软工结对项目作业
| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 班级博客 |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | 作业要求 |
| 教学班级 | 006 |
| 项目地址 | https://github.com/yorkyer/PairProgramming.git |
PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 35 | 20 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 35 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 780 | 705 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 150 | 200 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 50 | 50 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 50 | 60 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 15 | 5 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 150 | 100 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 200 | 100 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | 40 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | 150 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 70 | 90 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 35 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 25 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 30 |
| 合计 | 885 | 815 |
Information Hiding,Interface Design,Loose Coupling
- Information Hiding:
信息隐藏,就是把信息封装起来,让class把复杂的、敏感的、一旦被外界捕获可能会引起不良后果的内容封装在自身内部,防止外部随意调用其内部信息(public除外)。
结对编程中,把函数和数据成员都封装在类里,达到信息隐藏的目的。
- Interface Design:
接口设计,我们俩人负责不同的模块内部的设计,然后预留外部接口,从而可以并行编程,提高开发速度。
- Loose Coupling:
松耦合。不同模块之间的耦合程度低,一般是通过接口来实现的。当然,接口也应该适度使用,过多的接口会适得其反。
计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
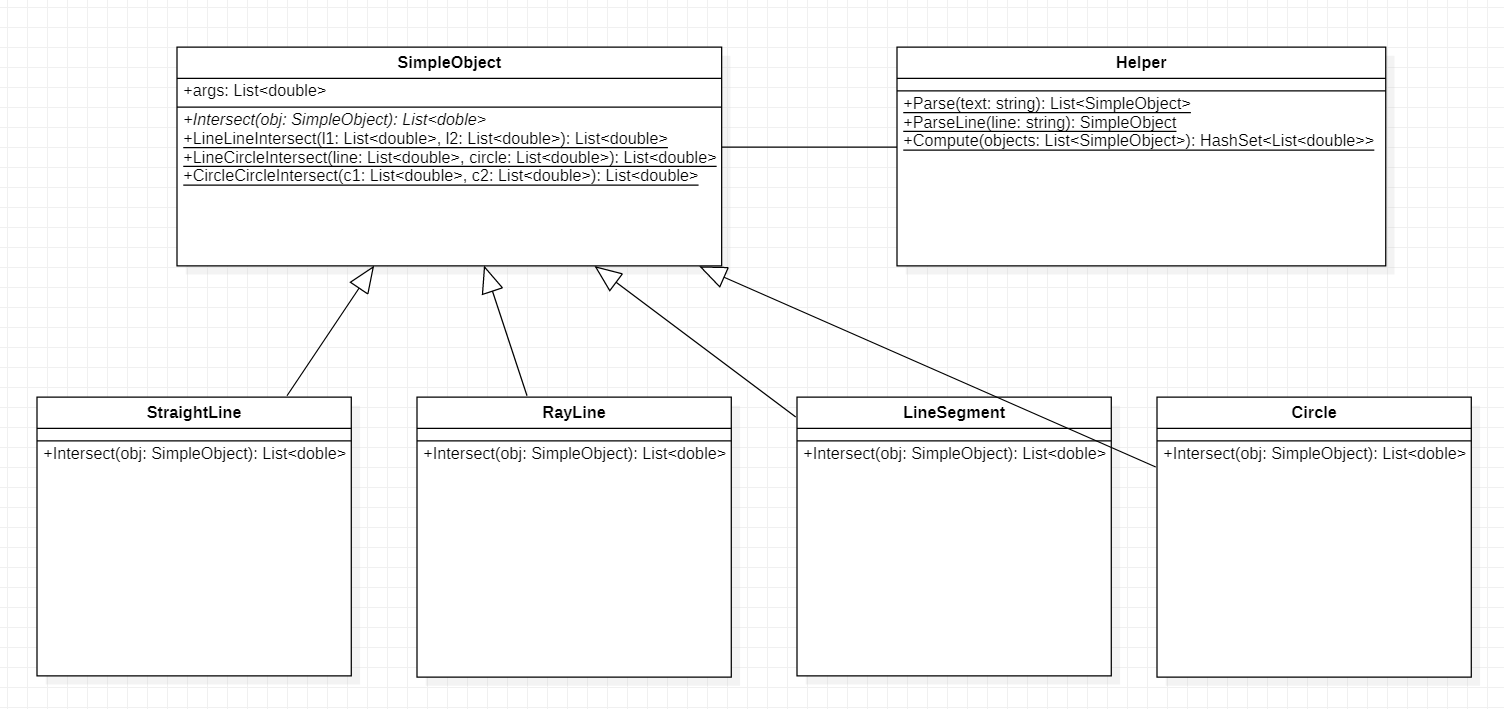
如下UML图,共有6各类.其中四个类表示几何对象.一个类是其基类.这些代表几何对象的类统一暴露出Intersect接口。核心函数是基类中的三个静态函数用于计算直线与直线、直线与圆、圆与圆的交点。然后在子类中利用这三个函数,外加判断交点是否在射线或线段上的条件,实现任意几何对象之间的交点计算。
之所以将辅助类也放入计算模块,是因为解析字符串、计算所有交点等一些函数ConsoleApp、UPWApp都会用到,故设计了一个静态类来进行代码复用。
UML类图
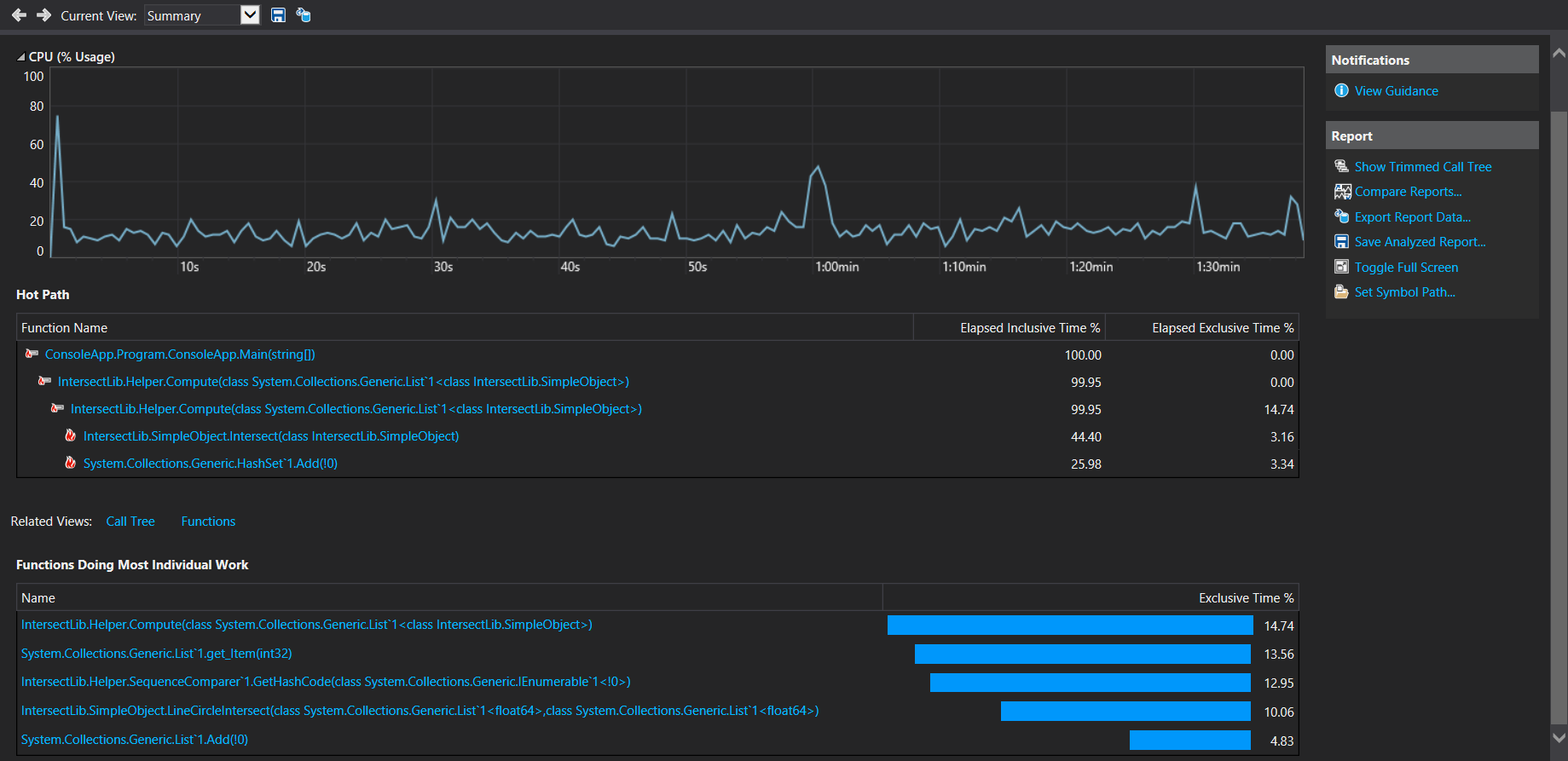
