“奇技淫巧” 话递归
“To Iterate is Human, to Recurs,Divine.” ---L. Peter Deutsch
“迭代是人,递归是神” 第一次见有人这样说,让我受伤的心得到些许安慰......
最近在琢磨算法,又见递归! 这是个绕不过去的坎! 当初,上大学时似懂非懂自欺欺人的蒙混过关,再次引证了那句名言:“出来混,迟早都是要还的......”。好吧,那就直面它!于是搜遍海内外,加上日思夜想,被这“奇技淫巧”折魔得真掉了不少头发(主要是8皇后问题~)。
大神王垠在谈程序语言最精华的原理时提到递归,并说递归比循环表达能力强很多,而且效率几乎一样!!!没有一定的内力,估计你很难理解他这句话,当然他说得没错!
务必要弄懂弄透它!抱着一股不服的拧劲和不死的初心,蒙生了收集所有经典递归案例写法作一汇总的想法。
如果您不能像大神一样一眼就看穿其本质并熟练的运用它(不自欺),不妨一起来领略领略这“奇技淫巧”的各案之美, 由简到难,慢慢的你一定会觉得它越来越美!
如发现还有文中没收集到的经典例子,欢迎补充添加,以泽后人,算积功德一件~
作者承诺:所有代码都经过测试,所有评论都是算法在脑中真真切切过了一遍之后的切肤反馈。
数学定义:
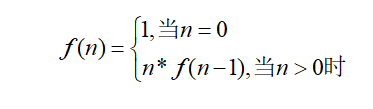
1 //求N! 2 long int F( long int N) 3 { 4 if(N==0) 5 return 1; 6 if(N>0) 7 return N*F(N-1); 8 }
1 2 int main( int argv, char** argc){ 3 long int N; 4 cin>>N; 5 cout<<F(N)<<endl; 6 }
对着数学公式写代码是不是很容易?这个用递归比循环更易写,更容易理解!闭着眼睛,想想循环怎么写?...是不是有点啰嗦~?
这个是编程用循环的入门思维,用for语句太简单,如果让以递归方式写,很多人可能又会卡一会儿了。但是如果你把它按数学公式的方式定义一下,和N!一样,递归就好写多了!
数学定义:
1 int Sum(int N) 2 { 3 4 if(N==1) 5 return 1; 6 if(N>1) 7 return N+Sum(N-1); 8 else 9 return 0; 10 } 11
按数学公式写代码,是不是让生活更美好!~
3. Fibonacci数列,F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)
数学定义:
1 int Fibonacci(int N) 2 { 3 if(N==1||N==2) 4 return 1; 5 if(N>2) 6 return Fibonacci(N-1)+Fibonacci(N-2); 7 else 8 return 0; 9 }
这个递归很好写,如果闭眼用循环写,估计要点时间,有几个变量需要耐心引入。
始祖殴基里德给出了辗转相除的递归原则,知道这个写起来就容易多了,但理解天才的想法是如何得来的还是要费点脑子的。
我曾试图去网上找找它的数学定义,很遗憾大都是些拗口的文字描述,代码反而容易理解一些。
1 int GCD(int a, int b) 2 { 3 if(a>0&&b>0){ 4 if(a%b==0){ 5 return b; 6 }else{ 7 return GCD(b,a%b); 8 } 9 } 10 }
于是从代码中反推出其数学公式~:
真是佩服那个出题的和尚,高僧!!!当然会解题的也是高人。
如上图,要把A中所有圆盘经B辅助移到C,移动过程中,要求园盘之上始终只能是比其小的圆盘。规则描述不复杂,但怎么把它转化成数学定义呢?懵!先从code入手?
