Java IO (1) - InputStream
Java IO (1) - InputStream
前言
JavaIO一共包括两种,一种是stream,一种是reader/writer,每种又包括in/out,所以一共是四种包。Java 流在处理上分为字符流和字节流。字符流处理的单元为 2 个字节的 Unicode 字符,分别操作字符、字符数组或字符串,而字节流处理单元为 1 个字节,操作字节和字节数组。
Java 内用 Unicode 编码存储字符,字符流处理类负责将外部的其他编码的字符流和 java 内 Unicode 字符流之间的转换。而类 InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter 处理字符流和字节流的转换。字符流(一次可以处理一个缓冲区)一次操作比字节流(一次一个字节)效率高。
0. 目录
1. InputStream
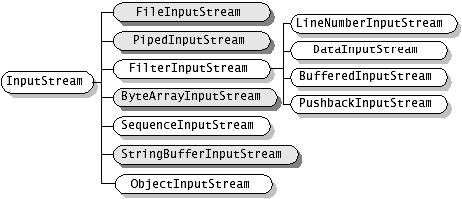
InputStream是一个抽象类,是所有InputStream的基类。
1.1. 基本方法
int available()
Returns an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or skipped over)
from this input stream without blocking by the next invocation of a method
for this input stream.
void close()
Closes this input stream and releases any system resources associated with the stream.
void mark(int readlimit)
Marks the current position in this input stream.
boolean markSupported()
Tests if this input stream supports the mark and reset methods.
abstract int read()
Reads the next byte of data from the input stream.
int read(byte[] b)
Reads some number of bytes from the input stream and stores them into the
buffer array b.
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
Reads up to len bytes of data from the input stream into an array of bytes.
void reset()
Repositions this stream to the position at the time the mark method was last
called on this input stream.
long skip(long n)
Skips over and discards n bytes of data from this input stream.
最主要的就是这几个read方法。
2. FileInputStream
FileInputStream从文件中读取字节,比较适合读取二进制数据,如果要读取字符文件,最好用FileReader。
2.1. 构造函数
FileInputStream(File file)
Creates a FileInputStream by opening a connection to an actual file,
the file named by the File object file in the file system.
FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj)
Creates a FileInputStream by using the file descriptor fdObj,
which represents an existing connection to an actual file in the file system.
FileInputStream(String name)
Creates a FileInputStream by opening a connection to an actual file,
the file named by the path name name in the file system.
有三个构造函数,其参数分别是文件、文件描述符、字符串
其主要用法如下:
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/123.txt");
FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream(new File("d:/123.txt"));
文件描述符那个不常用。
通过看源码,发现字符串那个会默认构造成文件
public FileInputStream(String paramString)
throws FileNotFoundException
{
this(paramString != null ? new File(paramString) : null);
}
public FileInputStream(File paramFile)
throws FileNotFoundException
{
String str = paramFile != null ? paramFile.getPath() : null;
SecurityManager localSecurityManager = System.getSecurityManager();
if (localSecurityManager != null) {
localSecurityManager.checkRead(str);
}
if (str == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (paramFile.isInvalid()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Invalid file path");
}
this.fd = new FileDescriptor();
this.fd.incrementAndGetUseCount();
this.path = str;
open(str);
}
注意,这两个构造函数都会抛出FileNotFoundException,但如果传的字符串是null,也会抛出空指针异常。
2.2. 主要方法
int available()
Returns an estimate of the number of remaining bytes that can be read
(or skipped over) from this input stream without blocking by the next
invocation of a method for this input stream.
void close()
Closes this file input stream and releases any system resources
associated with the stream.
protected void finalize()
Ensures that the close method of this file input stream is called when
there are no more references to it.
FileChannel getChannel()
Returns the unique FileChannel object associated with this file input stream.
FileDescriptor getFD()
Returns the FileDescriptor object that represents the connection to the
actual file in the file system being used by this FileInputStream.
int read()
Reads a byte of data from this input stream.
int read(byte[] b)
Reads up to b.length bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes.
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
Reads up to len bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes.
long skip(long n)
Skips over and discards n bytes of data from the input stream.
2.3. 代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/123.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[1000 * 20];
fis.read(b);
System.out.println(new String(b));
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
通常情况下,很少有人直接通过FileInputStream读取文本文件,会通过BufferedReader封装一下。
另外,FileInputStream也会遇到乱码问题,用InputStreamReader解决。



