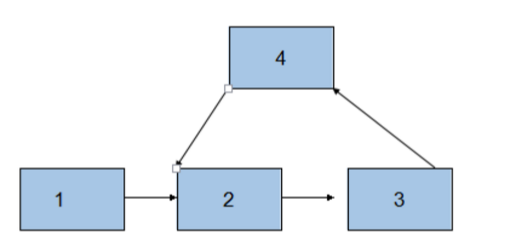
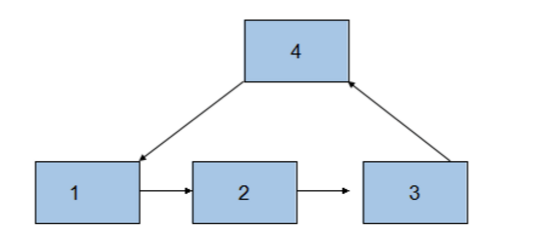
12.如果单链表有环,如何求出它的长度呢?
那怎么求出环的长度呢?
思路:这里面,我们需要先利用上一个题目的hasCycle方法(判断链表是否有环的那个方法),这个方法的返回值是
boolean型,但是现在要把这个方法稍做修改,让其返回值为相遇的那个结点。然后,我们拿到这个相遇的结点就好办了,这个结点肯定是在环里嘛,我们可以让
这个结点对应的指针一直往下走,直到它回到原点,就可以算出环的长度了。
方法:
// 方法:检测单链表是否有环 public Node hasCycle(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } Node first = head; Node second = head; while (second != null) { first = first.next; second = second.next.next; if (first == second) {// 一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的 return first; } } return null; } // 方法:有环链表中,获取环的长度。参数node代表的是相遇的那个结点 public int getCycleLength(Node node) { if (head == null) { return 0; } current = node; int length = 0; while (current != null) { current = current.next; length++; if (current == node) { return length;// 当current结点走到原点的时候 } } return length; }
测试代码:
public class LinkCycleLength { public Node head; public Node current; // 向链表中添加数据 public void add(int data) { // 判断链表为空的时候 if (head == null) {// 如果头结点为空,说明这个链表还没有创建,那就把新的结点赋给头节点 head = new Node(data); current = head; } else { current.next = new Node(data);// 创建新的结点,放在当前节点的后面(把新的节点和链表进行关联) current = current.next;// 把链表的当前索引向后移动一位,此步操作完成之后,current结点指向新添加的那个结点 } } // 方法重载:向链表中添加结点 public void add(Node node) { if (node == null) { return; } if (head == null) { head = node; current = head; } else { current.next = node; current = current.next; } } // 方法:遍历链表(打印输出链表。方法的参数表示从节点node开始进行遍历 public void print(Node node) { if (node == null) { return; } current = node; while (current != null) { System.out.println(current.data); current = current.next; } } class Node { // 注:此处的两个成员变量权限不能为private,因为private的权限是仅对本类访问 int data;// 数据域 Node next;// 指针域 public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } public int getData() { return data; } public void setData(int data) { this.data = data; } public Node getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node next) { this.next = next; } } // 方法:检测单链表是否有环 public Node hasCycle(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } Node first = head; Node second = head; while (second != null) { first = first.next; second = second.next.next; if (first == second) {// 一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的 return first; } } return null; } // 方法:有环链表中,获取环的长度。参数node代表的是相遇的那个结点 public int getCycleLength(Node node) { if (head == null) { return 0; } current = node; int length = 0; while (current != null) { current = current.next; length++; if (current == node) { return length;// 当current结点走到原点的时候 } } return length; } public static void main(String[] args) { LinkCycleLength list1 = new LinkCycleLength(); Node second = null; // 把第二个结点记下来 // 向链表中添加数据 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { list1.add(i); if (i == 1) { second = list1.current;// 把第二个结点记下来 } } list1.add(second);// 将尾结点指向链表的第二个结点,于是单链表就有环了 Node current1 = list1.hasCycle(list1.head);//获取相遇的那个结点 System.out.println("环的长度为" + list1.getCycleLength(current1)); System.out.print("\r\n"); System.out.print("\r\n"); LinkCycleLength list2 = new LinkCycleLength(); //向LinkList中添加数据 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { list2.add(i); } list2.add(list2.head); //将头结点添加到链表当中(将尾结点指向头结点),于是,单链表就有环了。备注:此时得到的这个环的结构,是本节中图1的那种结构。 Node current2= list1.hasCycle(list2.head); System.out.println("环的长度为" + list1.getCycleLength(current2)); } }
测试结果:
环的长度为3
环的长度为4
分别是如下这种情况: