企业级实战模块三:Kubernetes弹性伸缩
从传统意义上,弹性伸缩主要解决的问题是容量规划与实践负载的矛盾。

蓝色水位线表示集群资源容量随着负载的增加不断扩容,红色曲线表示集群资源实际负载变化。
弹性伸缩就是要解决当实际负载增大,而集群资源容量没来得及反应的问题。
1.1 Kubernetes中弹性伸缩存在的问题
常规的做法是给集群资源预留保障集群可用,通常20%左右。这种方式看似没什么问题,但放到Kubernetes中,就会发现如下2个问题。
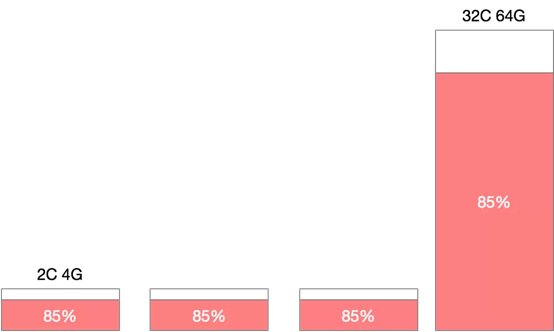
1)机器规格不统一造成机器利用率百分比碎片化
在一个Kubernetes集群中,通常不只包含一种规格的机器,假设集群中存在4C8G与16C32G两种规格的机器,对于10%的资源预留,这两种规格代表的意义是完全不同的。
<图片来自网络>
特别是在缩容的场景下,为了保证缩容后集群稳定性,我们一般会一个节点一个节点从集群中摘除,那么如何判断节点是否可以摘除其利用率百分比就是重要的指标。此时如果大规则机器有较低的利用率被判断缩容,那么很有可能会造成节点缩容后,容器重新调度后的争抢。如果优先缩容小规则机器,则可能造成缩容后资源的大量冗余。
2)机器利用率不单纯依靠宿主机计算
在大部分生产环境中,资源利用率都不会保持一个高的水位,但从调度来讲,调度应该保持一个比较高的水位,这样才能保障集群稳定性,又不过多浪费资源。
1.2 弹性伸缩概念的延伸
不是所有的业务都存在峰值流量,越来越细分的业务形态带来更多成本节省和可用性之间的跳转。
-
在线负载型:微服务、网站、API
-
离线任务型:离线计算、机器学习
-
定时任务型:定时批量计算
不同类型的负载对于弹性伸缩的要求有所不同,在线负载对弹出时间敏感,离线任务对价格敏感,定时任务对调度敏感。
2 kubernetes 弹性伸缩布局
在 Kubernetes 的生态中,在多个维度、多个层次提供了不同的组件来满足不同的伸缩场景。
有三种弹性伸缩:
-
CA(Cluster Autoscaler):Node级别自动扩/缩容cluster-autoscaler组件
-
HPA(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler):Pod个数自动扩/缩容
-
VPA(Vertical Pod Autoscaler):Pod配置自动扩/缩容,主要是CPU、内存addon-resizer组件
如果在云上建议 HPA 结合 cluster-autoscaler 的方式进行集群的弹性伸缩管理。
3 Node 自动扩容/缩容
3.1 Cluster AutoScaler
扩容:Cluster AutoScaler 定期检测是否有充足的资源来调度新创建的 Pod,当资源不足时会调用 Cloud Provider 创建新的 Node。
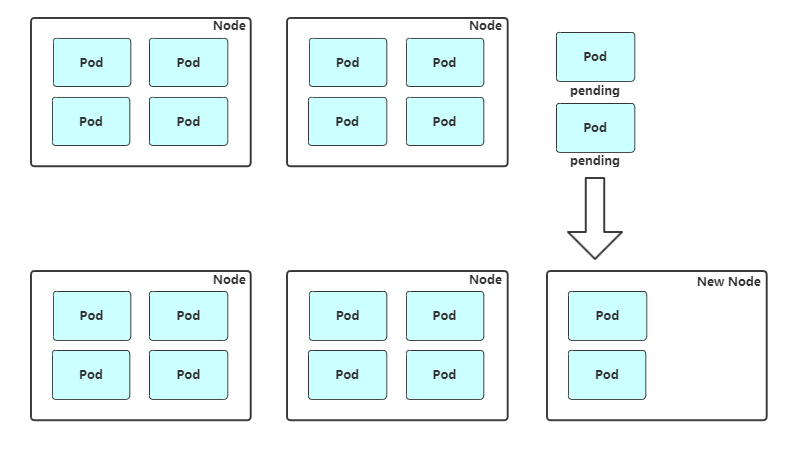
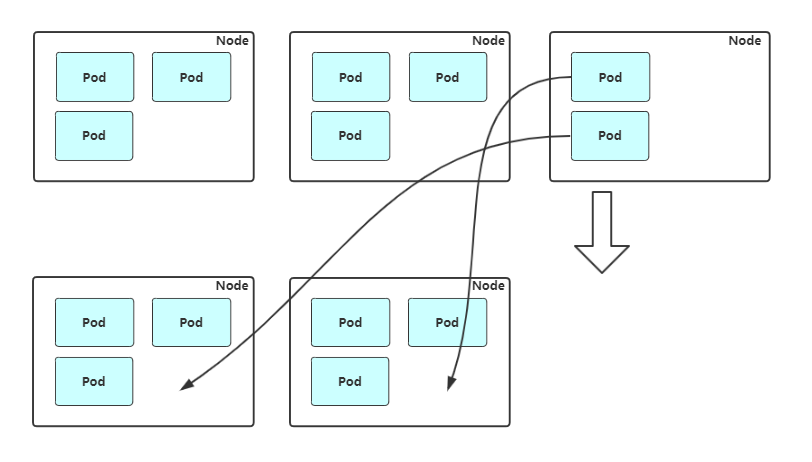
缩容:Cluster AutoScaler 也会定期监测 Node 的资源使用情况,当一个 Node 长时间资源利用率都很低时(低于 50%)自动将其所在虚拟机从云服务商中删除。此时,原来的 Pod 会自动调度到其他 Node 上面。
支持的云提供商:
-
AWS: https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/aws/README.md
3.2 Ansible扩容Node

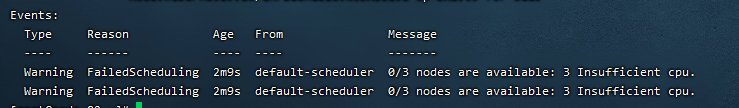
