'sno':101,'sname':"小张",'sgrade':88}, 3 {'sno':102,'sname':"小王",'sgrade':77}, 4 {'sno':103,'sname':"小李",'sgrade':99}, 5 {'sno':104,'sname':"小赵",'sgrade':66} 6 ] 7 8 students_sort = sorted(students,key=lambda x:x['sgrade']) 9 10 print(students) 11 12 print(students_sort)
习题十二:
读取成绩文件排序数据
输入文件:
三列:学号、姓名、成绩
列之间用逗号分隔,比如“101,小张,88”
行之间用\n换行分割
处理:
读取文件,按成绩倒序排列
输出:
排序后的三列数据

代码内容

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 def read_file(): 6 # 将文件读取内容放到一个空列表中 7 result = [] 8 with open(r"./students.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8") as fin: 9 for line in fin: 10 line = line[:-1] 11 result.append(line.split(',')) 12 return result 13 14 def sort_data(datas): 15 result = sorted(datas,key=lambda x: int(x[2]),reverse=True) 16 return result 17 18 def write_newfile(datas): 19 with open(r"./students_updata.txt","w",encoding="UTF-8") as fout: 20 for data in datas: 21 fout.write(",".join(data) + "\n") 22 23 #第一步:读取文件 24 datas = read_file() 25 #print(datas) 26 #第二步:对文件进行排序 27 datas = sort_data(datas) 28 #print(datas) 29 #第三版:将排序后的内容写入新文件 30 write_newfile(datas)
输出内容
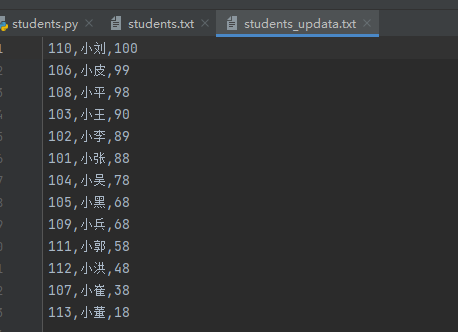
习题十三
统计学生成绩高分低分平均分
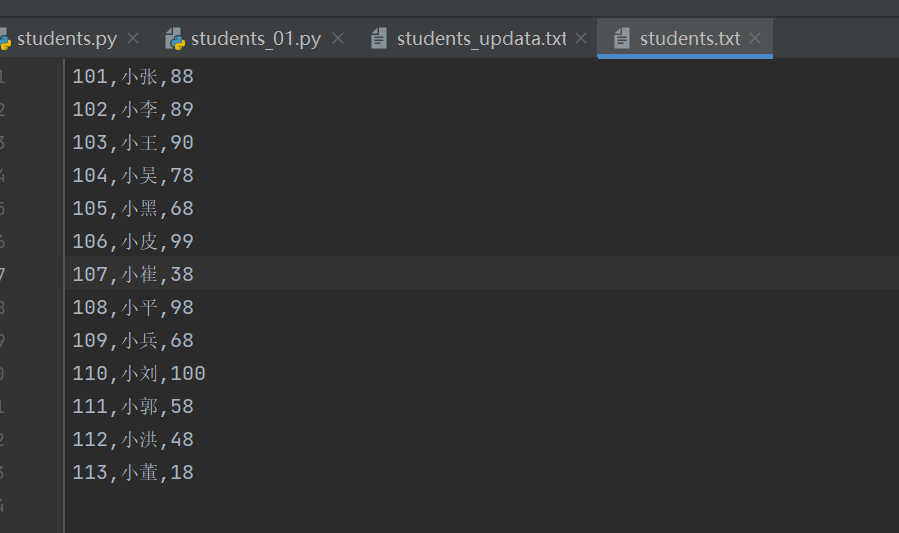
输入文件:
三列:学号、姓名、成绩
列之间用逗号分隔,比如“101,小张,88”
行之间用\n换行分割
输出:最高分、最低分、平均分

