图论:最短路径搜索--Dijkstra算法(c代码实现)
2013-03-12 11:46 钱吉 阅读(23646) 评论(5) 编辑 收藏 举报最近因为辞职,有不少闲功夫,重温下数据结构,顺便练练手。今天说说最短路径搜索算法中的Dijkstra原理和实现。
一:简介
这个算法用于解决图中单源最短路径问题。所谓单源节点是指给定源节点,求图中其它节点到此源节点的最短路径。如下图所示:给定源节点a,求节点b到a的最短距离。
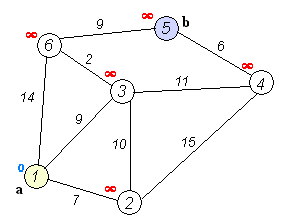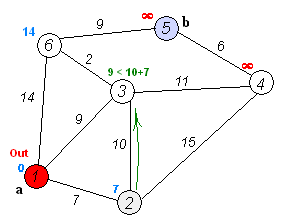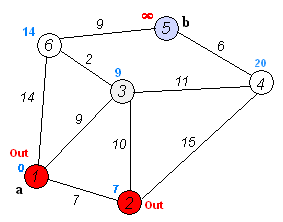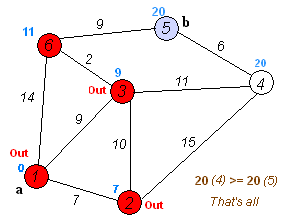
(图来自于参考资料2)
那么如何寻找?还是以上图为例:
1)初始化:设定除源节点以外的其它所有节点到源节点的距离为INFINITE(一个很大的数),且这些节点都没被处理过。
2)从源节点出发,更新相邻节点(图中为2,3,6)到源节点的距离。然后在所有节点中选择一个最段距离的点作为当前节点。
3)标记当前节点为done(表示已经被处理过),与步骤2类似,更新其相邻节点的距离。(这些相邻节点的距离更新也叫松弛,目的是让它们与源节点的距离最小。因为你是在当前最小距离的基础上进行更新的,由于当前节点到源节点的距离已经是最小的了,那么如果这些节点之前得到的距离比这个距离大的话,我们就更新它)。
4)步骤3做完以后,设置这个当前节点已被done,然后寻找下一个具有最小代价(cost)的点,作为新的当前节点,重复步骤3.
5)如果最后检测到目标节点时,其周围所有的节点都已被处理,那么目标节点与源节点的距离就是最小距离了。如果想看这个最小距离所经过的路径,可以回溯,前提是你在步骤3里面加入了当前节点的最优路径前驱节点信息。
看文字描述显得苍白无力,你可以结合上图,看下这个视频:http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMjQyOTY1NDQw.html (dijkstra演示),然后就清楚了。
二:源代码
直接给源代码,注释很清楚,不解释。
 Dijkstra.h
Dijkstra.h
1 #ifndef _DIJKSTRA_H 2 #define _DIJKSTRA_H 3 4 #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 100 //最大顶点数 5 #define MAX_EDGE_NUM 50 //相邻最大节点数 6 #define INFINITE 1E5 //表示节点之间无连接的一个较大的数 7 #define MAX_STRLEN 256 //最大字符串字节数 8 9 #define FALSE 0 10 #define TRUE 1 11 typedef int BOOL; 12 typedef unsigned int UINT; 13 14 #define SAFEFREE(p) {if(NULL!=(p)) free(p);} 15 16 extern int g_node_num; //一个图中,实际节点数的全局变量 17 typedef struct _vertex { //通用的顶点数据结构体 18 int id;//id 19 struct _vertex *pLinkList[MAX_EDGE_NUM]; //相邻顶点的指针数组 20 int nCost[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //与相邻顶点的权重数组 21 struct _vertex **next; //与剩余顶点之间的最短路径 22 int *pmincost; //与剩余顶点之间的最小代价 23 }vertex; 24 25 typedef struct _node { //组成图的顶点元素信息进行封装 26 int nID; 27 struct _vertex *pVer; 28 }node; 29 30 BOOL InitGraphic(char path[], node arr[], UINT nsize); 31 void UnitGraphic(node arr[]); 32 void ViewGraphic(node arr[]); 33 BOOL Dijkstra(node arr[]); 34 void MinRoute(node arr[], UINT nSrID, UINT nDsID); 35 36 #endif
 Dijkstra.c
Dijkstra.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include "Dijkstra.h" 5 6 int g_node_num;/*用于计算实际节点数的全局变量*/ 7 /**************************************** 8 *函数名:InitGraphic 9 *参数:path-图的信息文件路径;arr-储存图的数组;nsize-数组大小 10 *返回值:BOOL-成功返回1,错误返回0 11 *说明:根据图的信息文件,初始化数组 12 *****************************************/ 13 BOOL InitGraphic(char path[], node arr[], UINT nsize) 14 { 15 char buf[MAX_STRLEN]; 16 char *pos; 17 char ctemp; 18 int ncost; 19 int i; 20 UINT nid;//临时顶点ID 21 UINT ncid;//临时连接顶点的ID 22 UINT nlinkpos;//连接顶点数组中的位置 23 24 memset(arr, 0, sizeof(node)*nsize);//赋值0 25 FILE *pfile = fopen(path, "r"); 26 if(NULL == pfile) { 27 printf("Error opening file.