1 void Hanoi(int N, char source, char auxiliary, char target) 2 { 3 4 if(N==1){ 5 cout<<"Move disk: "<<N<<" from "<<source<<" to "<<target<<endl; 6 }else { 7 Hanoi(N-1,source,target,auxiliary); 8 cout<<"Move disk: "<<N<<" from "<<source<<" to "<<target<<endl; 9 Hanoi(N-1,auxiliary,source,target); 10 } 11 } 12 13 Hanoi(5,'A','B','C');
还是没法写成数学恒等式,为什么?因为在其递归终点不再是返回值以供调用者使用,而是执行了一次操作,依次返回过程中都是再执行一次操作,不是数量表达关系,因此较难用数学定义语言描述这类问题。
不用递归,够你死一丢脑细胞的。回文数是指前后对称的数,如(1,121,12321等)。
假设数字都以字符串的形式存储,为了大数判断和一般的通用回文判断,采用这种形式
1 bool isPali(string S, int startindex) 2 { 3 if(S.size()==1||startindex>=S.size()-1-startindex){ 4 return true; 5 } 6 if(S[startindex]!=S[S.size()-1-startindex]){ 7 return false; 8 } 9 10 return isPali(S, startindex+1); 11 } 12 13 int main(){ 14 string S; 15 cin>>S; 16 cout<<isPali(S,0)<<endl; 17 }
试试把它数学定义式写出来:
老祖宗蛮厉害,但这样说,似乎有点类我党自夸之嫌~
把它转化成(row,col)直角形式如下
要得到数字的值, 递归算法如下:
1 int GetVOfYangHui(int row, int col) 2 { 3 if(col<=row && col>=0){ 4 if(col==0||row==col){ 5 return 1; 6 }else{ 7 return GetVOfYangHui(row-1,col-1)+GetVOfYangHui(row-1,col); 8 } 9 }else { 10 return 0; 11 } 12 }
试试把它数学定义式写出来:
让你闷头写一个,是不是也有点难度啊?
主框架用递归的思维很简单,稍麻烦一点的是分割DPart,需要用到一点编程的技巧。
1 int DPart(int* A, int start, int end) 2 { 3 int key=A[end]; 4 int index=end; 5 while(start<end){ 6 7 while(A[start]<key){ start++;} 8 while(A[end]>=key){end--;} 9 if(start<end){ swap(A[start],A[end]);} 10 else{ 11 break; 12 } 13 14 } 15 swap(A[start],A[index]); 16 return start; 17 } 18 19 void QuickSort(int* A, int start, int end) 20 { 21 if(start>end||start<0||end<0){ 22 return; 23 } else { 24 int index=DPart(A,start,end); 25 QuickSort(A,start,index-1); 26 QuickSort(A,index+1,end); 27 } 28 29 } 30
主框架用递归的思维也很简单,关键在写Merge时,需要用到一点点编程的技巧。
1 void Merge(int A[], int low, int mid, int high) 2 { 3 int n1= mid-low+1; 4 int n2= high-mid; 5 6 int L[n1],R[n2]; 7 for(int i=0;i<n1;i++) 8 L[i]=A[i+low]; 9 10 for(int j=0;j<n2;j++) 11 R[j]=A[j+mid+1]; 12 13 int i=0,j=0,k=low; 14 15 while(i!=n1 && j!= n2) 16 { 17 if(L[i] <= R[j]) 18 A[k++] = L[i++]; 19 else 20 A[k++] = R[j++]; 21 } 22 23 while(i < n1) 24 A[k++] = L[i++]; 25 while(j < n2) 26 A[k++] = R[j++]; 27 28 } 29 30 void MergeSort(int A[], int low, int high) 31 { 32 if(low<high){ 33 int mid = (low+high)/2; 34 MergeSort(A,low,mid); 35 MergeSort(A,mid+1,high); 36 37 Merge(A,low,mid,high); 38 } 39 }
这个可算是搞数据结构设计的人把递归思想发挥到极致的经典案例吧?