计算模块接口部分的性能改进
Design by Contract,Code Contract
契约式设计:希望程序员能够在设计程序时明确地规定一个模块单元(具体到面向对象,就是一个类的实例)在调用某个操作前后应当属于何种状态。它包含三个概念:前置条件,后置条件和不变式。
-
优点:调用者必须提供正确的参数,被调用者必须保证正确的结果和调用者要求的不变性,因此保证了双方代码的质量,是保证软件质量(可靠性)的手段。
-
缺点:对于程序语言有一定的要求,契约式编程需要一种机制来验证契约的成立与否。而断言显然是最好的选择,但是并不是所有的程序语言都支持断言。那么强行使用契约式设计就会造成代码的冗余和不可读性的提高。
计算模块部分单元测试展示
- 部分单元测试代码
直线和直线相交
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithStraightLine()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(straightLine);
List<double> answer = new List<double> { -1, 0 };
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
直线和射线相交
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithRayLine()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(rayLine2);
List<double> answer = new List<double> { -1, 0 };
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
直线和线段相交
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithLineSegmentNoIntersection()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(lineSegment);
List<double> answer = new List<double>();
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
直线和圆相交
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithCircle()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(circle);
List<double> answer = new List<double> { 0, 0 };
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
圆和直线相交
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithStraightLine()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(straightLine);
List<double> answer = new List<double> { 2, 0 };
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
圆和圆相切、相离、相交
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithCircle1()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(circle1);
List<double> answer = new List<double> { 2, 0 };