1)模拟资源不够场景

# 创建控制器,制造硬件资源用尽的情况
apiVersion

2)扩容node资源
# 在ansible 项目中hosts 文件中添加主机信息
[newnode]
192.168.5.7 node_name=k8s-node-03
# 执行yml文件,完成扩容
ansible-playbook -i hosts add-node.yml -u root -k
3)查看集群状态
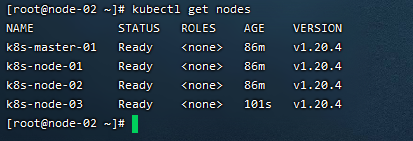
4)查看pod应用状态
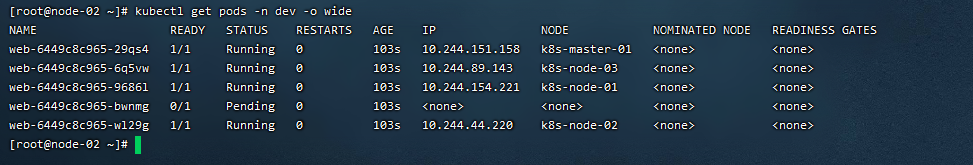
3.3 K8s缩容Node
1)查看集群状态
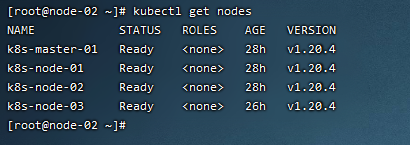
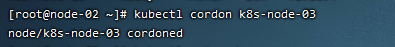
2)设置节点不可调度
# 设置不可调度
kubectl cordon k8s-node-03
# 取消不可调度
kubectl uncordon k8s-node-03
2)查看集群状态
kubectl get nodes
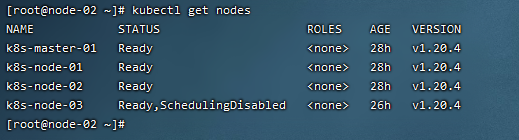
3)驱散节点已经运行的业务容器
kubectl drain --force --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data k8s-node-03
# 扩展内容
--force
当一些pod不是经 ReplicationController, ReplicaSet, Job, DaemonSet 或者 StatefulSet 管理的时候
就需要用--force来强制执行 (例如:kube-proxy)
--ignore-daemonsets
无视DaemonSet管理下的Pod
--delete-local-data
如果有mount local volumn的pod,会强制杀掉该pod并把料清除掉,另外如果跟本身的配置讯息有冲突时,drain就不会执行
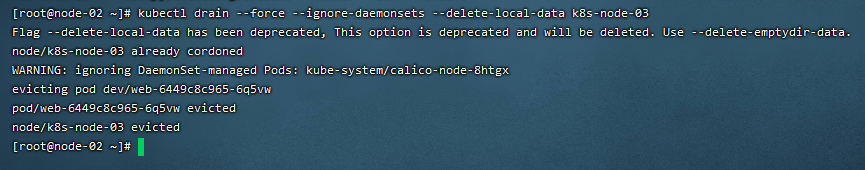
4)删除Node节点
kubectl delete node k8s-node-03
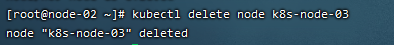
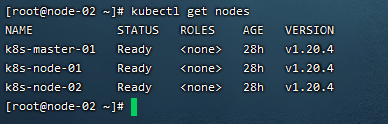
5)查看集群状态
kubectl get nodes
4 Pod自动扩容/缩容(HPA)
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler(HPA,Pod水平自动伸缩),根据资源利用率或者自定义指标自动调整replication controller, deployment 或 replica set,实现部署的自动扩展和缩减,让部署的规模接近于实际服务的负载。HPA不适于无法缩放的对象,例如DaemonSet。

4.1 HPA基本原理
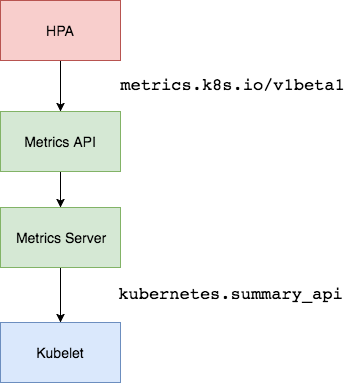
Kubernetes 中的 Metrics Server 持续采集所有 Pod 副本的指标数据。HPA 控制器通过 Metrics Server 的 API(Heapster 的 API 或聚合 API)获取这些数据,基于用户定义的扩缩容规则进行计算,得到目标 Pod 副本数量。当目标 Pod 副本数量与当前副本数量不同时,HPA 控制器就向 Pod 的副本控制器(Deployment、RC 或 ReplicaSet)发起 scale 操作,调整 Pod 的副本数量,完成扩缩容操作。如图所示。

