嵌入式Linux C进程间通信(二)——管道(有名和无名)
一、无名管道的使用
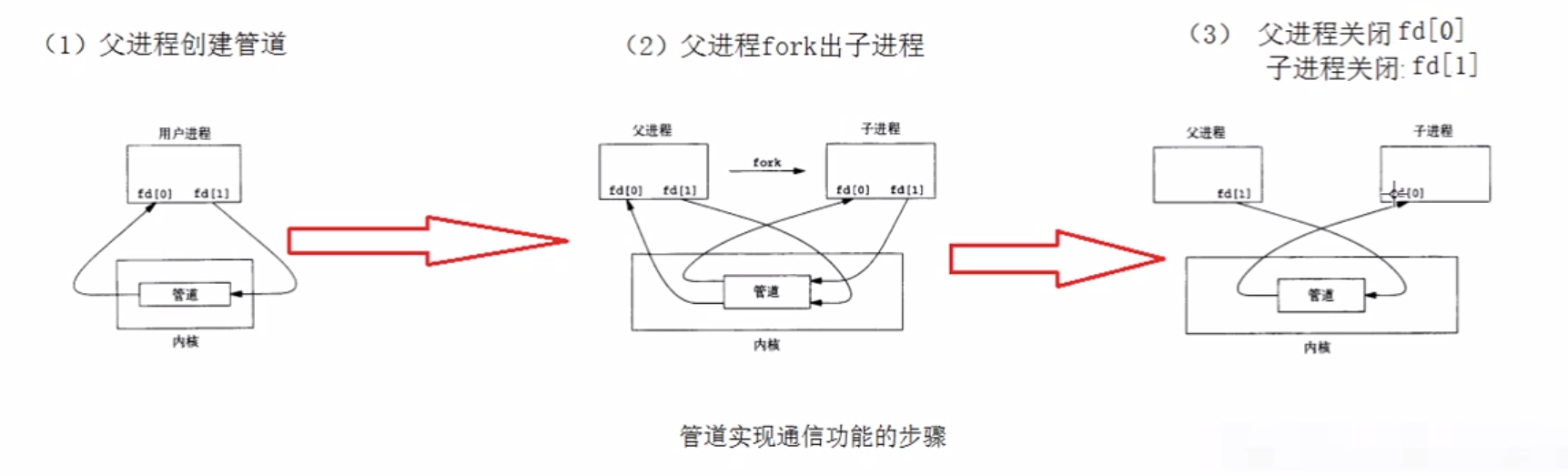
具体来说就是,内核会开辟-一个“管道”,通信的进程通过共享这个管道,从而实现通信。
只能是父子进程之间进行通信(要有血缘关系)
其他进程之间不行
int pipe(int pipefd[2])
管道只允许单向通信
读管道时,如果没有数据的话,读操作会休眠(阻塞入,写数据时,缓冲区写满会休眠(阻塞)
数据被读出,数据就会被管道删除;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
int p = pipe(fd);
if (p < 0)
{
perror("pipe error\n");
exit(1);
}
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fork error!\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0)
{
char buffer[1024];
close(fd[0]);
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s", buffer);
write(fd[1], buffer, strlen(buffer));
}
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
char buffer[1024];
close(fd[1]);
/*改成非阻塞
#include <fcntl.h>
int flags = fcntl(fd[0],F_GETFL);
flags = flags | O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd[0],F_SETFL,flags);
*/
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
sleep(1);
read(fd[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer));
printf("buffer = %s\n", buffer);
}
}
return 0;
}
二、SIGPIPE信号

SIGPIPE:写入没有读权限的管道文件---------终止
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
void my_exit(int b)
{
printf("SIGPIPE\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
int p = pipe(fd);
if (p < 0)
{
perror("pipe error\n");
exit(1);
}
pid = fork();
signal(SIGPIPE,my_exit);
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fork error!\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0)
{
char buffer[1024];
close(fd[0]);
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s", buffer);
write(fd[1], buffer, strlen(buffer));
}
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
char buffer[1024];
close(fd[1]);
close(fd[0]);
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
sleep(1);
read(fd[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer));
printf("buffer = %s\n", buffer);
}
}
return 0;
}
子进程会终止
可以用signal(SIGPIPE,SIG_ING);将信号忽略
三、有名管道
系统中任意两个进程,都能进行通信
为什么叫有名管道
管道应用的一个重大限制是它没有名字,只适合具有亲缘性质的进程之间通信。命名管道克服了这种限制,FIFO不同于管道之处在于它提供-一个路径名与之关联,以FIFO的文件形式存在于文件系统中。这样,即使与FIFO的创建进程不存在亲缘关系的进程,只要可以访问该路径,就能够彼此通过FIFO相互通信(能够访问该路径的进程以及FIFO的创建进程之间),因此,通过FIFO不相关的进程也能交换数据。
int mkfifo(const char * pathname, mode_ t mode);

有名管道的使用步骤
- 进程调用mkfifo创建有名管道
- open打开有名管道
- read/write读写管道进行通信
“有名管道”这种特殊文件,只能使用mkfifo函数来创建
为了保证管道一定被创建,最好是两个进程都包含创建管道的代码,谁先运行就谁先创建,后运行的发现管道已经创建好了,那就直接open打开使用。
不能以0_ RDWR模式打开命名管道FIFO文件,否则其行为是未定义的,管道是单向的,不能同时读写;
3.1 父子进程通信
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define FILE_NAME "./file"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
if (mkfifo(FILE_NAME,0655) < 0)
{
perror("mkfifo error!");
exit(1);
}
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fork error!\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0)
{
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_WRONLY);
char buffer[1024];
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s",buffer);
write(fd,buffer,strlen(buffer));
}
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_RDONLY);
char buffer[1024];
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
read(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
printf("buffer = %s\n",buffer);
}
}
return 0;
}
3.2 独立进程之间通信
3.2.1 read_mkfifo
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define FILE_NAME "./file"
void my_exit(int sig)
{
remove(FILE_NAME);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
signal(SIGINT, my_exit);
if (mkfifo(FILE_NAME, 0655) < 0)
{
perror("mkfifo error!");
exit(1);
}
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_RDONLY);
char buffer[1024];
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
read(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
printf("buffer = %s\n",buffer);
}
return 0;
}
3.2.2 write_mkfifo
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define FILE_NAME "./file"
// void my_exit(int sig)
// {
// remove(FILE_NAME);
// }
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//signal(SIGINT, my_exit);
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_WRONLY);
char buffer[1024];
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s",buffer);
write(fd,buffer,strlen(buffer));
}
return 0;
}
3.2.3 运行结果

分类:
嵌入式Linux C进程间通信




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理