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithCircle2()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(circle2);
List<double> answer = new List<double>();
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer));
}
[Test]
public void TestIntersectWithCircle3()
{
List<double> result = test.Intersect(circle3);
List<double> answer1 = new List<double> { 1, Math.Sqrt(3), 1, -1 * Math.Sqrt(3) };
List<double> answer2 = new List<double> { 1, -1 * Math.Sqrt(3), 1, Math.Sqrt(3) };
Assert.IsTrue(Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer1) |
Enumerable.SequenceEqual(result, answer2));
}
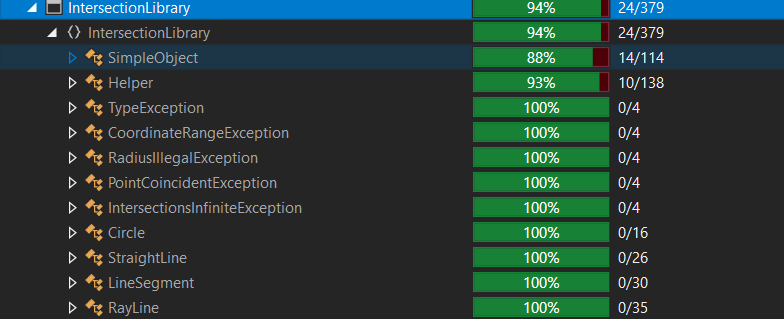
- 测试覆盖率94%
计算模块部分异常处理说明
| 异常 | 样例 | 场景 |
|---|---|---|
| TypeException | Q 1 2 3 4 | 用户输入不支持的几何类型 |
| CoordinateRangeException | L 100000 3 2 1 | 用户输入的坐标超出支持范围 |
| RadiusIllegalException | C 2 3 -3 | 用户输入的圆的坐标为负数 |
| PointCoincidentException | R 1 2 1 2 | 用户输入的点对重合 |
| IntersectionsInfiniteException | L 0 0 0 1 \n L 0 -1 0 -2 | 用户输入的直线、线段、射线对象部分重合使得交点无数个 |
[Test]
public void TestTypeException()
{
Assert.Throws<TypeException>(() => Helper.ParseLine("Q 1 2 3 4"));
}
[Test]
public void TestCoordinateRangeException()
{
Assert.Throws<CoordinateRangeException>(() => Helper.ParseLine("L 100000 3 2 1"));
}
[Test]
public void TestRadiusIllegalException()
{
Assert.Throws<RadiusIllegalException>(() => Helper.ParseLine("C 2 3 -3"));
}
[Test]
public void TestPointCoincidentException()
{
Assert.Throws<PointCoincidentException>(() => Helper.ParseLine("R 1 2 1 2"));
}
[Test]
public void TestIntersectionsInfiniteException()
{
Assert.Throws<IntersectionInfiniteException>(() => {
List<double> l1 = new List<double> { 0, 0, 0, 1 };
List<double> l2 = new List<double> { 0, -1, 0, -2 };
SimpleObject.LineLineIntersect(l1, l2);
});
}
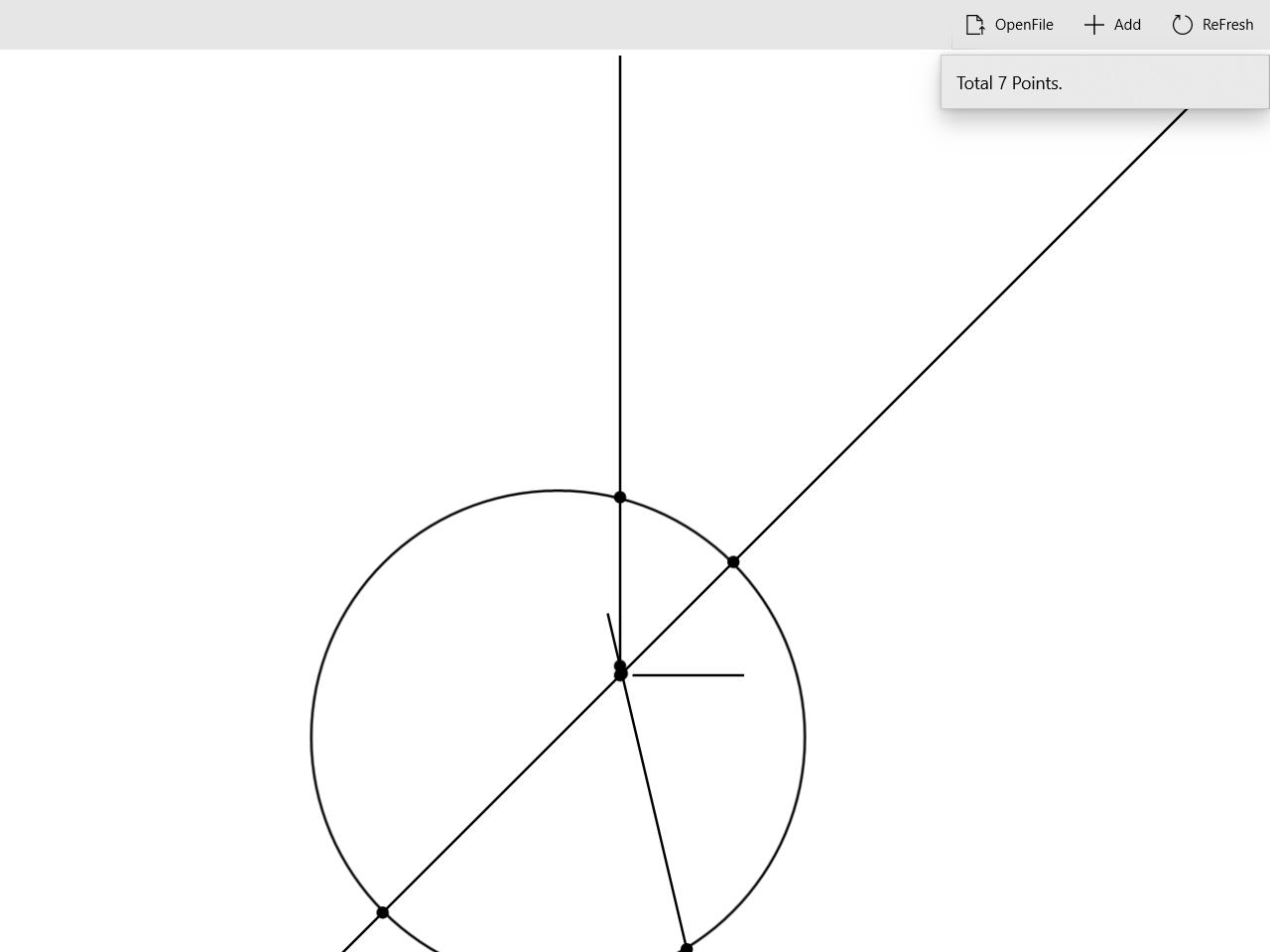
UI的详细设计过程
以下xaml文件定义了UI的主要界面.