在弹性伸缩中,冷却周期是不能逃避的一个话题, 由于评估的度量标准是动态特性,副本的数量可能会不断波动。有时被称为颠簸, 所以在每次做出扩容缩容后,冷却时间是多少。
在 HPA 中,默认的扩容冷却周期是 3 分钟,缩容冷却周期是 5 分钟。
可以通过调整kube-controller-manager组件启动参数设置冷却时间:
-
--horizontal-pod-autoscaler-downscale-delay :扩容冷却
-
--horizontal-pod-autoscaler-upscale-delay :缩容冷却
4.2 HPA的演进历程
目前 HPA 已经支持了 autoscaling/v1、autoscaling/v1beta1和autoscaling/v1beta2 三个大版本 。
目前大多数人比较熟悉是autoscaling/v1,这个版本只支持CPU一个指标的弹性伸缩。
而autoscaling/v1beta1增加了支持自定义指标,autoscaling/v1beta2又额外增加了外部指标支持。
而产生这些变化不得不提的是Kubernetes社区对监控与监控指标的认识认识与转变。从早期Heapster到Metrics Server再到将指标边界进行划分,一直在丰富监控生态。
示例:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
kind: AverageUtilization
averageUtilization: 50
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: packets-per-second
targetAverageValue: 1k
- type: Object
object:
metric:
name: requests-per-second
describedObject:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
name: main-route
target:
kind: Value
value: 10k
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
5 基于CPU指标缩放
也可参考教程:
5.1 Kubernetes API Aggregation
在 Kubernetes 1.7 版本引入了聚合层,允许第三方应用程序通过将自己注册到kube-apiserver上,仍然通过 API Server 的 HTTP URL 对新的 API 进行访问和操作。为了实现这个机制,Kubernetes 在 kube-apiserver 服务中引入了一个 API 聚合层(API Aggregation Layer),用于将扩展 API 的访问请求转发到用户服务的功能。

当你访问 apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 的时候,实际上访问到的是一个叫作 kube-aggregator 的代理。而 kube-apiserver,正是这个代理的一个后端;而 Metrics Server,则是另一个后端 。通过这种方式,我们就可以很方便地扩展 Kubernetes 的 API 了。
如果你使用kubeadm部署的,默认已开启。如果你使用二进制方式部署的话,需要在kube-APIServer中添加启动参数,增加以下配置:
# vi /opt/kubernetes/cfg/kube-apiserver.conf
...