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 def calc_score(): 6 #将读取成绩的文件内放到一个空列表中 7 result = [] 8 #读取成绩文件内容 9 with open(r'./students.txt','r',encoding='UTF-8') as fin: 10 for line in fin: 11 line = line[:-1] 12 fields = (line.split(',')) 13 result.append(int(fields[2])) 14 max_score = max(result) 15 min_score = min(result) 16 avg_score = round(sum(result) / len(result),2) 17 18 return max_score,min_score,avg_score 19 20 21 22 max_score,min_score,avg_score = calc_score() 23 print(f"max_score={max_score},min_score={min_score},avg_score={avg_score}")
习题十四:
统计英语文章每个单词的出现次数

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 words_count = {} 6 7 with open(r'./Enginsh_file.txt','r',encoding='UTF-8') as fin: 8 for line in fin: 9 line = line[:-1] 10 words = line.split() 11 for word in words: 12 if word.lower() not in words_count: 13 words_count[word.lower()] = 0 14 words_count[word.lower()] +=1 15 16 print(words_count.items()) 17 18 print(sorted(words_count.items(),key=lambda x: x[1],reverse=True)[:10])
习题十五:
统计目录下所有文件大小:

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 import os 6 #获取单个文件大小 7 #print(os.path.getsize("students.txt")) 8 9 #获取目录总大小 10 11 sum_size = 0 12 for file in os.listdir("."): 13 if os.path.isfile(file): 14 sum_size += os.path.getsize(file) 15 16 print("all size of dir:",sum_size/1000)
习题十六:
按文件后缀名整理文件夹
小知识:怎样获取文件的后缀名?
import os
os.path.splitext('/path/to/aaa.mp3')
输出:(‘/path/to/aaa’,'mp3')
小知识:怎样移动文件
import shutil
shutil.move("aaa.txt","dir/bbb.foo")

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 import os 6 import shutil 7 #指定文件的路径 8 dir = r"D:\PYTHON\Test\DYA2\test" 9 10 for file in os.listdir(dir): #读取路径下的文件和目录 11 ext = os.path.splitext(file)[1][1:] #获取文件后缀 12 if not os.path.isdir(f"{dir}/{ext}"): #判断目录是否存在,不存在测创建 13 os.mkdir(f"{dir}/{ext}") 14 15 source_path = f"{dir}/{file}" 16 target_path = f"{dir}/{ext}/{file}" 17 18 shutil.move(source_path,target_path) #将源目录文件移动到新目录中
习题十七
递归搜索目录找出最大文件
python怎样递归搜索目录?
import os
for root,dirs,files in os.walk('python/Lib/email'):
# root代表当前目录
# dirs代表当前目录下子目录
# files代表当前目录下普通文件

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 import os 6 7 search_path = r"D:\国美GOME" 8 9 result_path = [] 10 11 for root,dirs,files in os.walk(search_path): 12 for file in files: #循环目录下所有文件 13 if file.endswith(".py"): #对.py的文件进行判断 14 file_path = f"{root}/{file}" #将整个文件路径赋值为变量 15 #print(file_path) 16 result_path.append((file_path,os.path.getsize(file_path) / 1000)) #将文件全路径和文件大小保存为元组放到列表中 17 18 19 print( 20 sorted(result_path,key=lambda x: x[1],reverse=True)[:10] #将文件类别通过sorted函数进行排序取前十个 21 )
习题十八
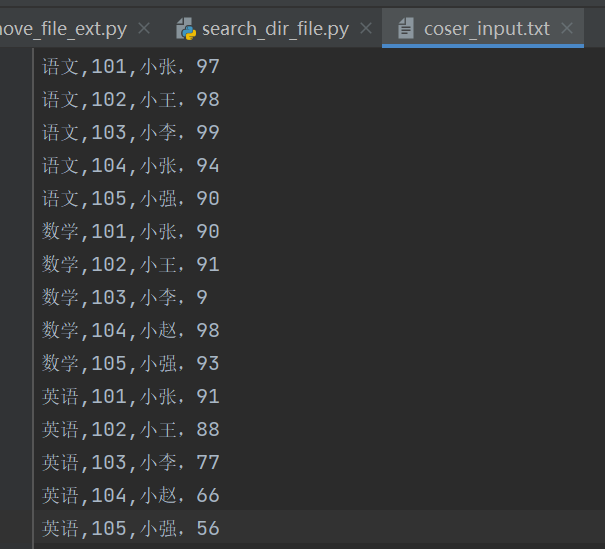
计算不同课程的最高分最低分平均分,本题解题思路为使用字典,将学科作为key,而成绩作为value存在列表中。
如下为文件内容示例:

