HDLbits——Mt2015 lfsr
1.描述电路图里面的一个子模块
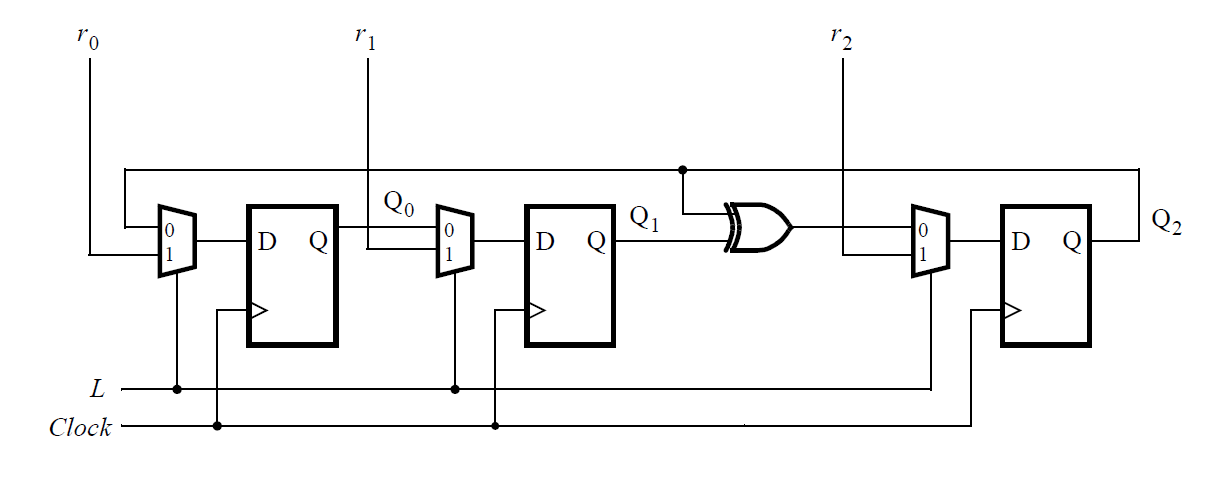
Assume that you want to implement hierarchical Verilog code for this circuit,
using three instantiations of a submodule that has a flip-flop and multiplexer in it.
Write a Verilog module (containing one flip-flop and multiplexer) named top_module for this submodule.
module dff(
input clk,
input q_in,
input L,
input r_in,
output reg Q
);
wire data;
always @(posedge clk) begin
Q <= data;
end
assign data = L ? r_in:q_in;
endmodule
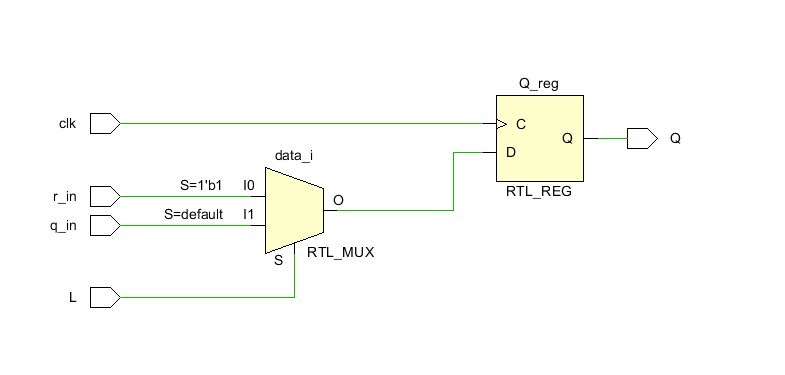
2.例化子模块
Write the Verilog code for this sequential circuit (Submodules are ok, but the top-level must be named top_module).
Assume that you are going to implement the circuit on the DE1-SoC board.
Connect the R inputs to the SW switches, connect Clock to KEY[0], and L to KEY[1]. Connect the Q outputs to the red lights LEDR.
```C
//Connect the R inputs to the SW switches, connect Clock to KEY[0], and L to KEY[1].
//Connect the Q outputs to the red lights LEDR.