--requestheader-client-ca-file=/opt/kubernetes/ssl/ca.pem \
--proxy-client-cert-file=/opt/kubernetes/ssl/server.pem \
--proxy-client-key-file=/opt/kubernetes/ssl/server-key.pem \
--requestheader-allowed-names=kubernetes \
--requestheader-extra-headers-prefix=X-Remote-Extra- \
--requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group \
--requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User \
--enable-aggregator-routing=true \
...
在设置完成重启 kube-apiserver 服务,就启用 API 聚合功能了。
5.2 部署 Metrics Server
Metrics Server是一个集群范围的资源使用情况的数据聚合器。作为一个应用部署在集群中。
Metric server从每个节点上Kubelet公开的摘要API收集指标。
Metrics server通过Kubernetes聚合器注册在Master APIServer中。
# git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/metrics-server
# cd metrics-server/deploy/1.8+/
# vi metrics-server-deployment.yaml # 添加2条启动参数
...
containers:
- name: metrics-server
image: lizhenliang/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.1
command:
- /metrics-server
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP
...
# kubectl create -f .
可通过Metrics API在Kubernetes中获得资源使用率指标,例如容器CPU和内存使用率。这些度量标准既可以由用户直接访问(例如,通过使用kubectl top命令),也可以由集群中的控制器(例如,Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)用于进行决策。
测试:
kubectl get --raw /apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes
kubectl top node
5.3 autoscaling/v1(CPU指标实践)
autoscaling/v1版本只支持CPU一个指标。
首先部署一个应用:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: web
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-php
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-php
spec:
containers:
- image: lizhenliang/nginx-php
name: java
resources:
requests:
memory: "300Mi"
cpu: "250m"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: web
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx-php
创建HPA策略:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: web
spec:
maxReplicas: 5
minReplicas: 1
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: web
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 60
scaleTargetRef:表示当前要伸缩对象是谁
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage:当整体的资源利用率超过50%的时候,会进行扩容。
开启压测:
yum install httpd-tools
ab -n 100000 -c 100 http://10.1.206.176/status.php
10.0.0.147 为ClusterIP。
检查扩容状态:
kubectl get hpa
kubectl top pods
kubectl get pods
关闭压测,过一会检查缩容状态。
5.4 autoscaling/v2beta2(多指标)
为满足更多的需求, HPA 还有 autoscaling/v2beta1和 autoscaling/v2beta2两个版本。
这两个版本的区别是 autoscaling/v1beta1支持了 Resource Metrics(CPU)和 Custom Metrics(应用程序指标),而在 autoscaling/v2beta2的版本中额外增加了 External Metrics的支持。
kubectl get hpa.v2beta2.autoscaling -o yaml > /tmp/hpa-v2.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: web
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: web
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- resource:
type: Resource
name: cpu
target:
averageUtilization: 60
type: Utilization
与上面v1版本效果一样,只不过这里格式有所变化。
v2还支持其他另种类型的度量指标,:Pods和Object。
type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: packets-per-second
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 1k
type: Object
object:
metric:
name: requests-per-second
describedObject:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
name: main-route
target:
type: Value
value: 2k
