[数据结构]排序算法的性能比较
写在前面
菜鸡博主最近放寒假了,打算接下来的一段时间内回顾一下以前学过的一些知识,也是为考研做一些准备吧。很菜,勿喷,希望能和大家一起学习,共同进步!
主要目标和具体要求
目标
排序对于数据处理是一项十分重要和基础的工作。采用如下算法实现排序功能:插入排序、交换排序、选择排序、归并排序、基数排序等。统计每种排序算法的性能(以相同计算机运行程序所花费的时间为准进行对比),并将数据序列和不同算法的运行时间记录到txt文件中。
要求
设计排序系统,能够实现以下功能:
(1) 利用随机函数产生N个随机整数(50000以上);
(2) 对这些数字进行排序,包括递增和递减两种形式;
(3) 分别采用插入、折半插入、2-路插入、希尔、冒泡、快速、选择、锦标赛、堆、归并、基数等排序算法解决问题;
(4) 对不同的排序算法进行性能比较并记录结果。
环境
操作系统:Windows 11
编译器:visual studio 2022
使用的头文件:iostream, algorithm, ctime, cstdlib, cstring, fsteam
一些设计
1.Random函数
作用:生成范围在l-r内的随机数。
首先通过srand(time(0))设置时间种子,然后通过循环和语句rand()%(r-l+1)+1生成随机数,随机数的范围为1-32767。
2.save函数
作用:文件操作
首先定义flag标记换行,然后打开文件,如果不存在文件则新建,通过time()记录所用的时间,通过for循环输出排序结果(其中flag换行是通过每记录一个数据使flag自加,当flag==100时使用endl语句换行,同时重置flag=0),在输出完所有内容后关闭文件。
3.直接插入排序
将第一个元素看作是一个有序序列,后面n-1个元素看作无序序列,对后面未排序序列中第一个元素在这个有序序列中进行从后向前的扫描,找到合适的位置进行插入,将有序序列长度+1。循环操作,知道未排序序列长度为0。当前插入元素与有序序列中元素相等时,插入到相等元素后。
4.折半插入排序
运用二分查找,定义temp来记录当前待插元素在有序序列中的合适位置,对temp进行后移,在temp位置插入待插元素。
5.2-路插入排序
2-路插入排序是对插入排序的改进,通过在首尾同时进行插入,使用临时数组tmp,定义front和rear记录tmp数组中当前的最大值和最小值位置。如果当前插入元素比最小的要小,更新最小值位置,并且将最小值重新赋值;如果当前插入元素比最大的要大,更新最大值位置,并且将最大值重新赋值;如果在最大和最小之间,将比当前插入值大的进行后移,然后插入,同时更新最大值位置,最后将临时数组复制到原数组中。
6.希尔排序
选择一个增量序列
7.快速排序
先从数列中取出一个数作为基准数;分区过程:将比这个数大的数全放到它的右边,小于或等于它的数全放到它的左边;对左右两个区间重复第二步直到各区间只有一个数。本算法使用三数取中的方法取基准值:取序列中最左边、中间、最右边的三个数进行比较,以这三个数大小为中的元素作为基准值。
8.选择排序
将比当前未排序序列的首位元素较小的数据元素交换到首位,最后每一趟比较都会将当前最小的元素交换到为排序序列的首位。改进后,通过定义min来确定未排序序列中的最小元素位置。
9.锦标赛排序
树形选择排序,由于其特殊性质,锦标赛排序构成的图结构是满二叉树。定义一个tree[]数组来储存满二叉树,录入叶子节点(需要排序的所有元素),因为二叉树某结点的下标为i,它的左右孩子节点下标必为2i+1和2i+2,因此比较叶子节点的值,可以得到父节点的值(两个叶子节点的值较小的那个),每次得到当前最小值的时候,通过minindex在tree[]中找到最小值的地址,将其设为MAX。
10.堆排序
使用大根堆对数组进行正向排序。
首先将当前的无序数组构成一个无序堆,某结点的下标为i,它的左右孩子节点下标必为2i+1和2i+2,然后将当前的无序堆进行调整至大根堆形成。接着交换首位元素(将当前堆顶的最大元素交换到末尾,将此元素归位。因为交换完首位元素后堆会再次变成一个无序堆,需要对剩余元素进行调整至重新变成大根堆。)重复操作至堆的大小为1完成堆排序。
11.归并排序
将长度为n的序列分解成两个长度为n/2的子序列,递归排序两个连续子序列,合并两个已经排序的连续子序列构成一个完整排序的序列。
12.基数排序
定义一个count[]数组(大小为10,下标0-9)用于统计每一位数字出现的次数,一个大小为n的临时数组tmp[]用于储存按照当前以为数字排序后的序列。进行d次排序,每次分配前先清空计数器,从低位开始,统计每一位数字出现的个数记录到count[]中,由递推式
13.计时
使用clock_t库,定义start和end,将不同的排序算法写在start和end之间,定义duration=(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC来输出需要的时间并打印。
源代码
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<ctime> #include<time.h> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<fstream> using namespace std; #define random(x) rand() % (x) void save(int a[], string str, double time) { int flag = 0;//标记换行 fstream f; f.open("data.txt", ios::out | ios::app); f << str << "所用的时间:" << time << "s" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) { flag++; f << a[i] << "-"; if (flag == 100) { f << endl; flag = 0; } } f << endl << endl; f.close(); } //生成范围在l~r的随机数 void Random(int* a, int n, int l, int r) { srand(time(0));//设置时间种子 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { a[i] = rand() % (r - l + 1) + 1;//生成随机数 } } //打印(测试用) void Print(int* a, int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << a[i] << " "; cout << endl; } //直接插入排序(正向) void InsertSort_up(int a[], int n) { int temp, i, j; for (i = 1; i < n; i++) { if (a[i] < a[i - 1]) { temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[i - 1]; for (j = i - 2; j >= 0 && a[j] > temp; --j) { a[j + 1] = a[j]; } a[j + 1] = temp; } } } //直接插入排序(逆向) void InsertSort_down(int a[], int n) { int