kafka 生产者(一)
1、生产者消息发送流程
1.1、发送原理
在消息发送的过程中,涉及到了两个线程——main线程和Sender线程。在main线程中创建了一个双端队列RecordAccumulator。main线程将消息发送给RecordAccumulator,Sender线程不断从RecordAccumulator中拉取消息发送到KafkaBroker。
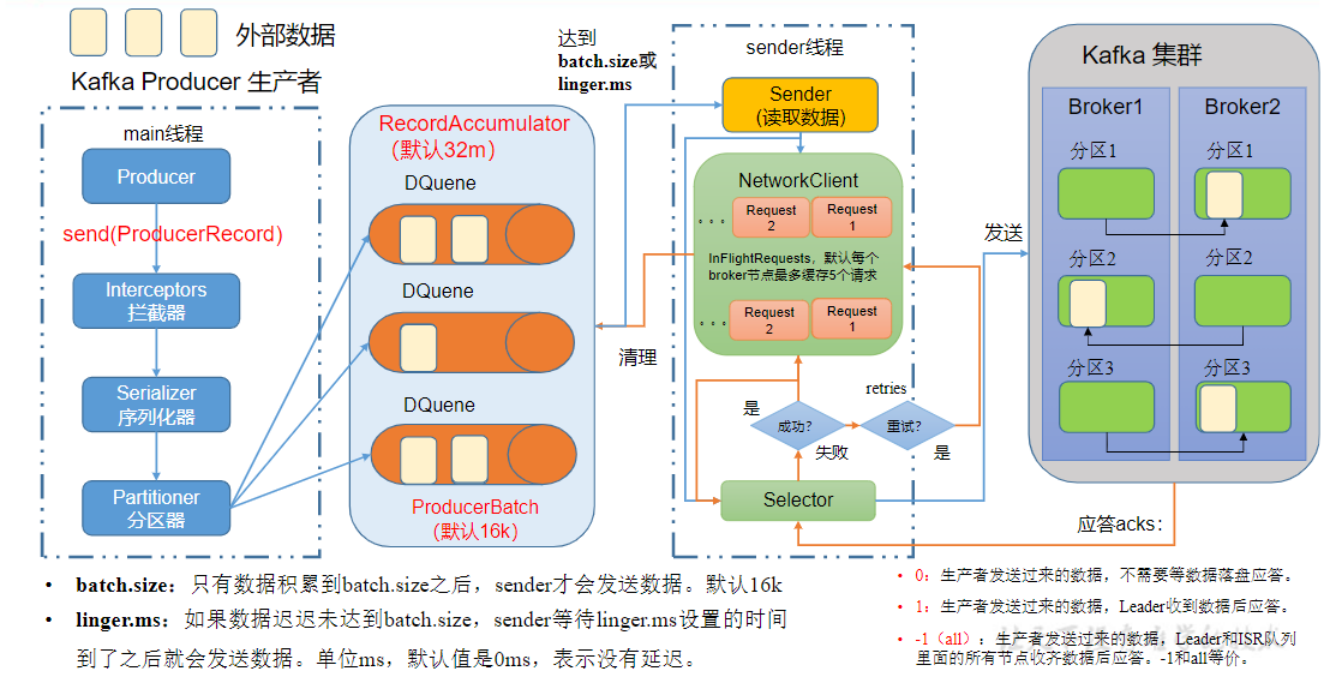
1.2、生产者参数列表

2、同步发送API
2.1、普通异步发送
引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency>
异步发送测试代码
public class CustomProducer { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = new Properties(); //连接ZK properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop103:9092,"); //设置KV序列化 properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); //指定 kv 的序列化类型 //1、创建 生产者 KafkaProducer<String, String> KafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties); //2、发送数据 put异步发送 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", i + " hello wdh01")); } //3、关闭资源 KafkaProducer.close(); } }
开启kafka 消费数据
[hui@hadoop103 kafka]$ bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server hadoop103:9092 --topic first 0 hello wdh01 1 hello wdh01 2 hello wdh01 3 hello wdh01 4 hello wdh01
2.2、带回调函数的异步发送
回调函数会在producer收到ack时调用,为异步调用,该方法有两个参数,分别是元数据信息(RecordMetadata)和异常信息(Exception),如果Exception为null,说明消息发送成功,如果Exception不为null,说明消息发送失败。
注意:消息发送失败会自动重试,不需要我们在回调函数中手动重试。
public class CustomProducerCallBack { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = new Properties(); //连接ZK properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop103:9092,"); //设置KV序列化 properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); //指定 kv 的序列化类型 //1、创建 生产者 KafkaProducer<String, String> KafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties); //2、发送数据 put异步发送 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", i + " hello wdh01"), new Callback() { // new Callback( 回调函数 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println("主题 " + metadata.topic() + " 分区 " + metadata.partition()); } } }); } //3、关闭资源 KafkaProducer.close(); } }
消费到数据
[hui@hadoop103 kafka]$ bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server hadoop103:9092 --topic first 0 hello wdh01 1 hello wdh01 2 hello wdh01 3 hello wdh01 4 hello wdh01
控制台输出回调信息
主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1
3、同步发送API
只需在异步发送的基础上,再调用一下get()方法即可
public class CustomProducerSync { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Properties properties = new Properties(); //连接ZK properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop103:9092,"); //设置KV序列化 properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); //指定 kv 的序列化类型 //1、创建 生产者 KafkaProducer<String, String> KafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties); //2、发送数据 同步发送 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", i + " hello wdh01")).get(); } //3、关闭资源 KafkaProducer.close(); } }
消费到数据
[hui@hadoop103 kafka]$ bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server hadoop103:9092 --topic first 0 hello wdh01 1 hello wdh01 2 hello wdh01 3 hello wdh01 4 hello wdh01
4、生产者分区
4.1、分区好处
- 便于合理使用存储资源,每个Partition在一个Broker上存储,可以把海量的数据按照分区切割成一块一块数据存储在多台Broker上。合理控制分区的任务,可以实现负载均衡的效果。
- 提高并行度,生产者可以以分区为单位发送数据;消费者可以以分区为单位进行消费数据。ConsumerConsumerConsumerss 100T资料le
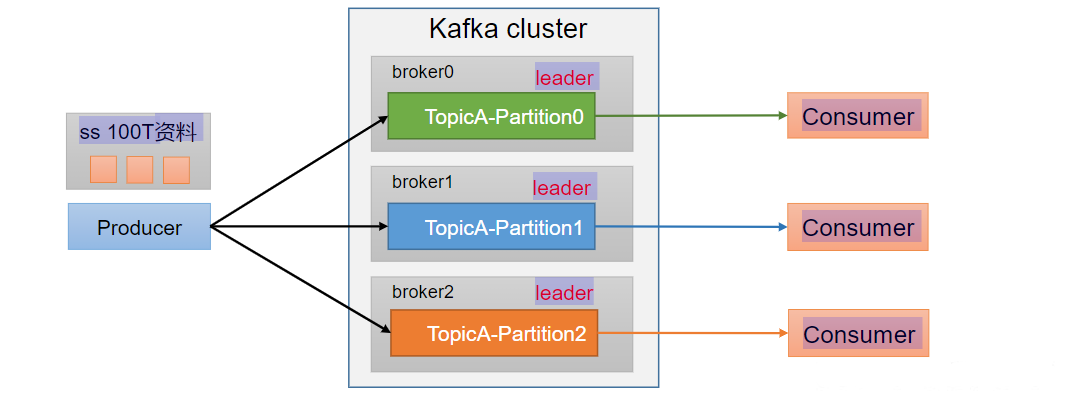
4.2、分区策略
分区策略在 DefaultPartitioner 有详细的说明,idea 里 ctrl + n 输入 DefaultPartitioner
/** * The default partitioning strategy: * <ul> * <li>If a partition is specified in the record, use it * <li>If no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key * <li>If no partition or key is present choose the sticky partition that changes when the batch is full. * * See KIP-480 for details about sticky partitioning. */ public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