module top_module (
input [2:0] SW, // R
input [1:0] KEY, // L and clk
output [2:0] LEDR); // Q
wire Q_0;
mt2015_muxdff mt2015_muxdff_ins0(
.clk(KEY[0]),
.L(KEY[1]),
.q_in(LEDR[2]),
.r_in(SW[0]),
.Q(LEDR[0])
);
mt2015_muxdff mt2015_muxdff_ins1(
.clk(KEY[0]),
.L(KEY[1]),
.q_in(LEDR[0]),
.r_in(SW[1]),
.Q(LEDR[1])
);
mt2015_muxdff mt2015_muxdff_ins2(
.clk(KEY[0]),
.L(KEY[1]),
.q_in(LEDR[1]^LEDR[2]),
.r_in(SW[2]),
.Q(LEDR[2])
);
endmodule
module mt2015_muxdff(
input clk,
input q_in,
input L,
input r_in,
output reg Q
);
wire data;
always @(posedge clk) begin
Q <= data;
end
assign data = L ? r_in:q_in;
endmodule
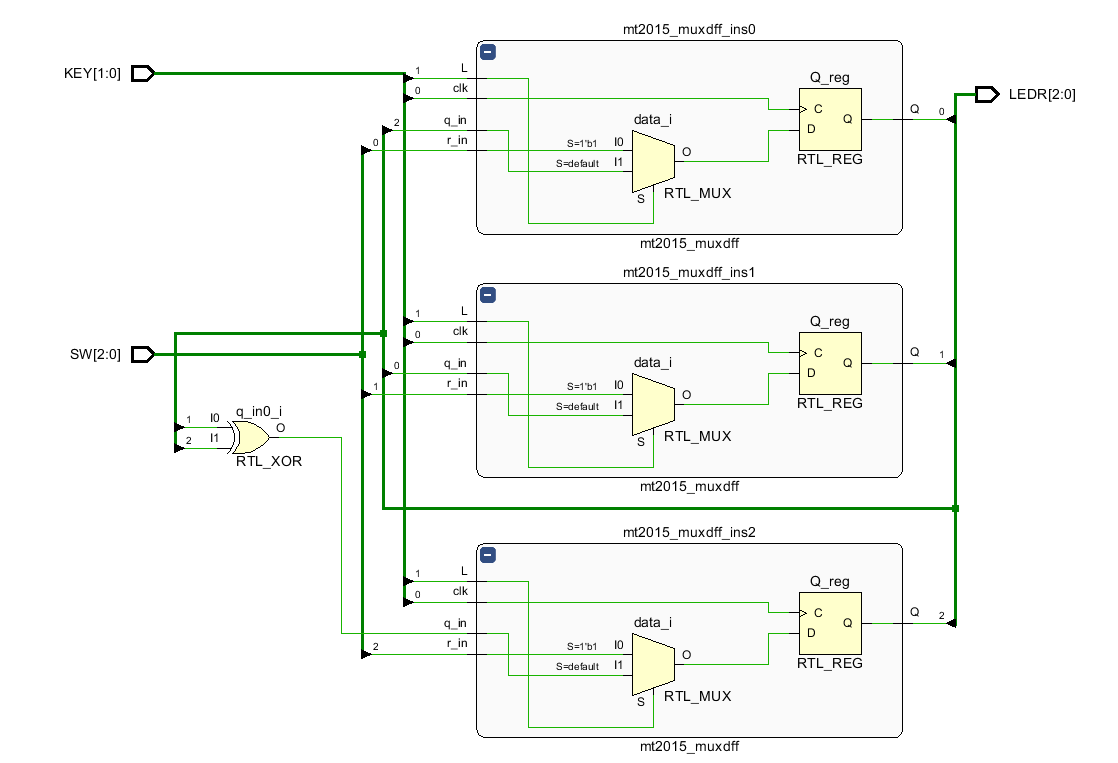
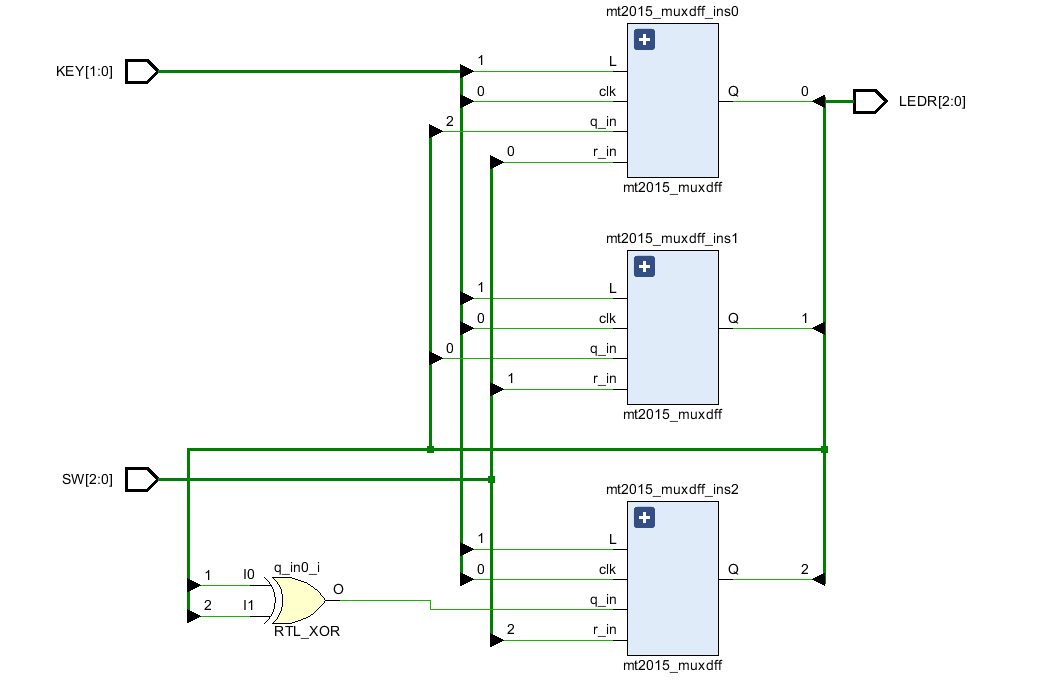
RTL原理图


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号