temp, i, j; for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { int end = i + 1; int temp = a[end]; if (a[end] > a[i]) { while (end > 0 && temp > a[end - 1]) { a[end] = a[end - 1]; end--; } } a[end] = temp; } } //折半插入排序(正向) void BinaryInsertionSort_up(int a[], int left, int right) { int i, j; int mid, temp; i = left, j = right; mid = a[(left + right) >> 1]; do { while (a[i] < mid && (i < right)) i++; while (a[j] > mid && (j > left)) j--; if (i <= j) { temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; i++; j--; } } while (i <= j); if (left < j) BinaryInsertionSort_up(a, left, j); if (right > i) BinaryInsertionSort_up(a, i, right); } //折半插入排序(逆向) void BinaryInsertionSort_down(int a[], int n) { BinaryInsertionSort_up(a, 0, n - 1); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //2-路插入排序(正向) void TwoInsertSort_up(int a[], int n) { int* tmp = new int[n]; //临时数组 int front = 0, rear = 0; //记录当前tmp数组中最大值和最小值的位置 tmp[0] = a[0]; //初始化tmp for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { int key = a[i]; //如果当前插入的元素比最小的元素更小 if (key < tmp[front]) { front = (front - 1 + n) % n; tmp[front] = key; } //如果当前插入元素比最大元素更大 else if (key > tmp[rear]) { rear = (rear + 1 + n) % n; tmp[rear] = key; } //如果在当前最小和最大之间 else { int k = (rear + n) % n; //将比当前插入值key大的进行后移 while (tmp[(k + n) % n] > key) { tmp[(k + 1 + n) % n] = tmp[(k + n) % n]; k = (k - 1 + n) % n; } tmp[(k + 1 + n) % n] = key; //当前插入值放到合适位置 rear = (rear + 1 + n) % n; //更新最大值位置(有序序列长度+1) } } //复制临时数组到原数组中 for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) a[k] = tmp[(front + k) % n]; delete[] tmp; } //2-路插入排序(逆向) void TwoInsertSort_down(int a[], int n) { int* tmp = new int[n]; //临时数组 int front = 0, rear = 0; //记录当前tmp数组中最大值和最小值的位置 tmp[0] = a[0]; //初始化tmp for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { int key = a[i]; //如果当前插入的元素比最小的元素更小 if (key < tmp[front]) { front = (front - 1 + n) % n; tmp[front] = key; } //如果当前插入元素比最大元素更大 else if (key > tmp[rear]) { rear = (rear + 1 + n) % n; tmp[rear] = key; } //如果在当前最小和最大之间 else { int k = (rear + n) % n; //将比当前插入值key大的进行后移 while (tmp[(k + n) % n] > key) { tmp[(k + 1 + n) % n] = tmp[(k + n) % n]; k = (k - 1 + n) % n; } tmp[(k + 1 + n) % n] = key; //当前插入值放到合适位置 rear = (rear + 1 + n) % n; //更新最大值位置(有序序列长度+1) } } //复制临时数组到原数组中 for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) a[k] = tmp[(front + k) % n]; reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]);//倒序 delete[] tmp; } //希尔排序(正向) void ShellSort_up(int a[], int n) { int temp = n;//初始化增量 while (temp > 1)//最后一次增量为1 { temp = temp / 3 + 1; for (int i = temp; i < n; i++) { int key = a[i];//当前需要插入的数 int j = i - temp; while (j >= 0 && a[j] > key) { a[j + temp] = a[j]; j -= temp; } a[j + temp] = key; } } } //希尔排序(逆向) void ShellSort_down(int a[], int n) { int temp = n;//初始化增量 while (temp > 1)//最后一次增量为1 { temp = temp / 3 + 1; for (int i = temp; i < n; i++) { int key = a[i];//当前需要插入的数 int j = i - temp; while (j >= 0 && a[j] > key) { a[j + temp] = a[j]; j -= temp; } a[j + temp] = key; } } reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //快速排序(正向) int GetMid(int a[], int left, int right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (a[left] < a[mid]) if (a[mid] < a[right]) return mid; else if (a[left] < a[right]) return right; else return left; else if (a[mid] > a[right]) return