以下几个方法都指明partition的情况,直接将指明的值作为partition值;例如partition=0,所有数据写入分区0
public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, Long timestamp, K key, V value, Iterable<Header> headers) { public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, Long timestamp, K key, V value) { public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, K key, V value, Iterable<Header> headers) { public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, K key, V value) {
方法内容详见

public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, Long timestamp, K key, V value, Iterable<Header> headers) { if (topic == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Topic cannot be null."); if (timestamp != null && timestamp < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException( String.format("Invalid timestamp: %d. Timestamp should always be non-negative or null.", timestamp)); if (partition != null && partition < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException( String.format("Invalid partition: %d. Partition number should always be non-negative or null.", partition)); this.topic = topic; this.partition = partition; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.timestamp = timestamp; this.headers = new RecordHeaders(headers); } /** * Creates a record with a specified timestamp to be sent to a specified topic and partition * * @param topic The topic the record will be appended to * @param partition The partition to which the record should be sent * @param timestamp The timestamp of the record, in milliseconds since epoch. If null, the producer will assign the * timestamp using System.currentTimeMillis(). * @param key The key that will be included in the record * @param value The record contents */ public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, Long timestamp, K key, V value) { this(topic, partition, timestamp, key, value, null); } /** * Creates a record to be sent to a specified topic and partition * * @param topic The topic the record will be appended to * @param partition The partition to which the record should be sent * @param key The key that will be included in the record * @param value The record contents * @param headers The headers that will be included in the record */ public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, K key, V value, Iterable<Header> headers) { this(topic, partition, null, key, value, headers); } /** * Creates a record to be sent to a specified topic and partition * * @param topic The topic the record will be appended to * @param partition The partition to which the record should be sent * @param key The key that will be included in the record * @param value The record contents */ public ProducerRecord(String topic, Integer partition, K key, V value) { this(topic, partition, null, key, value, null); }
下面这个分区逻辑没有指明partition值但有key的情况下,将key的hash值与topic的partition数进行取余得到partition值;例如:key1的hash值=5,key2的hash值=6,topic的partition数=2,那么key1对应的value1写入1号分区,key2对应的value2写入0号分区。
public ProducerRecord(String topic, K key, V value) { this(topic, null, null, key, value, null); }
最后一个分区既没有partition值又没有key值的情况下,Kafka采用StickyPartition(黏性分区器),会随机选择一个分区,并尽可能一直使用该分区,待该分区的batch已满或者已完成,Kafka再随机一个分区进行使用(和上一次的分区不同)。例如:第一次随机选择0号分区,等0号分区当前批次满了(默认16k)或者linger.ms设置的时间到,Kafka再随机一个分区进行使用(如果还是0会继续随机)。
public ProducerRecord(String topic, V value) { this(topic, null, null, null, value, null); }
测试1 将数据发往指定partition的情况下,例如,将所有数据发往分区1中。