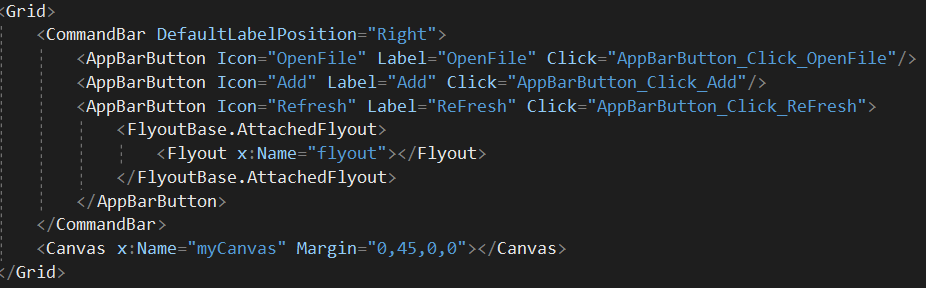
-
打开文件
点击
OpenFile按钮,触发AppBarButton_Click_OpenFile函数,该函数会打开win10的文件管理器。当用户选择文件后,将文件内容描绘出来。
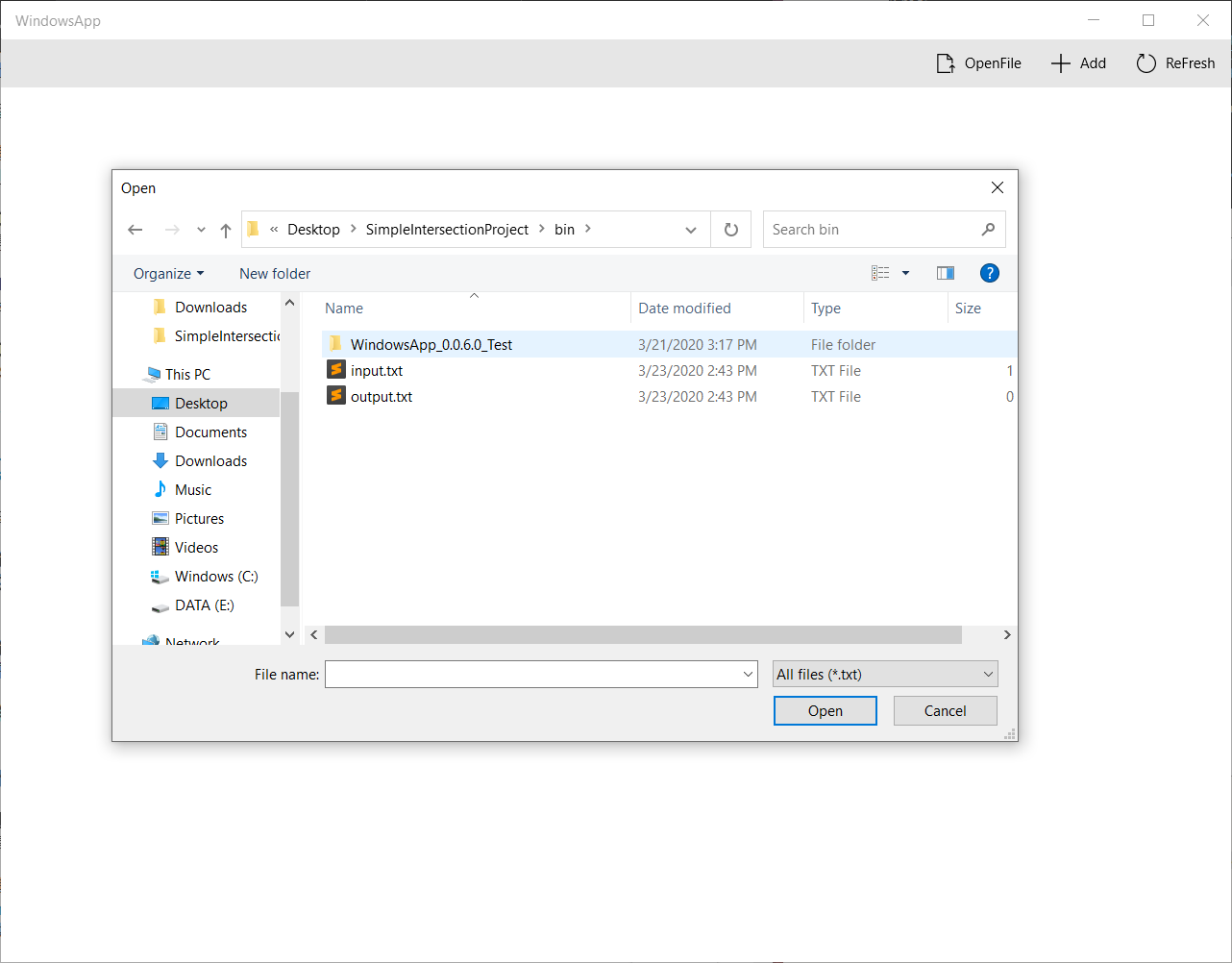
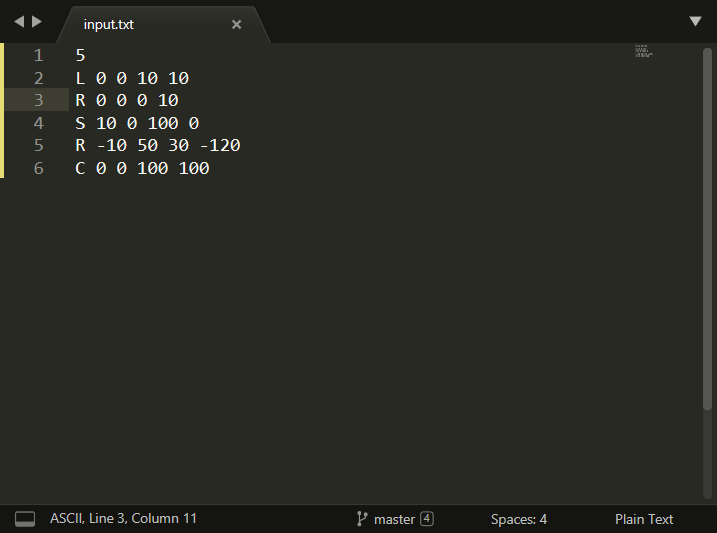
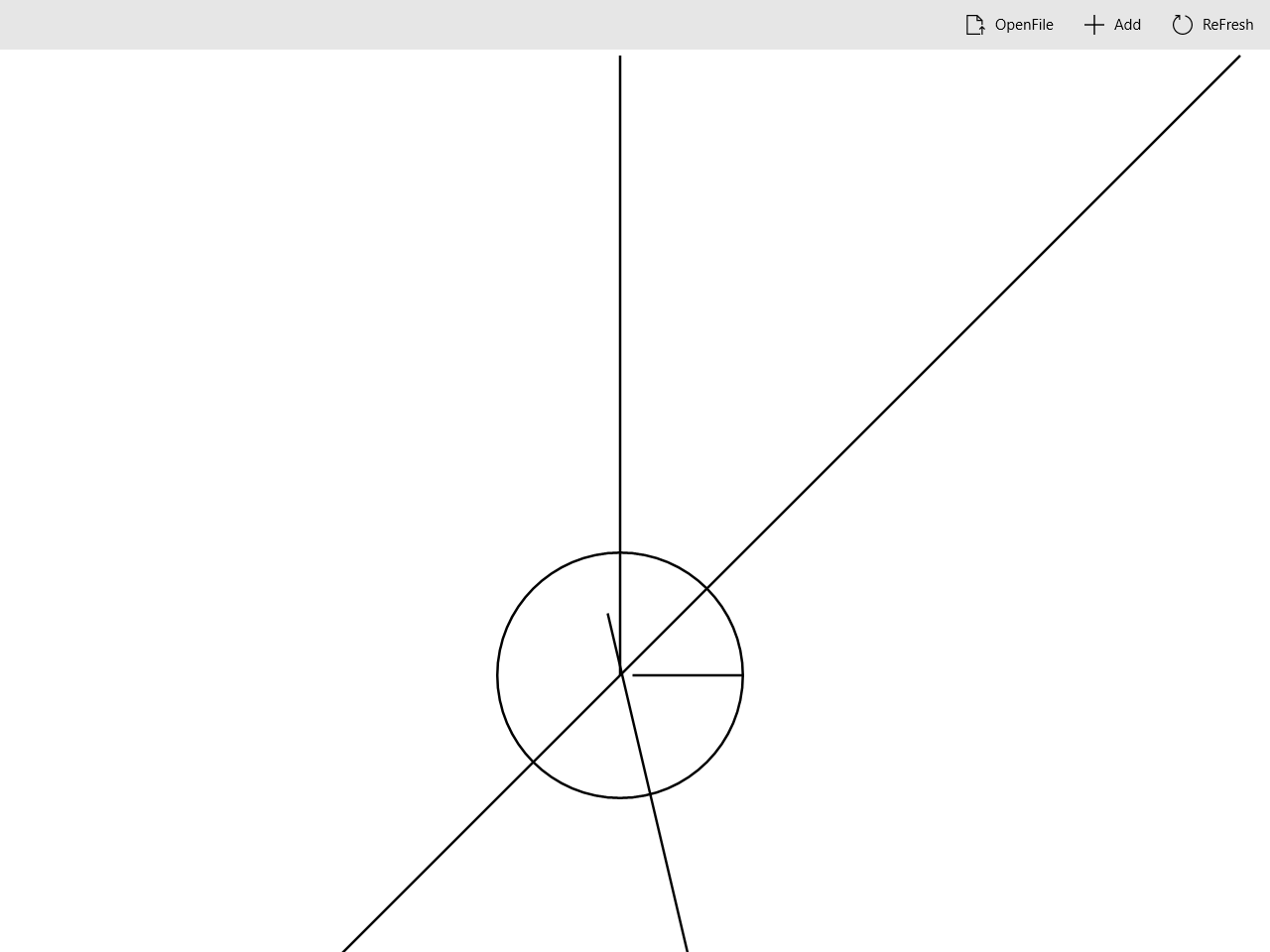