\n"); 28 return FALSE; 29 } 30 while(NULL != fgets(buf, MAX_STRLEN, pfile)) { 31 pos = strtok(buf, ":");//读取一行,解析第一个冒号之前的标号,即第几个节点 32 nid = atoi(pos); 33 if(nid < nsize) { 34 arr[nid-1].nID = nid; 35 arr[nid-1].pVer = (vertex*)malloc(sizeof(vertex));//申请一个顶点struct 36 if(NULL == arr[nid-1].pVer) { 37 printf("out of memory!\n"); 38 return FALSE; 39 } 40 memset(arr[nid-1].pVer, 0, sizeof(vertex));//赋值0 41 arr[nid-1].pVer->id = nid; 42 g_node_num++;//节点数加1 43 } else { 44 fprintf(stderr, "access the boundary of setting:%d\n", nid); 45 } 46 } 47 rewind(pfile);//文件指针跳转到开始处,读取各顶点的相邻节点 48 for(i=0; i<g_node_num; i++) { 49 fscanf(pfile, "%d", &nid);//读取第一个节点标号 50 nlinkpos = 0;//指示其相邻节点结构体的当前位置 51 while((ctemp=fgetc(pfile)) != ';') { 52 fscanf(pfile, "%u-%d", &ncid, &ncost); 53 if(ncid > nsize || ncost < 0) { 54 fprintf(stderr, "access the boundary of setting or find negative cost:%u-%d\n", ncid, ncost); 55 return FALSE; 56 } 57 58 arr[nid-1].pVer->pLinkList[nlinkpos] = arr[ncid-1].pVer;/*相邻节点指针数组赋值*/ 59 arr[nid-1].pVer->nCost[ncid-1] = ncost;/*此节点到相邻节点的cost*/ 60 arr[nid-1].pVer->pmincost = NULL; 61 arr[nid-1].pVer->next = NULL; 62 nlinkpos++; 63 } 64 } 65 fclose(pfile); 66 return TRUE; 67 } 68 /******************************************* 69 *函数名:ViewGraphic 70 *参数:arr-图的数组 71 *返回值:无 72 *说明:打印图的结构信息 73 *******************************************/ 74 void ViewGraphic(node arr[]) 75 { 76 int i, j; 77 int nidtemp;//临时节点序号 78 printf("\nID\tConnceted to-ID:cost"); 79 for(i=0; i<g_node_num; i++) { 80 printf("\n%d\t",arr[i].nID); 81 for(j=0; arr[i].pVer->pLinkList[j] != NULL; j++) { 82 nidtemp = arr[i].pVer->pLinkList[j]->id; 83 printf("%d:", nidtemp); 84 printf("%d ",arr[i].pVer->nCost[nidtemp-1]); 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 /************************************************* 89 *函数名:Dijkstra 90 *参数:arr-图的数组 91 *返回值:TRUE-成功;FALSE-失败 92 *说明:依次将每个节点作为起始节点,计算剩余节点与其之间的最短路径 93 *************************************************/ 94 BOOL Dijkstra(node arr[]) 95 { 96 UINT i, j, k; 97 vertex *pbegin, *ptemp, *ptemp1; 98 int *tcost;//用于储存其余节点到起始节点的最小代价 99 BOOL *pbDone;//用于判断节点是否计算完毕的数组 100 int nidtemp;//与当前节点相邻的其它节点中,cost最小的顶点序号 101 int nmixcost = INFINITE; 102 103 tcost = (int*)malloc(g_node_num * sizeof(int)); 104 pbDone = (BOOL*)malloc(g_node_num * sizeof(BOOL)); 105 if(NULL == tcost || NULL == pbDone) { 106 printf("out of memory\n"); 107 return FALSE; 108 } 109 for(i=0; arr[i].pVer!