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 #定义一个空字典 6 7 subject_score = {} 8 9 #读取成绩文件 10 11 with open(r"./coser_input.txt",encoding="UTF-8") as fin: 12 for line in fin: 13 line = line[:-1] 14 subject,son,sname,score = line.split(",") 15 16 if subject not in subject_score: 17 subject_score[subject] = [] 18 subject_score[subject].append(int(score)) 19 20 #print(subject_score) 21 22 #读取字典内容,对成绩列表进行最大值,最小值,平均值列取 23 24 for subject,score in subject_score.items(): 25 print( 26 subject, 27 max(score), 28 min(score), 29 sum(score) / len(score) 30 )
习题十九
实现不同文件的数据关联,并将关联后的文件更新到新的文件
如,第一个文件内容:
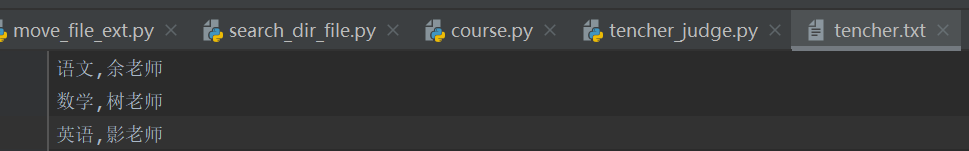
第二个文件内容:
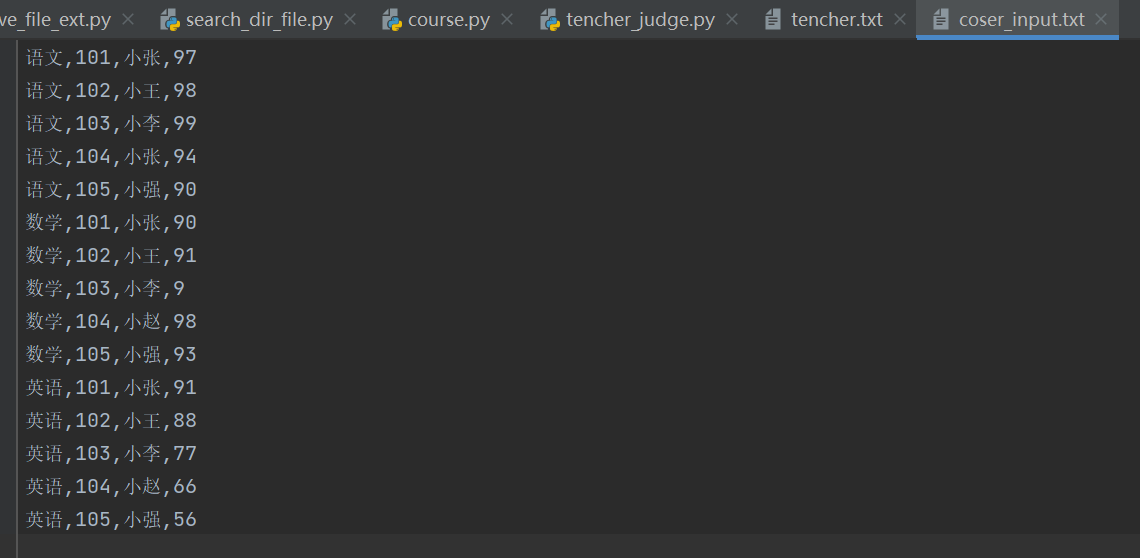
将第一个文件的老师名字增加到第二个文件中