right; else return left; } int PartitionBetter(int a[], int left, int right) { int pos = GetMid(a, left, right); swap(a[pos], a[left]); int i = left; int j = right; int key = a[left]; while (i != j) { while (i < j && a[j] >= key) j--; while (i < j && a[i] <= key) i++; swap(a[i], a[j]); } swap(a[i], a[left]); return i; } void QuickSort_up(int a[], int left, int right) { if (left >= right) return; int i = PartitionBetter(a, left, right); QuickSort_up(a, left, i - 1); QuickSort_up(a, i + 1, right); } //快速排序(逆向) void QuickSort_down(int a[], int n) { QuickSort_up(a, 0, n - 1); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //选择排序(正向) void SelectSort_up(int a[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int min = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (a[min] > a[j]) min = j; } swap(a[i], a[min]); } } //选择排序(逆向) void SelectSort_down(int a[], int n) { SelectSort_up(a, n); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //锦标赛排序(正向) void TreeSelectSort_up(int a[], int n) { int sum = n * 2 - 1;//满二叉树节点总数 int* tree = new int[sum]; //输入叶子节点 for (int i = n - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++) tree[sum - j - 1] = a[i]; //非叶子节点 for (int i = sum - n - 1; i >= 0; i--) tree[i] = tree[2 * i + 1] < tree[2 * i + 2] ? tree[2 * i + 1] : tree[2 * i + 2]; int k = 0; int minindex = -1; while (k < n) { int min = tree[0]; a[k++] = min; minindex = sum - 1; //从最后叶子节点开始找到最小值的位置,将其设置为MAXIUM while (tree[minindex] != min) minindex--; tree[minindex] = INT_MAX; //若该节点有父节点,将其兄弟结点提升为父节点 while (minindex > 0) { if (minindex % 2 == 1) { tree[(minindex - 1) / 2] = tree[minindex] < tree[minindex + 1] ? tree[minindex] : tree[minindex + 1]; minindex = (minindex - 1) / 2; } else { tree[minindex / 2 - 1] = tree[minindex] < tree[minindex - 1] ? tree[minindex] : tree[minindex - 1]; minindex = minindex / 2 - 1; } } } delete[] tree; } //锦标赛排序(逆向) void TreeSelectSort_down(int a[], int n) { TreeSelectSort_up(a, n); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //堆排序(正向) void Heapify(int a[], int i, int n) { int left = 2 * i + 1, right = 2 * i + 2;//二叉树当前节点的左右节点 int max = i;//默认i为最大值 if (left < n && a[left]>a[max]) max = left; if (right <n && a[right]>a[max]) max = right; if (max != i) { //调整最大值到非叶子节点处 swap(a[i], a[max]); //互换后,子节点变化,若子节点有其子节点仍需调整,递归 Heapify(a, max, n); } } void HeapSort_up(int a[], int n) { for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)//构建大根堆 Heapify(a, i, n); while (n > 1) { swap(a[0], a[n - 1]);//交换首位数据,尾部最大 Heapify(a, 0, --n);//重置大根堆 } } //堆排序(逆向) void HeapSort_down(int a[], int n) { HeapSort_up(a, n); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //归并排序(正向) void Merge(int a[], int left, int mid, int right) { int* temp = new int[right - left + 1]; int i = left, j = mid + 1, k = 0; while (i <= mid && j <= right) { if (a[i] < a[j]) { temp[k] = a[i]; i++; } else { temp[k] = a[j]; j++; } k++; } while (i <= mid) { temp[k] = a[i]; i++; k++; } while (j <= right) { temp[k] = a[j]; j++; k++; } i = left; for (int tempK = 0; ((tempK < k) && (i <= right)); tempK++) { a[i] = temp[tempK]; i++; } delete[] temp; temp = NULL; } void MergeSort_up(int a[], int left, int right) { if (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; MergeSort_up(a, left, mid); MergeSort_up(a, mid + 