07.k近邻算法kNN
1、将数据分为测试数据和预测数据
2、数据分为data和target,data是矩阵,target是向量
3、将每条data(向量)绘制在坐标系中,就得到了一系列的点
4、根据每条data的target的不同,给点赋予不同的颜色
5、当新数据来到时,比如只有一条数据,将新数据绘制在坐标系中,就得到了新的一个点
6、确定k值,比如k=3
7、计算所有数据和新数据点的距离,找出最近的3个
8、根据结果判断新数据应该归属的分类,即为预测数据确定target
生成测试数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt raw_data_a = np.random.random((10,2)) raw_data_b = np.random.randint(0,10,size=(10,2)) X_train = raw_data_a + raw_data_b X_train
array([[8.28164975, 4.19315143],
[2.92775657, 0.81556491],
[4.50761169, 2.84927016],
[6.53083961, 4.26093009],
[2.27051172, 4.05065263],
[7.7954489 , 8.68019714],
[4.43708588, 6.72986275],
[4.65529575, 4.7985332 ],
[3.52301327, 4.19730249],
[2.2773095 , 0.07817849]])
构造target
y_train = np.array([0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1])
y_train
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
绘制散点图
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train == 0,0], X_train[y_train == 0,1],color="b") plt.scatter(X_train[y_train == 1,0], X_train[y_train == 1,1],color="r")
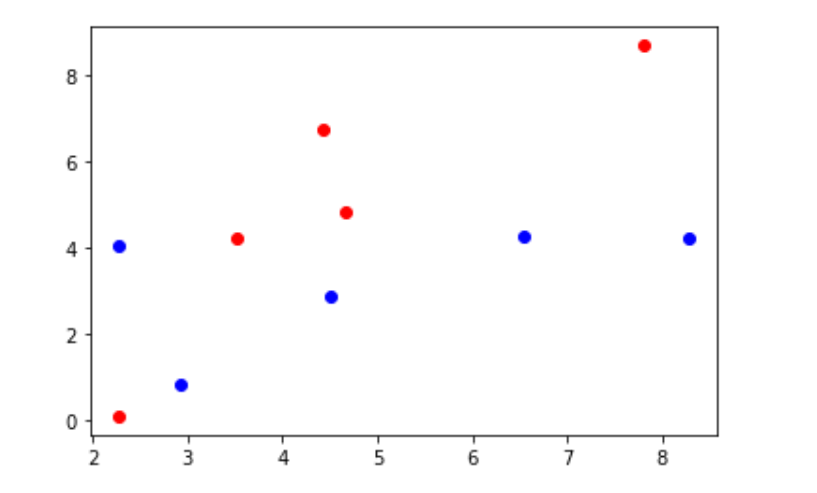
构造新数据
new_data_a = np.random.random((10,2)) new_data_b = np.random.randint(0,10,size=(10,2)) new_data = new_data_a + new_data_b new_data
array([[7.66654552, 3.43737304],
[9.00627805, 8.35944151],
[4.35322638, 5.29260333],
[2.9064343 , 0.05002835],
[8.68350808, 1.50262447],
[0.23152764, 9.688442 ],
[9.2139265 , 7.96068869],
[5.14763436, 2.40288244],
[9.52077384, 9.4833882 ],
[5.04330854, 4.96045193]])
预测数据(拿一条数据举例)
X_predict = new_data[0]
X_predict
array([3.05595894, 6.89591993])
原始数据和预测数据共同绘制在一个坐标系中
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train == 0,0], X_train[y_train == 0,1]) plt.scatter(X_train[y_train == 1,0], X_train[y_train == 1,1]) plt.scatter(X_predict[0], X_predict[1], color="g")
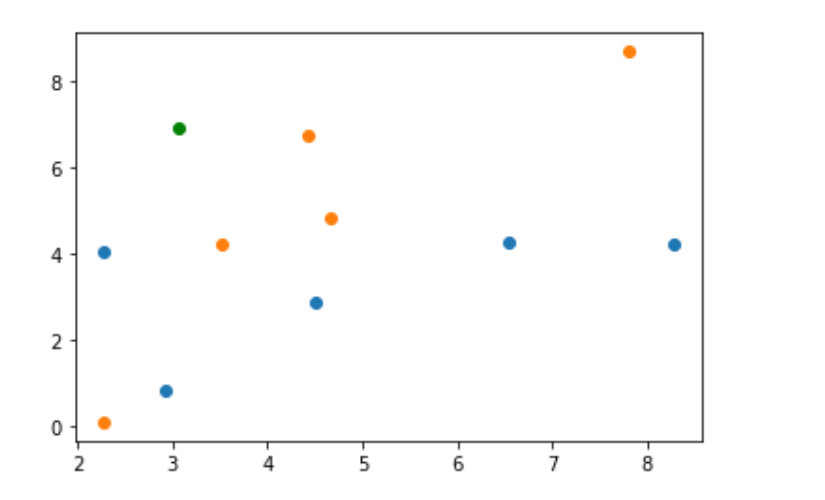
计算与测试点的距离
from math import sqrt distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x - X_predict)**2)) for x in X_train]
distances
[5.883264572139944, 6.0817064237981535, 4.299147591752391, 4.360959428669816, 2.951689913705071, 5.064228496651553, 1.3910739045173681, 2.637595368153982, 2.7387361757860287, 6.862061882958762]
K = 6,找出距离最近的6个点
k = 6 nearest = np.argsort(distances) topk_y = [y_train[i] for i in nearest[:k]] topk_y
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
结果
from collections import Counter Counter(topk_y)
Counter({1: 5, 0: 1})
votes = Counter(topk_y)
votes.most_common(1)
[(1, 5)]
votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
1
predic = votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
predic
1
使用scikit-learn中的kNN
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier kNN_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier() kNN_classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30, metric='minkowski',
metric_params=None, n_jobs=None, n_neighbors=5, p=2,
weights='uniform')
kNN_classifier.predict(new_data_1.reshape(1,-1))
array([1])
重新整理knn代码
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k): # 初始化KNN分类器 self.k = k self._X_train = None self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train): # 根据训练集X_train, Y_train训练分类器 self._X_train = X_train self._y_train = y_train return self def predict(self, X_predict): # 给定待遇测的数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量 y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict] return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x): # 给定单个待遇测数据x,返回x的预测结果值 distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in self._X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self): return "KNN=(%d)" % self.k
knn_clf = KNNClassifier(k=6)
knn_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
KNN=(6)
y_predict = knn_clf.predict(X_predict)
y_predict
array([0, 1])