这部分code 有些冗长,为了完整性,还是把它全贴出来。主要目的是体会其前,中,后序遍历的递归写法。为了建树方便,我们以数据输入顺序按层序方式建树,它需要用到队列技巧(与递归无关,暂不讨论),同时加入一个层序遍历方法来验证输入。注意层序遍历很难用递归方法实现,我思考了很久都没有结果,如果你有想到,一定告知一声,万谢!(mathmad@163.com)
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 struct Node { 8 int data; 9 Node* left; 10 Node* right; 11 }; 12 13 class Btree 14 { 15 public: 16 Btree(); 17 ~Btree(); 18 19 Node *createNode(int data); 20 Node *GetRoot(); 21 void insert(Node *newNode); 22 void destroy_tree(); 23 void levOrder(Node *root); 24 void preOrder(Node *root); 25 void midOrder(Node *root); 26 void posOrder(Node *root); 27 private: 28 void destroy_tree(Node *leaf); 29 Node *root; 30 queue<Node *> q; 31 }; 32 33 Btree::Btree() 34 { 35 root=NULL; 36 } 37 Btree::~Btree() 38 { 39 if(root!=NULL){ 40 destroy_tree(root); 41 } 42 } 43 44 void Btree::destroy_tree(Node *leaf) 45 { 46 if(leaf!=NULL) 47 { 48 destroy_tree(leaf->left); 49 destroy_tree(leaf->right); 50 delete leaf; 51 } 52 } 53 Node* Btree::createNode(int data) 54 { 55 Node* n=new Node; 56 n->left=NULL; 57 n->right=NULL; 58 n->data=data; 59 return n; 60 } 61 Node* Btree::GetRoot() 62 { 63 return root; 64 } 65 66 void Btree::insert(Node *newnode) 67 { 68 if(NULL==root){ 69 root=newnode; 70 q.push(root); 71 }else{ 72 Node *f=q.front(); 73 if(f->left&&f->right){q.pop(); f=q.front();} 74 if(!f->left){ f->left=newnode;} 75 else if(!f->right){ f->right=newnode;} 76 q.push(newnode); 77 78 } 79 80 } 81 82 void Btree::levOrder(Node* root) 83 { 84 if(root){ 85 queue<Node*> Q; 86 Q.push(root); 87 88 while(!Q.empty()){ 89 Node *d=Q.front(); 90 cout<<d->data<<" "; 91 Q.pop(); 92 if(d->left){Q.push(d->left);} 93 if(d->right){Q.push(d->right);} 94 } 95 96 } 97 98 } 99 100 void Btree::preOrder(Node* root) 101 { 102 if(NULL==root) { return;} 103 else{ 104 cout<<root->data<<" "; 105 preOrder(root->left); 106 preOrder(root->right); 107 } 108 109 } 110 111 void Btree::midOrder(Node *root) 112 { 113 if(NULL==root) { return;} 114 else{ 115 midOrder(root->left); 116 cout<<root->data<<" "; 117 midOrder(root->right); 118 } 119 120 } 121 122 void Btree::posOrder(Node *root) 123 { 124 if(NULL==root) { return;} 125 else{ 126 posOrder(root->left); 127 posOrder(root->right); 128 cout<<root->data<<" "; 129 } 130 131 } 132 133 int main( int argv, char** argc){ 134 135 Btree btree; 136 Node * newnode; 137 int data; 138 cout<<"Please input a sequences number to create a Complete Binary Tree:"<<endl; 139 140 do{ 141 cin>>data; 142 newnode=btree.createNode(data); 143 btree.insert(newnode); 144 }while(getchar()!='\n'); 145 146 cout<<"BTree Level order is:"<<endl; 147 btree.levOrder(btree.GetRoot()); 148 cout<<endl<<"Pre Order is:"<<endl; 149 btree.preOrder(btree.GetRoot()); 150 cout<<endl<<"mid Order is:"<<endl; 151 btree.midOrder(btree.GetRoot()); 152 cout<<endl<<"pos Order is:"<<endl; 153 btree.posOrder(btree.GetRoot()); 154 cout<<endl; 155 }
用g++ 编译上述代码(g++ BTree.cpp),测试输出如下:
这个有点难想清楚!特别是第二个swap交换!
N个元素的全排列,有高中数学基础的人都易知道它总共有N!(阶乘)种。若要全部打印出来,当N>4时还是有一定麻烦,特别是当用循环思路正面强攻时,会让人陷入无尽的深渊!
下面以5个数字为例简述其原理:
假设数据集为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, 如何编写全排列的递归算法?