-
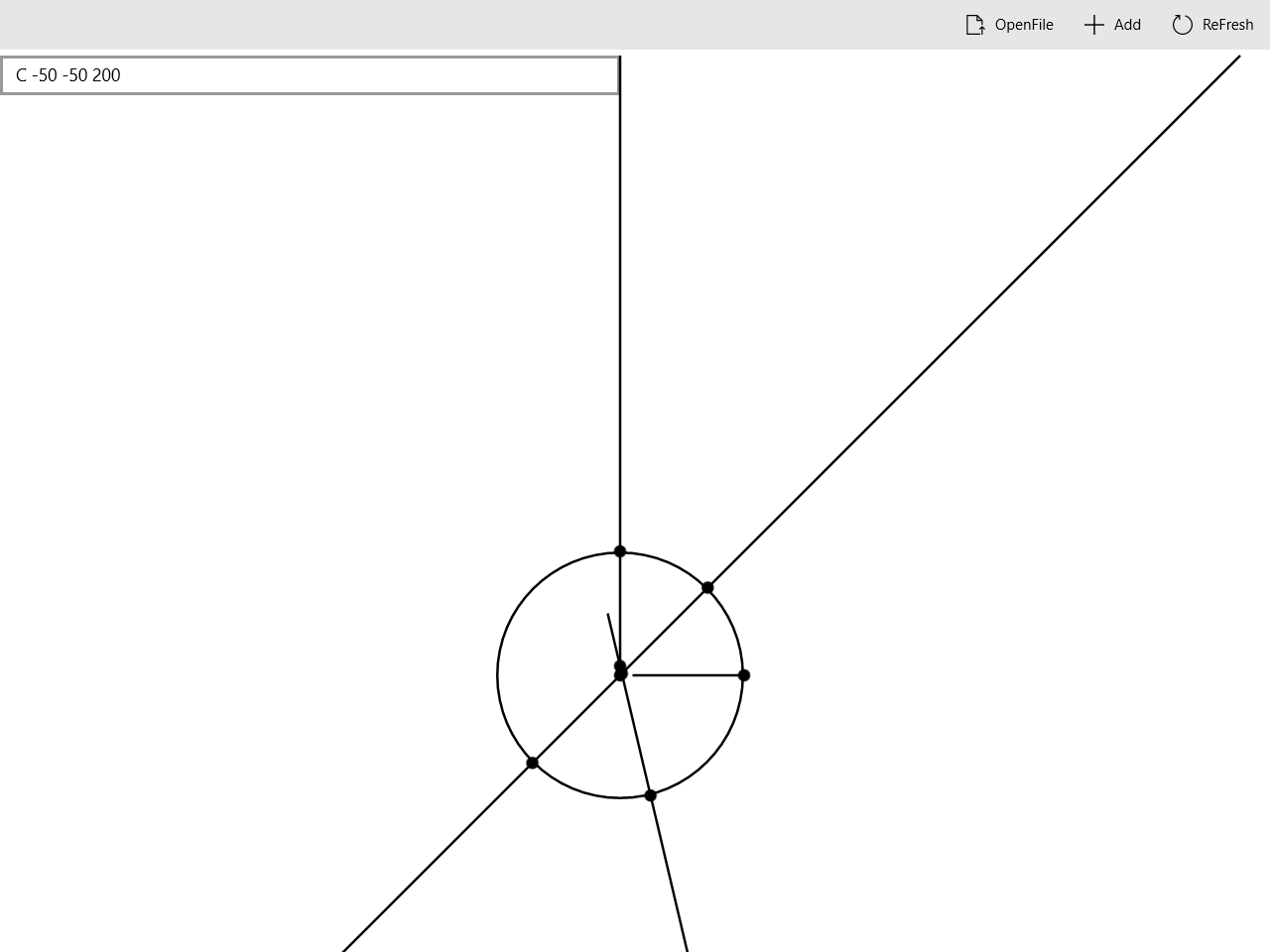
计算交点
点击
ReFresh按钮,会触发AppbarButton_Click_ReFresh函数,该函数计算交点个数并显示,同时绘制交点。
-
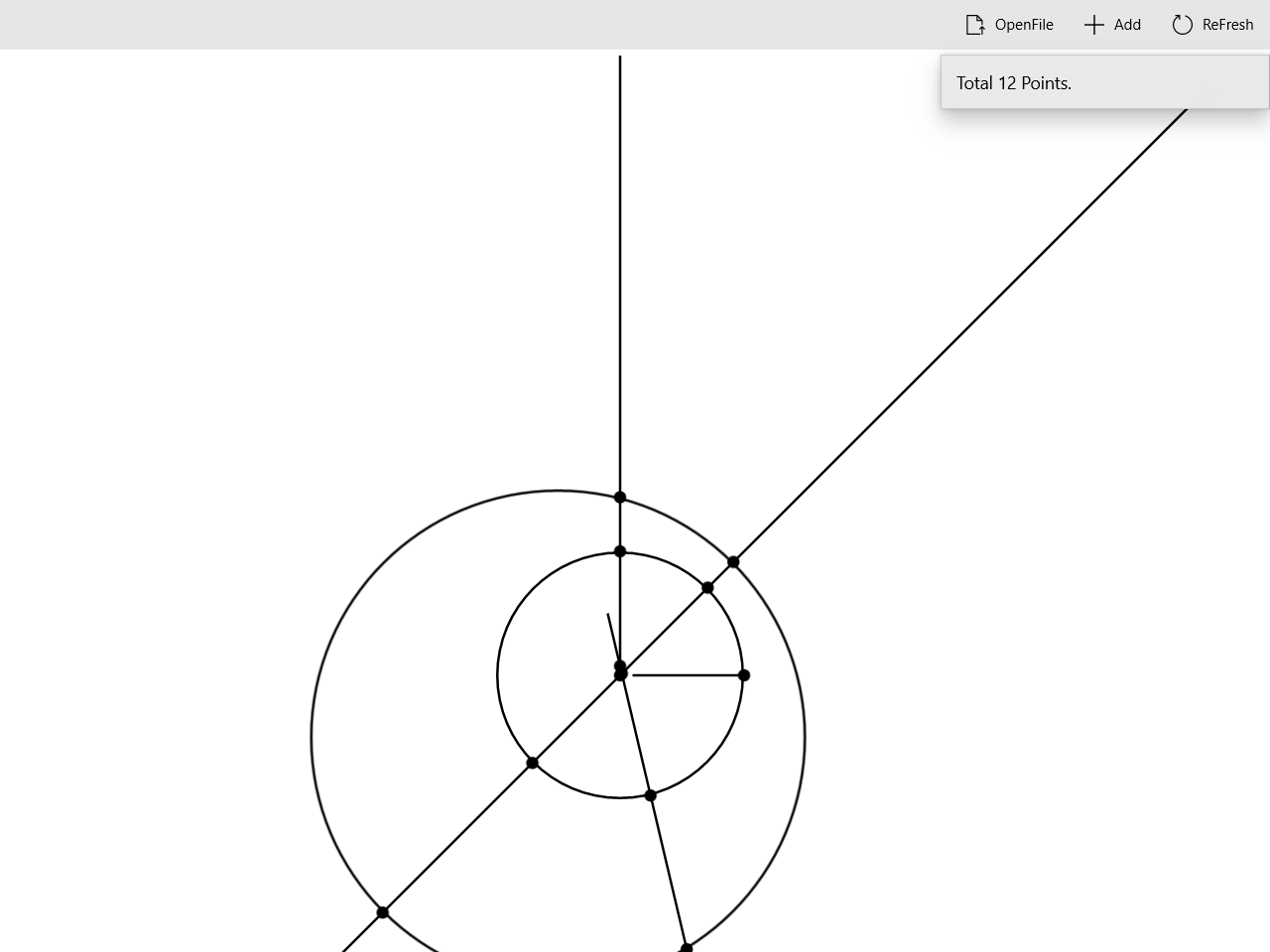
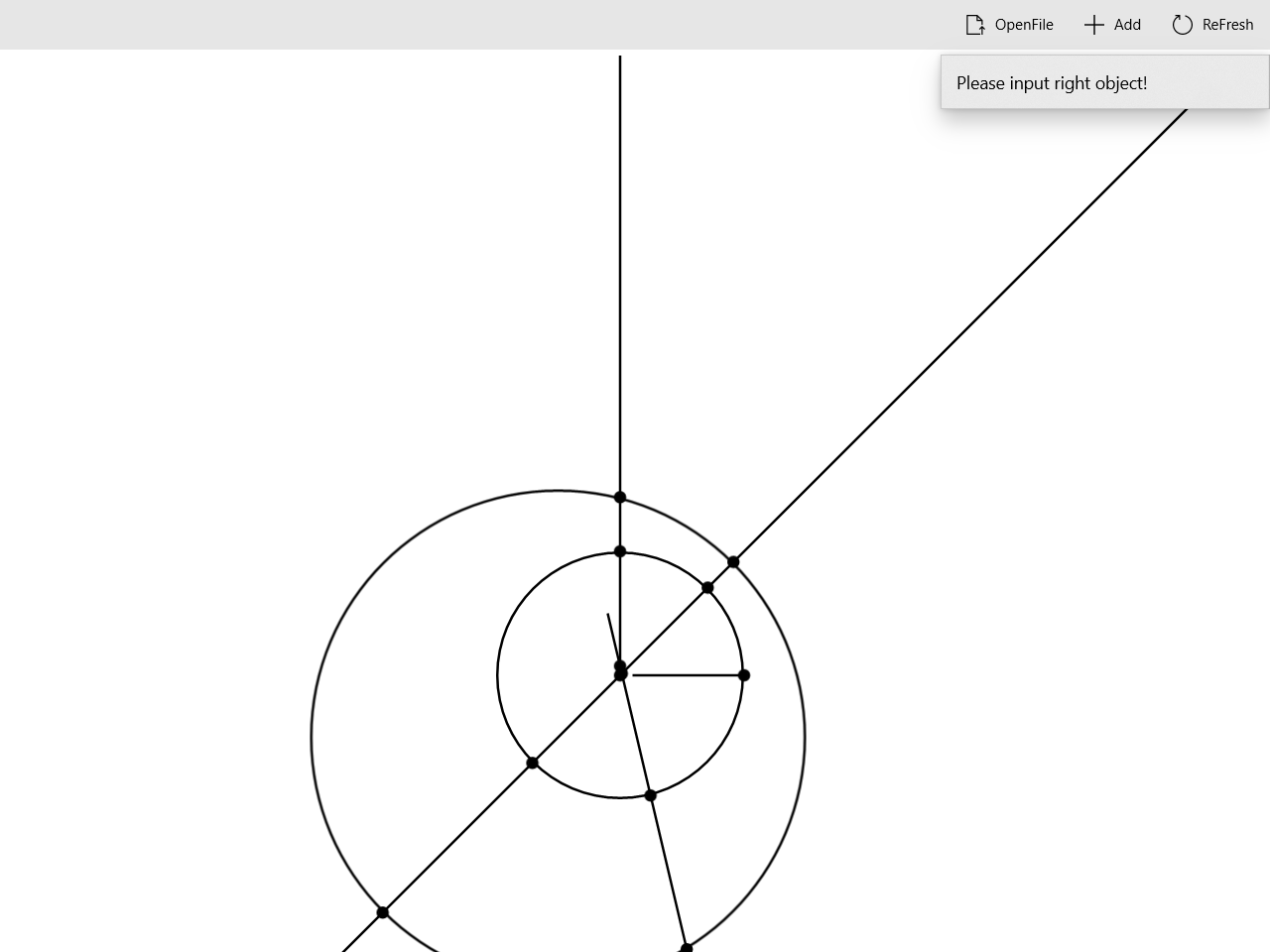
添加对象
点击
