二叉树遍历汇总
二叉树的遍历
二叉树的遍历有递归遍历,分别为前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历。
这三种遍历的差别,是根节点的访问顺序,
- 前序遍历
先访问根节点,然后访问左子树,最后访问右子树 - 中序遍历
先访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后访问右子树 - 后序遍历
先访问左子树,然后访问右子树,最后访问根节点
非递归遍历,上述遍历都可以将递归遍历,改为非递归的遍历,本文介绍,层次遍历,
就是一层一层地去遍历。本文的层次遍历有两种方式,如下:
4. 从上至下,一个节点一个节点的去打印,打印的时候,看不出层次。
5. 从上至下,一个节点一个节点的去打印,打印是分层次的。
层次遍历主要用到queue的数据结构,每访问到一个节点时,如果它有左节点,就放入队列,
如果它有右节点就放入队列,这样便可以遍历完整棵树了。
针对以上5中遍历,用如下的例子说明,
有如下的一个二叉树:

遍历结果分别为:
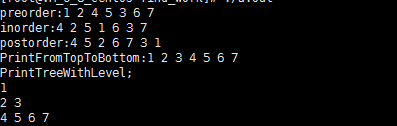
- 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
- 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
- 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
5 . 1
2 3
4 5 6 7
实现的代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x):val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}};
int i = 0;
struct TreeNode *buildTree(int n)
{
if (i == n) {
return NULL;
}
/*
if( (i&0x1) ){
++i;
return NULL;
}
*/
struct TreeNode *node;
node = new struct TreeNode (i);
// node->val = i;
++i;
node->left = buildTree(n);
node->right = buildTree(n);
return node;
/*
struct TreeNode *root= NULL,*p =NULL,*node;
node = new struct TreeNode();
node->val = i;
node->left = NULL:
node->right = NULL;
++i;
if( root == NULL){
root = p = node;
continue;
}
if(p->left == NULL){
p->left = node;
}else{
}
return root;
*/
}
struct TreeNode *buildTree2()
{
struct TreeNode *root = NULL, *p = NULL, *node;
struct TreeNode *nodes[8];
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) {
nodes[i] = new struct TreeNode (i);
}
nodes[1]->left = nodes[2];
nodes[1]->right = nodes[3];
nodes[2]->left = nodes[4];
nodes[2]->right = nodes[5];
nodes[3]->left = nodes[6];
nodes[3]->right = nodes[7];
return nodes[1];
}
class Solution {
public:
void PreorderTraversal(TreeNode * root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
cout << root->val << " ";
PreorderTraversal(root->left);
PreorderTraversal(root->right);
}
void InorderTraversal(TreeNode * root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
InorderTraversal(root->left);
cout << root->val << " ";
InorderTraversal(root->right);
}
void PostorderTraversal(TreeNode * root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
PostorderTraversal(root->left);
PostorderTraversal(root->right);
cout << root->val << " ";
}
vector < int >PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode * root) {
vector < int >res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
queue < TreeNode * >q;
q.push(root);
cout << "PrintFromTopToBottom:";
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = q.front();
cout << node->val << " ";
q.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left != NULL) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
cout << endl;
return res;
}
vector < int >PrintTreeWithLevel(TreeNode * root) {
vector < int >res;
if (root == NULL)
return res;
queue < TreeNode * >q;
q.push(root);
int curLevel = 1;
int count = 0;
int nextLevel = 0;
cout << "PrintTreeWithLevel;" << endl;
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *node = q.front();
cout << node->val << " ";
q.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
++count;
/*
if(count == curLevel){
cout<<endl;
curLevel = nextLevel;
nextLevel = 0;
count = 0;
} */
if (node->left != NULL) {
q.push(node->left);
++nextLevel;
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
q.push(node->right);
++nextLevel;
}
if (count == curLevel) {
cout << endl;
curLevel = nextLevel;
nextLevel = 0;
count = 0;
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
TreeNode *root = NULL;
int n = 5;
// root = buildTree(5);
root = buildTree2();
cout << "preorder:";
s.PreorderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "inorder:";
s.InorderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "postorder:";
s.PostorderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
s.PrintFromTopToBottom(root);
// cout<<"PrintTreeWithLevel:"<<endl;
s.PrintTreeWithLevel(root);
return 0;
}
程序结果如下:
作者: 盛夏落木
出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/wanshuafe/
关于作者:专注云存储,文件系统领域,请多多赐教!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出, 原文链接 如有问题, 可邮件(wanshuafe@163.com)咨询.