public class CustomProducerCallBackPartitions { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = new Properties(); //连接ZK properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop103:9092,"); //设置KV序列化 properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); //指定 kv 的序列化类型 //1、创建 生产者 KafkaProducer<String, String> KafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties); //2、发送数据 put异步发送 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", 1, "", i + " hello wdh01"), new Callback() { // new Callback( 回调函数 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println("主题 " + metadata.topic() + " 分区 " + metadata.partition()); } } }); } //3、关闭资源 KafkaProducer.close(); } }
执行后回调信息
主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1
消费数据
[hui@hadoop103 kafka]$ bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server hadoop103:9092 --topic first 0 hello wdh01 1 hello wdh01 2 hello wdh01 3 hello wdh01 4 hello wdh01
测试2 没有指明partition值但有key的情况下,将key的hash值与topic的partition数进行取余得到partition值。
KafkaProducer<String, String> KafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties); //2、发送数据 put异步发送 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "a", i + " hello wdh01"), new Callback() { // new Callback( 回调函数 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println(" a 主题 " + metadata.topic() + " 分区 " + metadata.partition()); } } }); } Thread.sleep(1000); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "b", i + " hello wdh01"), new Callback() { // new Callback( 回调函数 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println(" b 主题 " + metadata.topic() + " 分区 " + metadata.partition()); } } }); } Thread.sleep(1000); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "f", i + " hello wdh01"), new Callback() { // new Callback( 回调函数 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println(" f 主题 " + metadata.topic() + " 分区 " + metadata.partition()); } } }); } //3、关闭资源 KafkaProducer.close();
回调结果

a 主题 first 分区 1 a 主题 first 分区 1 a 主题 first 分区 1 a 主题 first 分区 1 a 主题 first 分区 1 b 主题 first 分区 2 b 主题 first 分区 2 b 主题 first 分区 2 b 主题 first 分区 2 b 主题 first 分区 2 f 主题 first 分区 0 f 主题 first 分区 0 f 主题 first 分区 0 f 主题 first 分区 0 f 主题 first 分区 0
4.3、自定义分区
kafka 支持自定义分区,只要实现一个 Partitioner 即可
案例
public class MyPartitioner implements Partitioner { @Override public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) { //过滤数据 int partiton; String mag = value.toString(); if (mag.contains("wdh01")) { partiton = 0; } else { partiton = 1; } return partiton; } @Override public void close() { } @Override public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) { } }
自定义分区测试
public class CustomProducerCallBackPartitionsCustom { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop103:9092,"); properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName()); //关联自定义分区器 properties.put(ProducerConfig.PARTITIONER_CLASS_CONFIG, "org.wdh01.kk.MyPartitioner"); //指定 kv 的序列化类型 //1、创建 生产者 KafkaProducer<String, String> KafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties); //2、发送数据 put异步发送 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { KafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", i + " hello wdh1"), new Callback() { // new Callback( 回调函数 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println("主题 " + metadata.topic() + " 分区 " + metadata.partition()); } } }); } //3、关闭资源 KafkaProducer.close(); } }
回调结果
主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1 主题 first 分区 1







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下