=0; i++) {//依次将每个顶点作为起始节点 110 for(j=0; j<g_node_num; j++) {//初始化数组 111 tcost[j] = INFINITE;//其它节点到起始节点的代价 112 pbDone[j] = 0; 113 } 114 pbegin = arr[i].pVer;//起始顶点 115 pbegin->next = (vertex**)malloc(g_node_num * sizeof(vertex*));//储存每个顶点最优的前驱顶点的id的数组 116 pbegin->pmincost = (int*)malloc(g_node_num * sizeof(int));//储存每个顶点到起始顶点的最小代价数组 117 tcost[i] = 0;//初始化 118 pbDone[i] = 1; 119 pbegin->pmincost[i] = 0; 120 ptemp = pbegin;//设定起始顶点为当前顶点 121 122 while(1) { 123 for(j=0; ptemp->pLinkList[j]!=0; j++) {//遍历当前顶点的相邻节点,更新最小代价(松弛边) 124 ptemp1 = ptemp->pLinkList[j]; 125 if(tcost[ptemp1->id-1] > tcost[ptemp->id-1] + ptemp->nCost[ptemp1->id-1] \ 126 && pbDone[ptemp1->id-1] == 0) { 127 tcost[ptemp1->id-1] = tcost[ptemp->id-1] + ptemp->nCost[ptemp1->id-1]; 128 pbegin->next[ptemp1->id-1] = ptemp;//设定顶点更新后的前驱顶点 129 } 130 } 131 nmixcost = INFINITE; 132 for(j=0; j<g_node_num; j++) {//找出更新后,所有顶点中,代价最小的顶点,重新作为当前顶点。这一步可以优化。 133 if(pbDone[arr[j].nID-1] != 1 && tcost[arr[j].nID-1] < nmixcost && tcost[arr[j].nID-1] != 0) { 134 nmixcost = tcost[arr[j].nID-1]; 135 nidtemp = arr[j].nID; 136 } 137 } 138 if(nmixcost == INFINITE) {//除起始顶点外的所有节点都已经被处理完毕,退出 139 break; 140 } 141 pbegin->pmincost[nidtemp-1] = nmixcost; 142 ptemp = arr[nidtemp-1].pVer;//重新设定当前顶点 143 pbDone[nidtemp-1] = 1;//表示当前顶点已经被处理过了,其路径已经最短,代价最小 144 } 145 } 146 free(pbDone); 147 free(tcost); 148 return TRUE; 149 } 150 /********************************************************** 151 *函数名:MinRoute 152 *参数:arr-图的数组;nSrID-起始节点序号;nDsID-目的节点序号 153 *返回值:无 154 *说明:给定图的数组,利用Dijkstra函数处理之后,根据设定的起始和终止节点序号,打印 155 *最短路径和最小代价。 156 ***********************************************************/ 157 void MinRoute(node arr[], UINT nSrID, UINT nDsID) 158 { 159 if(nSrID<0 || nSrID>g_node_num || nDsID<0 || nDsID>g_node_num) { 160 printf("Invalid node number!\n"); 161 } 162 int nid; 163 vertex *ptemp = arr[nSrID-1].pVer; 164 printf("the total cost is: %d\n", ptemp->pmincost[nDsID-1]); 165 printf("the path is:"); 166 nid = nDsID; 167 printf("%d->",arr[nid-1].nID); 168 while(ptemp->next[nid-1]->id != arr[nSrID-1].nID) { 169 nid = ptemp->next[nid-1]->id;//回溯路径 170 printf("%d->",nid); 171 } 172 printf("%d\n",arr[nSrID-1]); 173 } 174 /***************************************** 175 *函数名:UnitGraphic 176 *参数:arr-图的数组 177 *返回值:无 178 *说明:释放内存 179 *****************************************/ 180 void UnitGraphic(node arr[]) 181 { 182 UINT i; 183 for(i=0; i<g_node_num; i++) { 184 if(arr[i].pVer != NULL) { 185 SAFEFREE(arr[i].pVer->next); 186 SAFEFREE(arr[i].pVer->pmincost); 187 } 188 } 189 }
