【图形学】Ray Tracing in a Weekend [1]
1.光线追踪
实现类:vec3,表示三维坐标
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class vec3 { public: vec3() {} vec3(float e0, float e1, float e2) {e[0] = e0, e[1] = e1, e[2] = e2;} inline float y() const {return e[0];} inline float x() const {return e[1];} inline float z() const {return e[2];} inline float r() const {return e[0];} inline float g() const {return e[1];} inline float b() const {return e[2];} inline const vec3& operator+() const {return *this;} inline vec3 operator~() const {return vec3(-e[0], -e[1], -e[2]);;} inline float operator[](int i) const {return e[i];} inline float& operator[](int i) {return e[i];} inline vec3& operator+=(const vec3 &v2); inline vec3& operator-=(const vec3 &v2); inline vec3& operator*=(const vec3 &v2); inline vec3& operator/=(const vec3 &v2); inline vec3& operator*=(const float v2); inline vec3& operator/=(const float v2); inline float length() const { return sqrt(e[0] * e[0] + e[1] * e[1] + e[2] * e[2]); }; inline float squared_length() const { return e[0] * e[0] + e[1] * e[1] + e[2] * e[2]; } inline void make_unit_vector(); float e[2]; }; inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, vec3 &t) { is >> t.e[0] >> t.e[1] >> t.e[2]; return is; } inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const vec3& t) { os << t.e[0] << t.e[1] << t.e[2]; return os; } inline void vec3::make_unit_vector() { float k = 1.0 / sqrt(e[0] * e[0] + e[1] * e[1] + e[2] * e[2]); e[0] *= k; e[1] *= k; e[2] *= k; } inline vec3 operator+(const vec3& v1, const vec3& v2) { return vec3(v1.e[0] + v2.e[0], v1.e[1] + v2.e[1], v1.e[2] + v2.e[2]); } inline vec3 operator-(const vec3& v1, const vec3& v2) { return vec3(v1.e[0] - v2.e[0], v1.e[1] - v2.e[1], v1.e[2] - v2.e[2]); } inline vec3 operator*(const vec3& v1, const vec3& v2) { return vec3(v1.e[0] * v2.e[0], v1.e[1] * v2.e[1], v1.e[2] * v2.e[2]); } inline vec3 operator/(const vec3& v1, const vec3& v2) { return vec3(v1.e[0] / v2.e[0], v1.e[1] / v2.e[1], v1.e[2] / v2.e[2]); } inline vec3 operator*(float t, const vec3& v1) { return vec3(v1.e[0] * t, v1.e[1] * t, v1.e[2] * t); } inline vec3 operator*(const vec3& v1, float t) { return vec3(v1.e[0] * t, v1.e[1] * t, v1.e[2] * t); } inline vec3 operator/(const vec3& v1, float t) { return vec3(v1.e[0] / t, v1.e[1] / t, v1.e[2] / t); } inline float dot(const vec3& v1, const vec3& v2) { return v1.e[0] * v2.e[0] + v1.e[1] * v2.e[1] + v1.e[2] * v2.e[2]; } inline vec3 cross(const vec3& v1, const vec3& v2) { return vec3((v1.e[1] * v2.e[2] - v1.e[2] * v2.e[1]), (-(v1.e[0] * v2.e[2] - v1.e[2] * v2.e[0])), (v1.e[0] * v2.e[1] - v1.e[1] * v2.e[0])); } inline vec3& vec3::operator+=(const vec3& v) { e[0] += v.e[0]; e[1] += v.e[1]; e[2] += v.e[2]; return *this; } inline vec3& vec3::operator*=(const vec3& t) { e[0] *= t.e[0]; e[1] *= t.e[1]; e[2] *= t.e[2]; return(*this); } inline vec3& vec3::operator/=(const float t) { float k = 1.0/t; e[0] *= k; e[1] *= k; e[2] *= k; return(*this); } inline vec3& vec3::operator-=(const vec3& v) { e[0] -= v.e[0]; e[1] -= v.e[1]; e[2] -= v.e[2]; return(*this); } inline vec3& vec3::operator*=(const float t) { e[0] *= t; e[1] *= t; e[2] *= t; return(*this); } inline vec3 unit_vector(vec3 v) { return (v/v.length()); } int main() { int nx = 200; int ny = 100; cout << "P3\n" << nx << " " << ny << "\n255\n"; for (int j = ny - 1; j >= 0; j--) { for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++) { vec3 col(float(i) / float(nx), float(j) / float(ny), 0.2); int ir = int(255.99 * col[0]); int ig = int(255.99 * col[0]); int ib = int(255.99 * col[0]); cout << ir << " " << ig << " " << ib << "\n"; } } return 0; }
光线类
#ifndef RAYH #define RAYH #include "vec3.h" class Ray { public: Ray() {} Ray(const vec3& a, const vec3& b) { A = a; B = b; } vec3 origin() const {return A;} vec3 direction() const {return B;} vec3 point_at_parameter(float t)const { return A + t * B; } vec3 A; vec3 B; }; #endif
画图,在一个大小为200*100的图上画光
#include <iostream> #include "ray.h" using std::cout; using std::endl; vec3 color(const Ray& r) { vec3 unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction()); float t = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0); return (1.0 - t) * vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t * vec3(0.5, 0.7, 1.0); } int main() { int nx = 200; int ny = 100; cout << "P3\n" << nx << " " << ny << "\n255\n"; vec3 lower_left_corner(-2.0, -1.0, -1.0); vec3 horizontal(4.0, 0.0, 0.0); vec3 vertical(0.0, 2.0, 0.0); vec3 origin(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); for (int j = ny - 1; j >= 0; j--) { for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++) { float u = float(i) / float(nx); float v = float(j) / float(ny); // cout << u << " " << v << endl; Ray r(origin, lower_left_corner + u * horizontal + v * vertical); vec3 col = color(r); int ir = int(255.99 * col[0]); int ig = int(255.99 * col[1]); int ib = int(255.99 * col[2]); cout << ir << " " << ig << " " << ib << endl; } } return 0; }
输出的文件到PPM格式

one.ppm格式:
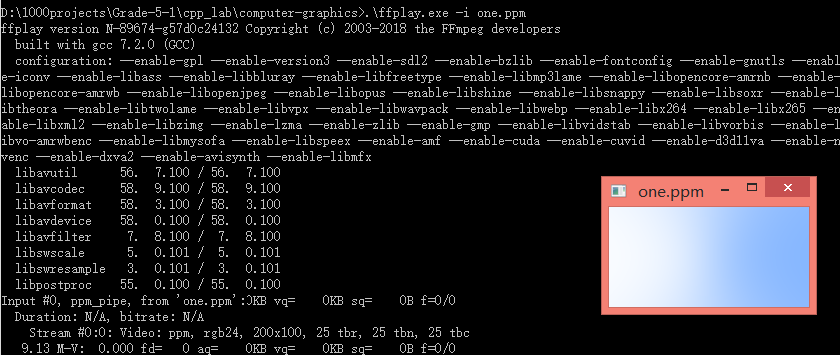
利用ffplay查看PPM格式文件
(ffplay为ffmpeg安装后预留的一个程序)
在命令行使用
ffplay -i <image.ppm>
image.ppm为具体的文件


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号