1、首先看最后两个数4, 5。 它们的全排列为4 5和5 4, 即以4开头的5的全排列和以5开头的4的全排列。
由于一个数的全排列就是其本身,从而得到以上结果。
2、再看后三个数3, 4, 5。它们的全排列为3 4 5、3 5 4、4 3 5、4 5 3、5 4 3、5 3 4 六组数。
是以3开头的和4,5的全排列的组合、以4开头的和3,5的全排列的组合和以5开头的和4,3的全排列的组合,即k与(k+1,..N)的全排列组合加上k’与(k+1,...N)的全排列组合,其中k’是k与(k+1,...N)的任一置换。
网上通用一般描述为,设一组数p = {r1, r2, r3, ... ,rn}, 全排列为perm(p),令pn = p - {rn}。
因此perm(p) = r1perm(p1), r2perm(p2), r3perm(p3), ... , rnperm(pn)。当n = 1时perm(p} = r1。
为了更容易理解,将整组数中的所有的数分别与第一个数交换,这样就总是在处理后n-1个数的全排列。(下面给出C++版, 以字符串为数据集的全排列算法)
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 /* 4 全排列算法改进 5 Author: Liang 2018-09-21 6 7 */ 8 9 int Perm(string s, int k, int m) { 10 static int n=0; 11 12 if (s!= ""&& m>=k && m<=s.size()-1 && k>=0){ 13 if(k == m){ 14 cout<<s<<endl; 15 n++; 16 }else { 17 Perm(s, k+1, m); 18 19 for(int i = k+1; i <= m; i++) { 20 swap(s[k],s[i]); 21 Perm(s, k+1, m); 22 swap(s[k],s[i]); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 return n; 27 } 28 29 int main(){ 30 string str; 31 cin>>str; 32 int n=str.size(); 33 cout<<"total: "<<Perm(str,0,n-1)<<endl; 34 }
国际象棋棋盘上放8个皇后,问有多少种放法(皇后的走法是水平垂直线和对角线位置可以互相攻击) 著名的8皇后问题,这个Gauss都只得出76种解(实际有92种),一想到这,我心理就平衡一点~
8 皇后问题后演变成N皇后问题,其中N=1时有一个解, 2,3无解,N=4时有两个解,N=5时比N=6的解多。这说明什么问题? 一个“老婆”最稳定,2个3个后宫没法处理,挺到4个时就会有办法,5个“老婆”比6个老婆好处置,超过6个就是多多益善了,要想处理8个皇后,高斯都没想清楚,可见多了后宫难治啊,哈哈,闲扯远了~
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define StackSize 8 // could be set to 1, 4, 5, 6, 7,....N 5 6 int ans=0; 7 int top=-1; 8 int ColOfRow[StackSize]; //index represent the row, value is col 9 10 void Push(int col) 11 { 12 top++; 13 ColOfRow[top]=col; 14 } 15 16 void Pop() 17 { 18 top--; 19 } 20 // check put a Queen to position(row, col) is safe or not. 21 bool isPosSafe(int row, int col) 22 { 23 for(int i=0;i<row;i++) 24 { 25 //check col is ok, row is increase invoke, same is impossible 26 if(col==ColOfRow[i]){ 27 return false; 28 } 29 // Y=kX+b, k=1 or k=-1, the Queen will attack each other 30 if(abs(col-ColOfRow[i])==(row-i)){ 31 return false; 32 } 33 } 34 return true; 35 } 36 37 void PrintBoard() 38 { 39 cout<<"NO."<<ans<<":"<<endl; 40 for(int i=0;i<StackSize;i++) 41 { 42 for(int j=0;j<ColOfRow[i];j++) 43 cout<<"_ "; 44 cout<<"Q"; 45 for(int j=StackSize-1;j>ColOfRow[i];j--) 46 cout<<" _"; 47 cout<<endl; 48 } 49 cout<<endl; 50 } 51 // Should be start from 0 row, since the start point will impact future steps desision 52 void PlaceQueen(int row) 53 { 54 for (int col=0;col<StackSize;col++) 55 { 56 Push(col); 57 if (isPosSafe(row,col)) 58 { 59 if (row<StackSize-1) 60 PlaceQueen(row+1); 61 else 62 { 63 ans++; 64 PrintBoard(); 65 } 66 } 67 Pop(); 68 } 69 } 70 71 72 int main() 73 { 74 // Since Recursion invoke, start point should be 0, the first row 75 PlaceQueen(0); 76 cout<<"the total solutions is:"<<ans<<endl; 77 return 0; 78 } 79 80
没有数学递归公式,循环怕是很难搞清