 main.c
main.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include "Dijkstra.h" 5 6 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 7 { 8 char filepath[MAX_STRLEN];//图的信息文件 9 node graphic[MAX_VERTEX_NUM] = {0};//图的数组 10 int sid, did; 11 int selnum; 12 13 if(argc < 2) { 14 printf("usage:*.exe input\n"); 15 exit(1); 16 } 17 strcpy(filepath, argv[1]); 18 /***********初始化图***************/ 19 if(!InitGraphic(filepath, graphic, MAX_VERTEX_NUM)) { 20 UnitGraphic(graphic); 21 exit(1); 22 } 23 printf("**** Print The Graphic information ****"); 24 ViewGraphic(graphic);//打印图 25 /************dijkstra运算***********/ 26 if(!Dijkstra(graphic)) { 27 UnitGraphic(graphic); 28 exit(1); 29 } 30 31 printf("\n****Find the shortest path between nodes****"); 32 printf("\n1.View minimum route between nodes."); 33 printf("\n2.Exit."); 34 35 for(;;) { 36 printf("\nEnter Your Selection:"); 37 scanf("%d",&selnum); 38 switch(selnum) { 39 case 1: { 40 printf("\nEnter source node ID:"); 41 scanf("%d",&sid); 42 printf("\nEnter destination node ID:"); 43 scanf("%d",&did); 44 45 MinRoute(graphic, sid, did);//打印最优路径 46 break; 47 } 48 case 2: 49 exit(1); 50 default: { 51 printf("\nEnter proper choice.\n"); 52 break; 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 UnitGraphic(graphic); 57 return 0; 58 }
demo:
输入文件内容:
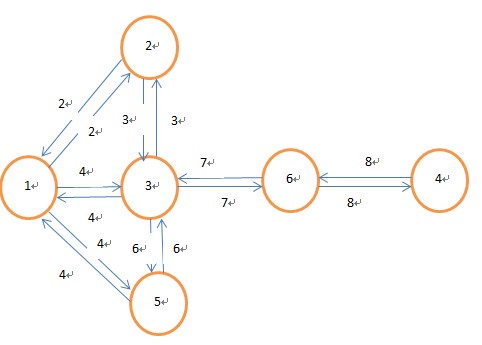
1:2-2:3-4:5-4;
2:1-2:3-3;
3:1-4:2-3:5-6:6-7;
4:6-8;
5:1-4:3-6;
6:3-7:4-8;
格式说明:
起始节点:连接节点1-权值:连接节点2-权值:连接节点3-权值.....
图的结构:
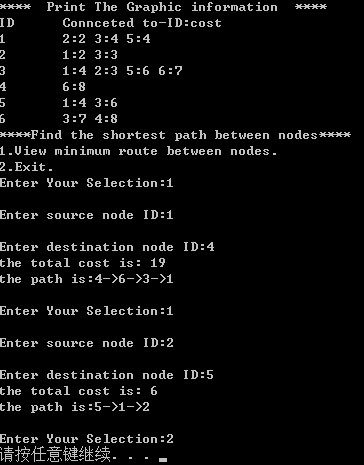
运行结果:
三:总结
Dijkstra最短路径搜索属于广度优先搜索(BFS, Breadth-First-Search),即不断去搜索当前节点的所有相邻节点,并更新它们的cost。更新的前提是认为:当前节点是目前与起始节点之间cost最小的节点,它认为自己是最优解,要想到达目的节点,经过我这里必然错不了,接着在此基础上不断去寻找其它最优路径,运用的是一种贪婪算法的思想。但是有时候并不是最优解,典型的例子就是:最小数目找零的例子,现有10元,5元,1元的纸币,如果要找15块钱,贪婪算法的结果是-10元+5元。但是如果现在假设银行发行了12元一张的纸币(银行闲的蛋疼),还用贪婪算法,结果是12+1+1+1(坑爹的,找这么多硬币!!)。但是实际上最优解仍然是10元+5元。所以有时候,具体问题要具体分析。另外,最优路径搜素还有带有启发性的A*搜索,双向广度优先搜索(BFS),它们比Dijkstra算法的搜索效率要高。改天再续。
再说一下,我的代码中,在寻找下一个当前节点时,用了全局搜索,这显然是一个很笨的方法,复杂度太高。一般的方法都是定义一个开集,一个闭集,用来存储未处理过的节点和已被处理的节点,所以我们可以用FIFO队列去优化。参考资料1。
参考资料:
1,《数据结构与算法分析-c++描述》,weiss
2,http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra's_algorithm
3,http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20662820-id-142445.html
4,http://www.rawbytes.com/dijkstras-algorithm-in-c/