Add按钮,会触发AppBarButton_Click_Add函数,该函数提示对话框让用户需要添加的集合对象。若用户输入不合法,则进行提示。之后点击ReFresh按钮计算新的交点。
)

-
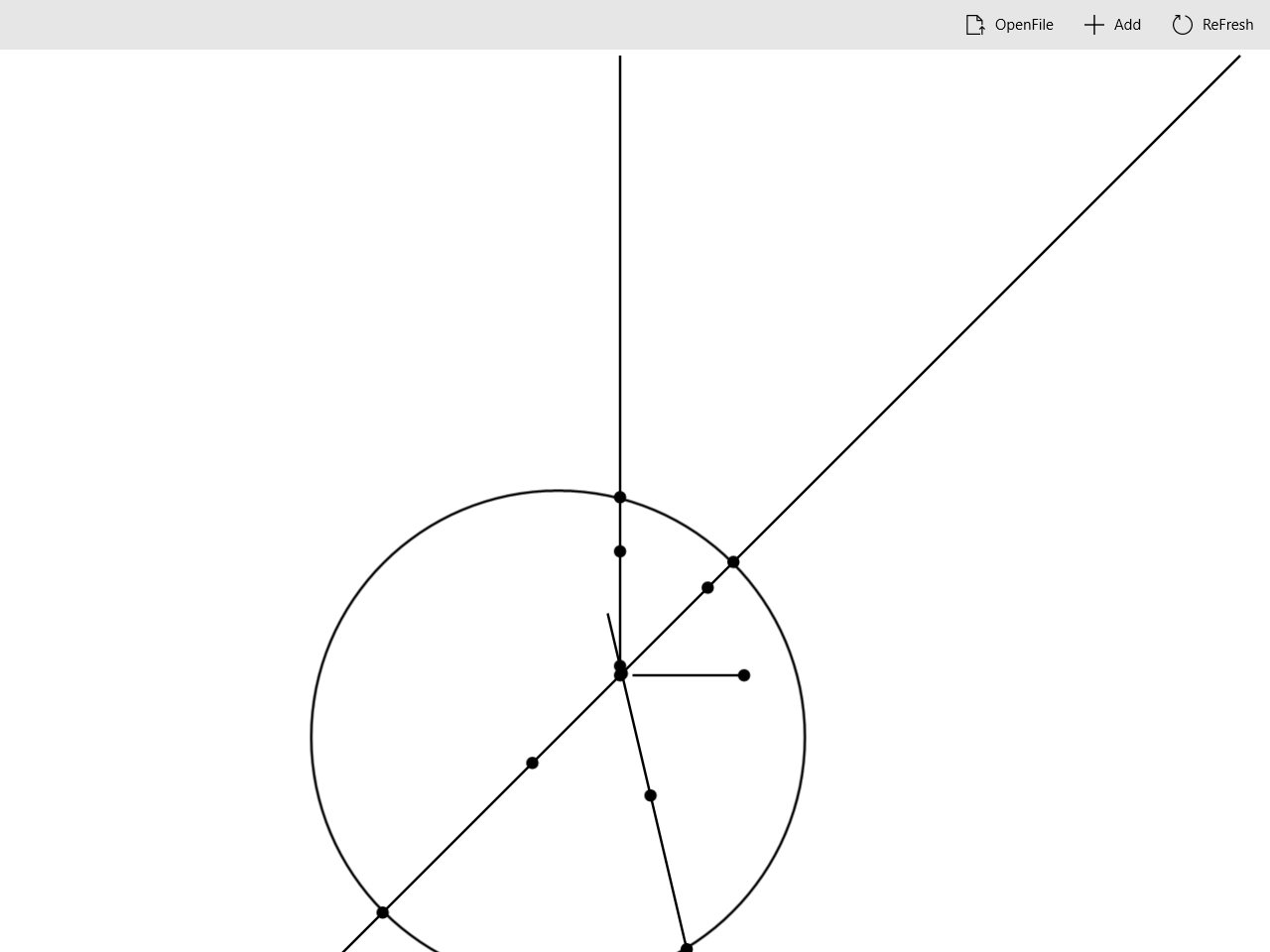
删除对象
鼠标双击需要删除的对象,会触发
Object_DoubleTapped函数,该函数删除该对象。之后点击ReFresh按钮计算会绘制。
UI 的完善方向:
- 实现画布的缩放与拖动
- 绘制坐标轴
- 优化交互流程
- 优化错误提示
界面模块与计算模块的对接
界面模块的设计采用了 MVC 的思想,分离 UI 代码和 Model 代码。对于UI部分,仅仅是交互逻辑,而把描绘、计算的任务放在了 Model 里。
在界面模块里,存储 SimpleObject 的列表,然后通过调用 Helper 里的函数来完成数据解析和计算。
如图,点击ReFresh会触发core模块里的Intersect函数

结对的过程
结对编程的优点和缺点
-
优点
结对编程能提供更好的设计质量和代码质量
结对工作可以给开发人员带来更多的信心
结对能更有效的交流、相互学习和传递经验从而共同进步
在编码过程中更容易发现隐藏的bug
-
缺点
与合不来的人一起编程容易发生争执,不利于团队和谐。
开发人员可能会在工作时交谈一些与工作无关的事,分散注意力,造成效率低下。
结对对象的优点和缺点
| 我 | 结对伙伴 | |
|---|---|---|
| 优点 | 高效负责;编程能力优秀;细致严谨 | 学习热情高;编程能力优秀;认真负责;有效沟通 |
| 缺点 | 沟通不够主动 | 测试不够细致 |
Code Quality Analysis