【POJ SOJ HDOJ】HDU 2196 Computer 树中的最长路径
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
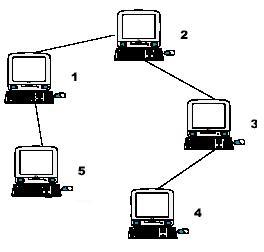
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
题解:
求树最长路的套路:DFS和标定访问节点
变种问题:有圈无向图,有圈有向图
算法复杂度:时间O(N),空间O(N)
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string.h> #include<stdio.h> using namespace std; #define MAXN 10010 struct Edge { int v, c; Edge() {} Edge(int _a, int _b):v(_a), c(_b) {} }; vector<Edge> M[MAXN]; bool vis[MAXN]; int dist[MAXN]; int st = 0, maxlen; void dfs(int u, int len) { if (len > maxlen) maxlen = len, st = u; vis[u] = true; int v, c; for (int i = 0; i < M[u].size(); i++) { v = M[u][i].v; c = M[u][i].c; if (vis[v]) { continue; } if (len + c > dist[v]) dist[v] = len + c; dfs(v, len + c); } vis[u] = false; } int main() { int N; while (~scanf("%d", &N)) { for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { M[i].clear(); } int v, c; memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); memset(dist, 0, sizeof(dist)); for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) { scanf("%d %d", &v, &c); M[v].push_back(Edge(i, c)); M[i].push_back(Edge(v, c)); } maxlen = 0, st = 1; dfs(1, 0); dfs(st, 0); dfs(st, 0); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { printf("%d\n", dist[i]); } } return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号