metrics中的type字段有四种类型的值:Object、Pods、Resource、External。
-
Resource:指的是当前伸缩对象下的pod的cpu和memory指标,只支持Utilization和AverageValue类型的目标值。
-
Object:指的是指定k8s内部对象的指标,数据需要第三方adapter提供,只支持Value和AverageValue类型的目标值。
-
Pods:指的是伸缩对象Pods的指标,数据需要第三方的adapter提供,只允许AverageValue类型的目标值。
-
External:指的是k8s外部的指标,数据同样需要第三方的adapter提供,只支持Value和AverageValue类型的目标值。
# hpa-v2.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: web
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: web
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: packets-per-second
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 1k
- type: Object
object:
metric:
name: requests-per-second
describedObject:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
name: main-route
target:
type: Value
value: 10k
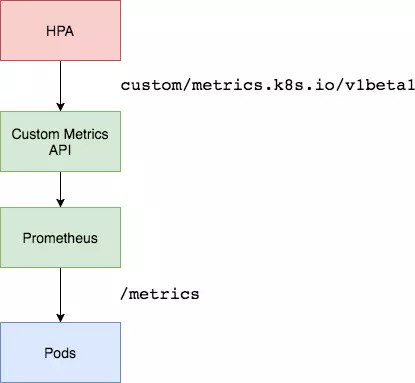
6 基于Prometheus自定义指标缩放
资源指标只包含CPU、内存,一般来说也够了。但如果想根据自定义指标:如请求qps/5xx错误数来实现HPA,就需要使用自定义指标了,目前比较成熟的实现是 Prometheus Custom Metrics。自定义指标由Prometheus来提供,再利用k8s-prometheus-adpater聚合到apiserver,实现和核心指标(metric-server)同样的效果。
6.1 部署Prometheus
Prometheus(普罗米修斯)是一个最初在SoundCloud上构建的监控系统。自2012年成为社区开源项目,拥有非常活跃的开发人员和用户社区。为强调开源及独立维护,Prometheus于2016年加入云原生云计算基金会(CNCF),成为继Kubernetes之后的第二个托管项目。
Prometheus 特点:
-
多维数据模型:由度量名称和键值对标识的时间序列数据
-
PromSQL:一种灵活的查询语言,可以利用多维数据完成复杂的查询
-
不依赖分布式存储,单个服务器节点可直接工作
-
基于HTTP的pull方式采集时间序列数据
-
推送时间序列数据通过PushGateway组件支持
-
通过服务发现或静态配置发现目标
-
多种图形模式及仪表盘支持(grafana)
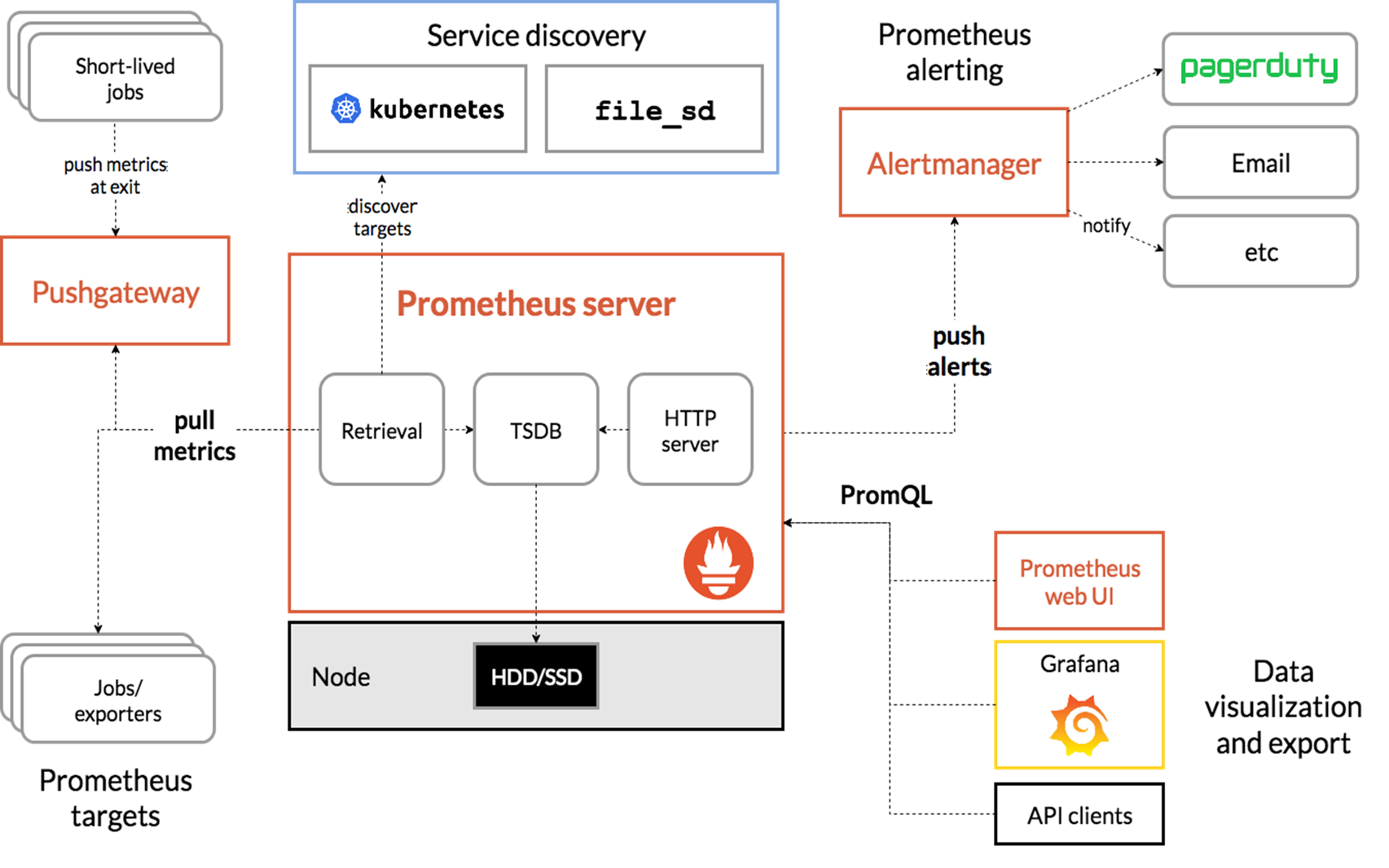
Prometheus组成及架构:
-
Prometheus Server:收集指标和存储时间序列数据,并提供查询接口
-
ClientLibrary:客户端库
-
Push Gateway:短期存储指标数据。主要用于临时性的任务
-
Exporters:采集已有的第三方服务监控指标并暴露metrics
-
Alertmanager:告警
-
Web UI:简单的Web控制台
部署:
