校验字段的局部钩子和全局钩子源码分析
view中使用is_valid()方法:
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 新增
response = {'status': 100, 'msg': '新增成功'}
book_ser = BookSerializer(data=request.data)
# 提交的字段校验通过
if book_ser.is_valid():
book_ser.save()
response['book'] = book_ser.data
else:
response['msg'] = book_ser.errors
return Response(response)
局部钩子和全局钩子函数代码
#局部钩子
def validate_title(self,value):
from rest_framework import exceptions
if value.startswith('sb'):
raise exceptions.ValidationError('xxx')
return value
#全局
def validate(self, attrs):
from rest_framework import exceptions
if attrs.get('title')== attrs.get('title2'):
return attrs
else:
raise exceptions.ValidationError('不想等啊')
通过is_valid()方法找到源码中的run_validation
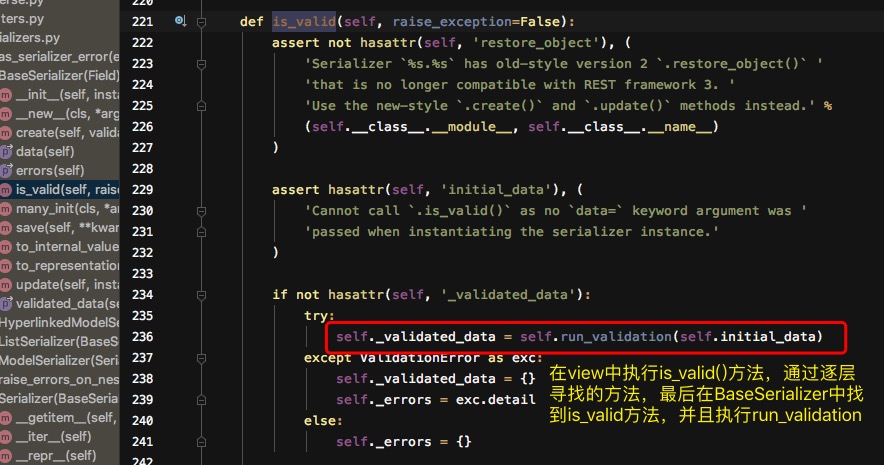
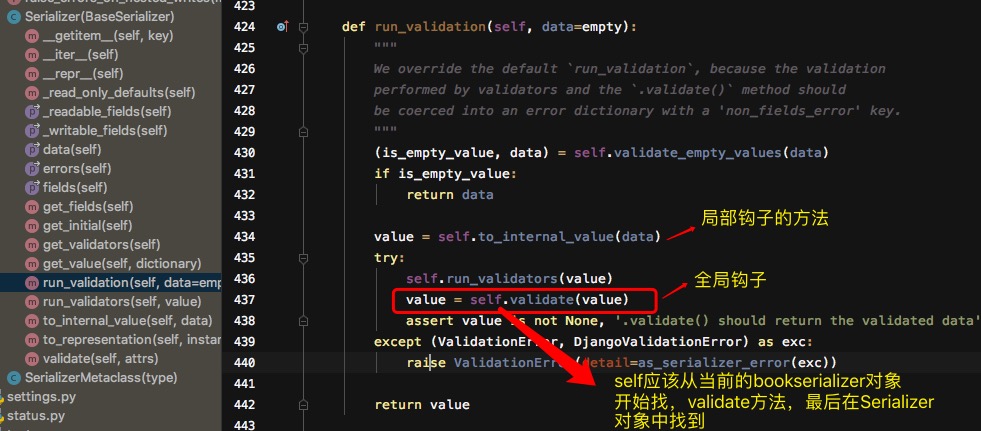
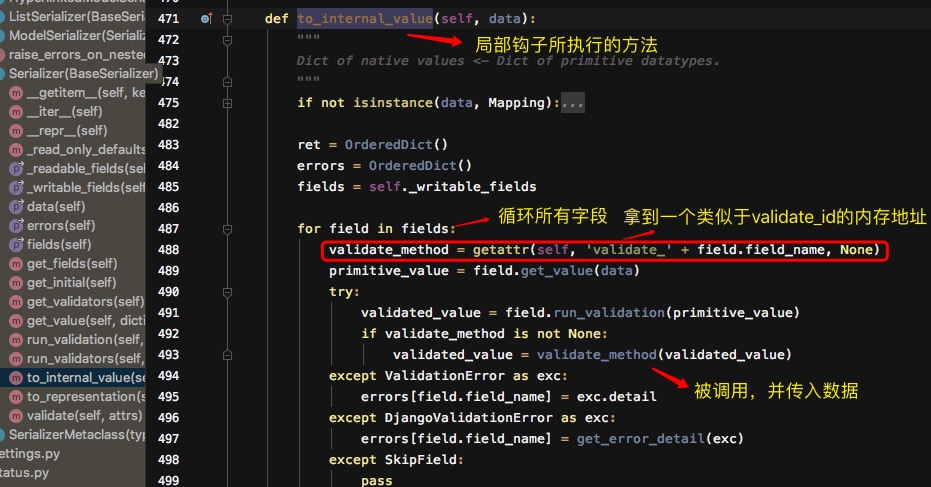
最后执行self.to_internal_value(data)
流程总结:
- is_valid---->self.run_validation-(执行Serializer的run_validation)
- 然后执行self.to_internal_value(data)
- 循环字段,完成校验功能
Time the study pain is temporary,has not learned the pain is life-long.