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 tencher_dic = {} 6 with open(r"./tencher.txt",encoding="UTF-8") as fin: 7 for line in fin: 8 line = line[:-1] 9 subject,tencher = line.split(",") 10 if subject not in tencher_dic: 11 tencher_dic[subject] = tencher 12 13 #print(tencher_dic) 14 15 16 with open(r"./coser_input.txt",encoding="UTF-8") as fin: 17 for line in fin: 18 line = line[:-1] 19 subject,son,sname,score = line.split(",") 20 tencher = tencher_dic.get(subject) 21 print(subject,son,sname,score,tencher)
习题二十
统计每个兴趣的学生人数,如下图所示,统计喜欢篮球的人数,喜欢羽毛球的人数。。。
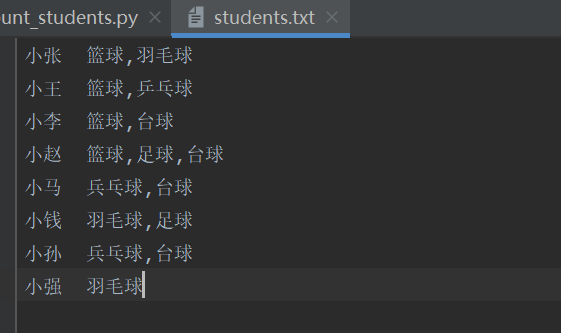

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 like_count = {} 6 7 with open(r"./students.txt",encoding="UTF-8") as fin: 8 for line in fin: 9 line = line.strip() 10 name,likes = line.split(" ") 11 like_list = likes.split(",") 12 for like in like_list: 13 if like not in like_count: 14 like_count[like] = 0 15 like_count[like] += 1 16 17 print(like_count)
习题二十一
判断一个日期,输入间隔日期,判断几天前的日期是多少?

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 5 import datetime 6 7 def get_diff_days(pdate,days): 8 pdate_obj = datetime.datetime.strptime(pdate,"%Y-%m-%d") 9 time_gap = datetime.timedelta(days=days) 10 pdate_result = pdate_obj - time_gap 11 return pdate_result.strftime("%Y-%m-%d") 12 13 print(get_diff_days("2022-08-3",1)) 14 print(get_diff_days("2022-08-3",5)) 15 print(get_diff_days("2022-08-3",7))
习题二十二
计算开始和结束范围的所有日期
输入:
开始日期,例如2021-04-28
结束日志,例如2021-05-03
输出:
[
2021-04-28,2021-04-29,2021-04-30,2021-05-01,2021-05-02,2021-05-03
]
知识点:
怎样给日期加1天?
怎样比较两个日期?

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 import datetime 5 6 def get_date_range(begin_date,end_date): 7 date_list = [] 8 while begin_date <= end_date: 9 date_list.append(begin_date) 10 begin_date_obj = datetime.datetime.strptime(begin_date,"%Y-%m-%d") 11 days_timedelta = datetime.timedelta(days=1) 12 begin_date = (begin_date_obj + days_timedelta).strftime("%Y-%m-%d") 13 return date_list 14 15 begin_date = "2022-07-28" 16 end_date = "2022-08-03" 17 date_list = get_date_range(begin_date,end_date) 18 print(date_list)
习题二十三
将unix时间转换为日期时间

1 #!/usr/bin/evn python 2 # --*-- coding: utf-8 --*-- 3 # Auther : Liu WeiDong 4 import datetime 5 6 unix_time = 1659510802 7 8 datetime_obj = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(unix_time) 9 datetime_str = datetime_obj.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") 10 print(datetime_str)