# cd prometheus-k8s
# kubectl apply -f .
# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-state-metrics-7f7cfc4f54-xjnk7 2/2 Running 0 10m
metrics-server-7dbbcf4c7-8m8x9 1/1 Running 0 10m
prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 10m
# kubectl get svc -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kube-state-metrics ClusterIP 10.1.243.160 <none> 8080/TCP,8081/TCP 3d6h
metrics-server ClusterIP 10.1.56.84 <none> 443/TCP 13h
prometheus NodePort 10.1.36.8 <none> 9090:30090/TCP 10m
访问Prometheus UI:http://NdeIP:30090
6.2 部署 Custom Metrics Adapter
但是prometheus采集到的metrics并不能直接给k8s用,因为两者数据格式不兼容,还需要另外一个组件(k8s-prometheus-adpater),将prometheus的metrics 数据格式转换成k8s API接口能识别的格式,转换以后,因为是自定义API,所以还需要用Kubernetes aggregator在主APIServer中注册,以便直接通过/apis/来访问。
https://github.com/DirectXMan12/k8s-prometheus-adapter
该 PrometheusAdapter 有一个稳定的Helm Charts,我们直接使用。
先准备下helm环境:
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.0.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar zxvf helm-v3.0.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/bin/
helm repo add stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts
helm repo update
helm repo list
部署prometheus-adapter,指定prometheus地址:
# helm install prometheus-adapter stable/prometheus-adapter --namespace kube-system --set prometheus.url=http://prometheus.kube-system,prometheus.port=9090
# helm list -n kube-system
# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
prometheus-adapter-77b7b4dd8b-ktsvx 1/1 Running 0 9m
验证,确保适配器注册到APIServer:
# kubectl get apiservices |grep custom
# kubectl get --raw "/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1"
6.3 基于QPS指标实践
部署一个应用:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: metrics-app
name: metrics-app
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: metrics-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: metrics-app
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "80"
prometheus.io/path: "/metrics"
spec:
containers:
- image: lizhenliang/metrics-app
name: metrics-app
ports:
- name: web
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: metrics-app
labels:
app: metrics-app
spec:
ports:
- name: web
port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: metrics-app
该metrics-app暴露了一个Prometheus指标接口,可以通过访问service看到:
# curl 10.1.181.193/metrics
# HELP http_requests_total The amount of requests in total
# TYPE http_requests_total counter
http_requests_total 115006
# HELP http_requests_per_second The amount of requests per second the latest ten seconds
# TYPE http_requests_per_second gauge
http_requests_per_second 0.5
创建HPA策略:
# vi app-hpa-v2.yml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: metrics-app-hpa
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: metrics-app
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: http_requests_per_second
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 800m # 800m 即0.8个/秒
这里使用Prometheus提供的指标测试来测试自定义指标(QPS)的自动缩放。
6.4 配置适配器收集特定的指标
当创建好HPA还没结束,因为适配器还不知道你要什么指标(http_requests_per_second),HPA也就获取不到Pod提供指标。
ConfigMap在default名称空间中编辑prometheus-adapter ,并seriesQuery在该rules: 部分的顶部添加一个新的:
# kubectl edit cm prometheus-adapter -n kube-system
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus-adapter
chart: prometheus-adapter-v0.1.2
heritage: Tiller
release: prometheus-adapter
name: prometheus-adapter
data:
config.yaml: |
rules:
- seriesQuery: 'http_requests_total{kubernetes_namespace!="",kubernetes_pod_name!=""}'
resources:
overrides:
kubernetes_namespace: {resource: "namespace"}
kubernetes_pod_name: {resource: "pod"}
name:
matches: "^(.*)_total"
as: "${1}_per_second"
metricsQuery: 'sum(rate(<<.Series>>{<<.LabelMatchers>>}[2m])) by (<<.GroupBy>>)'
...
该规则将http_requests在2分钟的间隔内收集该服务的所有Pod的平均速率。
测试API:
kubectl get --raw "/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/default/pods/*/http_requests_per_second"
压测:
ab -n 100000 -c 100 http://10.1.181.193/metrics
查看HPA状态:
kubectl get hpa
kubectl describe hpa metrics-app-hpa
小结

-
通过/metrics收集每个Pod的http_request_total指标;
-
prometheus将收集到的信息汇总;
-
APIServer定时从Prometheus查询,获取request_per_second的数据;
-
HPA定期向APIServer查询以判断是否符合配置的autoscaler规则;
-



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话