1, right); Merge(a, left, mid, right); } } //归并排序(逆向) void MergeSort_down(int a[], int n) { MergeSort_up(a, 0, 50000); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } //基数排序(正向) //求数据的最大位数, 决定排序次数 int maxbit(int a[], int n) { int d = 1; //保存最大的位数 int p = 10; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { while (a[i] >= p) { p *= 10; ++d; } } return d; } void RadixSort_up(int a[], int n) //基数排序 { int d = maxbit(a, n); int tmp[50001]; int count[10]; //计数器 int i, j, k; int radix = 1; for (i = 1; i <= d; i++) //进行d次排序 { for (j = 0; j < 10; j++) count[j] = 0; //每次分配前清空计数器 for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { k = (a[j] / radix) % 10; //统计每个桶中的记录数 count[k]++; } for (j = 1; j < 10; j++) count[j] = count[j - 1] + count[j]; //将tmp中的位置依次分配给每个桶 for (j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) //将所有桶中记录依次收集到tmp中 { k = (a[j] / radix) % 10; tmp[count[k] - 1] = a[j]; count[k]--; } for (j = 0; j < n; j++) //将临时数组的内容复制到a中 a[j] = tmp[j]; radix = radix * 10; } } //基数排序(逆向) void RadixSort_down(int a[], int n) { RadixSort_up(a, n); reverse(&a[0], &a[50001]); } int main() { srand(time(0)); clock_t start1, end1; clock_t start2, end2; clock_t start3, end3; clock_t start4, end4; clock_t start5, end5; clock_t start6, end6; clock_t start7, end7; clock_t start8, end8; clock_t start9, end9; clock_t start10, end10; clock_t start11, end11; clock_t start12, end12; clock_t start13, end13; clock_t start14, end14; clock_t start15, end15; clock_t start16, end16; clock_t start17, end17; clock_t start18, end18; clock_t start19, end19; clock_t start20, end20; double duration; int a[50001]; int n = 50001;//数组元素的个数,即随机数的个数 Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start9 = clock(); QuickSort_up(a, 0, n - 1); end9 = clock(); duration = (double)(end9 - start9) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "快速排序(正向)", duration); cout << "快速排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start10 = clock(); QuickSort_down(a, n); end10 = clock(); duration = (double)(end10 - start10) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "快速排序(反向)", duration); cout << "快速排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start1 = clock(); InsertSort_up(a, n); end1 = clock(); duration = (double)(end1 - start1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "直接插入排序(正向)", duration); cout << "直接插入排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start2 = clock(); InsertSort_down(a, n); end2 = clock(); duration = (double)(end2 - start2) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "直接插入排序(反向)", duration); cout << "直接插入排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start3 = clock(); BinaryInsertionSort_up(a, 0, n - 1); end3 = clock(); duration = (double)(end3 - start3) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "折半插入排序(正向)", duration); cout << "折半插入排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start4 = clock(); BinaryInsertionSort_down(a, n); end4 = clock(); save(a, "折半插入排序(反向)", duration); cout << "折半插入排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start5 = clock(); TwoInsertSort_up(a, n); end5 = clock(); duration = (double)(end5 - start5) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "2-路插入排序(正向)", duration); cout << "2-路插入排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start6 = clock(); TwoInsertSort_down(a, n); end6 = clock(); duration = (double)(end6 - start6) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "2-路插入排序(反向)", duration); cout << "2-路插入排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start7 = clock(); ShellSort_up(a, n); end7 = clock(); duration = (double)(end7 - start7) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "希尔排序(正向)", duration); cout << "希尔排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start8 = clock(); ShellSort_down(a, n); end8 = clock(); duration = (double)(end8 - start8) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "希尔排序(反向)", duration); cout << "希尔排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start11 = clock(); SelectSort_up(a, n); end11 = clock(); duration = (double)(end11 - start11) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "选择排序(正向)", duration); cout << "选择排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start12 = clock(); SelectSort_down(a, n); end12 = clock(); duration = (double)(end12 - start12) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "选择排序(反向)", duration); cout << "选择排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start13 = clock(); TreeSelectSort_up(a, n); end13 = clock(); duration = (double)(end13 - start13) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "锦标赛排序(正向)", duration); cout << "锦标赛排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start14 = clock(); TreeSelectSort_down(a, n); end14 = clock(); duration = (double)(end14 - start14) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "锦标赛排序(反向)", duration); cout << "锦标赛排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start15 = clock(); HeapSort_up(a, n); end15 = clock(); duration = (double)(end15 - start15) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "堆排序(正向)", duration); cout << "堆排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start16 = clock(); HeapSort_down(a, n); end16 = clock(); duration = (double)(end16 - start16) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "堆排序(反向)", duration); cout << "堆排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start17 = clock(); MergeSort_up(a, 0, 50000); end17 = clock(); duration = (double)(end17 - start17) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "归并排序(正向)", duration); cout << "归并排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start18 = clock(); MergeSort_down(a, 50001); end18 = clock(); duration = (double)(end18 - start18) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "归并排序(反向)", duration); cout << "归并排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start19 = clock(); RadixSort_up(a, n); end19 = clock(); duration = (double)(end19 - start19) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "基数排序(正向)", duration); cout << "基数排序(正向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; Random(a, n, 1, 32767); start20 = clock(); RadixSort_down(a, n); end20 = clock(); duration = (double)(end20 - start20) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; save(a, "基数排序(反向)", duration); cout << "基数排序(反向):" << duration << "seconds" << endl; return 0; }
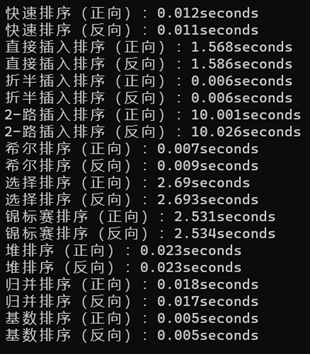
运行结果
本文作者:拂云堂 诩言
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanyy-home/p/17978152
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步